Abstract
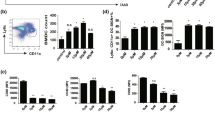
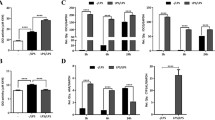
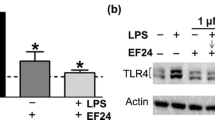
Modulation of dendritic cell (DC) fate and function may be one approach for the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. n-Butylidenephthalide (BP), derived from Angelica sinensis, at 40 μg/ml significantly decreased the secretion of interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated activation of cultured murine DC2.4 cells (P < 0.01). LPS-induced major histocompatibility complex class II (P < 0.05), CD86 (P < 0.01) and CD40 (P < 0.01) expression on DC2.4 cells was also inhibited by BP. The endocytic capacity of LPS-stimulated DC2.4 cells was increased by BP (P < 0.01). The antigen-presenting capacity of LPS-stimulated DC2.4 cells was decreased by BP (P < 0.05). Moreover, we confirmed BP attenuates the responses of LPS-stimulated activation of DCs via suppression of NF-κB-dependent pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banchereau J, Briere F, Caux C, Davoust J, Lebecque S, Liu YJ, Pulendran B, Palucka K (2000) Immunobiology of dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol 18:767–811
Chao WW, Kuo YH, Li WC, Lin BF (2009) The production of nitric oxide and prostaglandin E2 in peritoneal macrophages is inhibited by Andrographis paniculata, Angelica sinensis and Morus alba ethyl acetate fractions. J Ethnopharmacol 122:68–75
Chao WW, Hong YH, Chen ML, Lin BF (2010) Inhibitory effects of Angelica sinensis ethyl acetate extract and major compounds on NF-kappaB trans-activation activity and LPS-induced inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol 129:244–249
Chen Z, Lu J, Srinivasan N, Tan BK, Chan SH (2009) Polysaccharide-protein complex from Lycium barbarum L. is a novel stimulus of dendritic cell immunogenicity. J Immunol 182:3503–3509
Figdor CG, de Vries IJ, Lesterhuis WJ, Melief CJ (2004) Dendritic cell immunotherapy: mapping the way. Nat Med 10:475–480
Fujii S, Liu K, Smith C, Bonito AJ, Steinman RM (2004) The linkage of innate to adaptive immunity via maturing dendritic cells in vivo requires CD40 ligation in addition to antigen presentation and CD80/86 costimulation. J Exp Med 199:1607–1618
Guha M, Mackman N (2001) LPS induction of gene expression in human monocytes. Cell Signal 13:85–94
Kaisho T, Tanaka T (2008) Turning NF-kappaB and IRFs on and off in DC. Trends Immunol 29:329–336
Kim JS, Jobin C (2005) The flavonoid luteolin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-kappaB signalling and gene expression by blocking IkappaB kinase activity in intestinal epithelial cells and bone-marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunology 115:375–387
Ko WC (1980) A newly isolated antispasmodic—butylidenephthalide. Jpn J Pharmacol 30:85–91
Ko WC, Sheu JR, Tzeng SH, Chen CM (1998) The selective antianginal effect without changing blood pressure of butylidenephthalide in conscious rats. Planta Med 64:229–232
Lin PC, Chen YL, Chiu SC, Yu YL, Chen SP, Chien MH, Chen KY, Chang WL, Lin SZ, Chiou TW, Harn HJ (2008) Orphan nuclear receptor, Nurr-77 was a possible target gene of butylidenephthalide chemotherapy on glioblastoma multiform brain tumor. J Neurochem 106:1017–1026
Liu Y, Chen Y, Lamb JR, Tam PK (2007) Triptolide, a component of Chinese herbal medicine, modulates the functional phenotype of dendritic cells. Transplantation 84:1517–1526
Lu YC, Yeh WC, Ohashi PS (2008) LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42:145–151
Mimura Y, Kobayashi S, Naitoh T, Kimura I, Kimura M (1995) The structure-activity relationship between synthetic butylidenephthalide derivatives regarding the competence and progression of inhibition in primary cultures proliferation of mouse aorta smooth muscle cells. Biol Pharm Bull 18:1203–1206
Mitsui S, Torii K, Fukui H, Tsujimura K, Maeda A, Nose M, Nagatsu A, Mizukami H, Morita A (2010) The herbal medicine compound falcarindiol from Notopterygii Rhizoma suppresses dendritic cell maturation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 333:954–960
Reis e Sousa C (2006) Dendritic cells in a mature age. Nat Rev Immunol 6:476–483
Rhule A, Rase B, Smith JR, Shepherd DM (2008) Toll-like receptor ligand-induced activation of murine DC2.4 cells is attenuated by Panax notoginseng. J Ethnopharmacol 116:179–186
Shen Z, Reznikoff G, Dranoff G, Rock KL (1997) Cloned dendritic cells can present exogenous antigens on both MHC class I and class II molecules. J Immunol 158:2723–2730
Teng CM, Chen WY, Ko WC, Ouyang CH (1987) Antiplatelet effect of butylidenephthalide. Biochim Biophys Acta 924:375–382
Tsai NM, Lin SZ, Lee CC, Chen SP, Su HC, Chang WL, Harn HJ (2005) The antitumor effects of Angelica sinensis on malignant brain tumors in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res 11:3475–3484
Wei CW, Lin CC, Yu YL, Lin CY, Lin PC, Wu MT, Chen CJ, Chang W, Lin SZ, Chen YL, Harn HJ (2009) n-Butylidenephthalide induced apoptosis in the A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cell line by coupled down-regulation of AP-2 alpha and telomerase activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 30:1297–1306
Yu YL, Chen IH, Shen KY, Huang RY, Wang WR, Chou CJ, Chang TT, Chu CL (2009) A triterpenoid methyl antcinate K isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea promotes dendritic cell activation and Th2 differentiation. Eur J Immunol 39:2482–2491
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by China Medical University (CMU98-N2-01 and CMU98-CT-31), and the Taiwan Department of Health Clinical Trial and Research Center of Excellence (DOH99-TD-B-111-004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, RH., Hran, HJ., Chu, CL. et al. Lipopolysaccharide-stimulated activation of murine DC2.4 cells is attenuated by n-butylidenephthalide through suppression of the NF-κB pathway. Biotechnol Lett 33, 903–910 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0528-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0528-5