Abstract
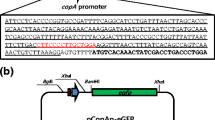
The metalloprotein, CadR, was redesigned to optimize cadmium and mercury specificity of CadR-based E. coli biosensors. By truncating 10 and 21 amino acids from the C-terminal extension of CadR, CadR-TC10 and CadR-TC21 were obtained, respectively. The genes cadR, cadR-TC10 and cadR-TC21 were used as sensing elements to construct green fluorescent protein based E.coli biosensors. Induction at 30 °C for 4 h in supplemented M9 medium was the optimized condition for the biosensor. Compared with CadR-based biosensor, there was a clear decline in induction coefficient for CadR-TC21-based biosensor (decreased by 86 % in Zn(II), 44 % in Hg(II), and only 37 % in Cd(II)). While in CadR-TC10-based biosensor, the induction coefficient decreased by 95 % in Zn(II), 70 % in Hg(II), and 67 % in Cd(II). Improved performances of CadR mutants based E. coli biosensors indicated that truncating C-terminal extension of CadR could improve the specificity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu MB, Mitchell RJ, Kim BC (2004) Whole-cell-based biosensors for environmental biomonitoring and application. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 87:269–306
Hakkila KM, Nikander PA, Junttila SM, Lamminmäki UJ, Virta MP (2011) Cd-specific mutants of mercury-sensing regulatory protein MerR, generated by directed evolution. Appl Environ Microb 77(17):6215–6224
Haouem S, Hmad N, Najjar MF, El Hani A, Sakly R (2007) Accumulation of cadmium and its effects on liver and kidney functions in rats given diet containing cadmium-polluted radish bulb. Exp Toxicol Pathol 59(1):77–80
Ivask A, Virta M, Kahru A (2002) Construction and use of specific luminescent recombinant bacterial sensors for the assessment of bioavailable fraction of cadmium, zinc, mercury and chromium in the soil. Soil Biol Biochem 34(10):1439–1447
Ivask A, Rõlova T, Kahru A (2009) A suite of recombinant luminescent bacterial strains for the quantification of bioavailable heavy metals and toxicity testing. BMC Biotechnol 9(1):41. doi:10.1186/1472-6750-9-41
Joe MH, Lee KH, Lim SY, Im SH, Song HP, Lee IS, Kim DH (2012) Pigment-based whole-cell biosensor system for cadmium detection using genetically engineered Deinococcus radiodurans. Bioproc Biosyst Eng 35(1–2):265–272
Mandon CA, Diaz C, Arrigo AP, Blum LJ (2005) Chemical stress sensitive luminescent human cells: molecular biology approach using inducible Drosophila melanogaster hsp22 promoter. Biochem Biophy Res Commun 335(2):536–544. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.07.112
Miller WG, Leveau JHJ, Lindow SE (2000) Improved gfp and inaZ broadhost-range promoter-probe vectors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13(11):1243–1250
Park JN, Sohn MJ, Oh DB, Kwon O, Rhee SK, Hur CG, Lee SY, Gellissen G, Kang HA (2007) Identification of the cadmium-inducible Hansenula polymorpha SEO1 gene promoter by transcriptome analysis and its application to whole-cell heavy-metal detection systems. Appl Environ Microb 73(19):5990–6000
Tauriainen S, Karp M, Chang W, Virta M (1998) Luminescent bacterial sensor for cadmium and lead. Biosens Bioelectron 13(9):931–938
van der Meer JR, Belkin S (2010) Where microbiology meets microengineering: design and applications of reporter bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(7):511–522
Wu CH, Le D, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2009) Optimization of a whole-cell cadmium sensor with a toggle gene circuit. Biotechnol Prog 25(3):898–903
Yagi K (2007) Applications of whole-cell bacterial sensors in biotechnology and environmental science. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73(6):1251–1258
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Shenzhen Municipal Government under a grant for Key Lab Construction (CXB201111240110A). We thank Yu-Jie Liang for help in fluorescent assay and Priscilla Young for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, HC., Peng, ZW., Li, PS. et al. Optimizing cadmium and mercury specificity of CadR-based E. coli biosensors by redesign of CadR. Biotechnol Lett 35, 1253–1258 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1216-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1216-4