Abstract
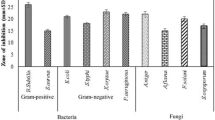
A Streptomyces strain, NT0401, was isolated from soil that selectively inhibited Microcystis strains but did not affect other microorganisms. Based on its morphology, physiology and 16S rDNA sequence, it was identified as Streptomyces grisovariabilis. The active substance produced by NT0401 was a water-soluble compound with a Mr <1 kDa that was stable over a broad pH range and at 100°C for 20 min. This organism should be a potential environment-friendly strain for control of Microcystis blooms.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn CY, Joung SH, Jeon JW, Kim HS, Yoon BD, Oh HM (2003) Selective control of cyanobacteria by surfactin-containing culture broth of Bacillus subtilis C1. Biotechnol Lett 25:1137–1142
Choi HJ, Kim BH, Kim JD, Han MS (2005) Streptomyces neyagawaensis as a control for the hazardous biomass of Microcystis aeruginosa (Cyanobacteria) in eutrophic freshwaters. Biol Control 33:335–343
Hehmann A, Kaya K, Watanabe MM (2002) Selective control of Microcystis using an amino acid a laboratory assay. J Appl Phycol 14:85–89
Marker AFH, Nusch EA, Rai H, Riemann B (1980) The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwaters and standardization of methods: conclusions and recommendations. Arch Hydrobiol Beih Ergebn Limnol 14:91–106
Martin EL (1976) Biological control of blue-green algae. National Technical Information Service Report PB-288 311, Nebraska, LISA
Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Genetic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
Sigee DC, Glenn R, Andrews MJ, Bellinger EG, Butler RD, Epton HAS, Hendry RD (1999) Biological control of cyanobacteria: principles and possibilities. Hydrobiologia 395(396):161–172
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Cheng-Cai Zhang and W. L. Shao for making constructive commentaries on the manuscript. The project was sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars, State Education Ministry.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, XH., Li, JH., Li, JJ. et al. Selective inhibition of the cyanobacterium, Microcystis, by a Streptomyces sp.. Biotechnol Lett 31, 1531–1535 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0051-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0051-0