Abstract
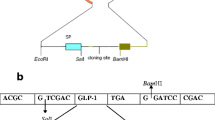
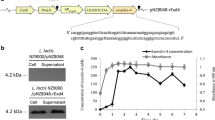
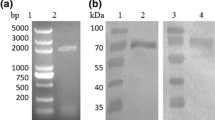
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide (GLP-1), a gut hormone released into the blood stream after feeding, can stimulate insulin secretion by potentiating the insulinotropic action of glucose. An expression vector pET-22bG8, encoding a fusion protein containing eight tandem repeat GLP-1 ([Ser8, Gln26, Asp34]-GLP-1) analogues, was constructed and transformed into the Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) strain over-expressing the His-tagged fusion protein under the IPTG promoter. SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis demonstrated that the His-tagged GLP-1 fusion protein migrated as a single protein with a molecular weight of 32 kDa. Following chronic (10 days) oral administration (20 mg kg−1 day−1) of the fusion protein to diabetic rats, serum glucose levels were significantly lowered from 26 ± 2.5 to 7.9 ± 1.4 mmol/l. Further studies are needed to evaluate the potential use for GLP-1 analogue short peptide in the treatment of diabetes mellitus.




Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ahrén B (1995) Insulinotropic action of truncated glucagon-like peptide-1 in mice. Acta Physiol Scand 153:205–206
Ahrén B (1998) Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1): a gut hormone of potential interest in the treatment of diabetes. BioEssays 20:642–651
Burcelin R, Eddouks M, Maury J, Kande J, Assan R, Girard J (1995) Excessive glucose production, rather than insulin resistance, accounts for hyperglycaemia in recent-onset streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 38:283–290
Deacon CF, Johnsen AH, Holst JJ (1995) Degradation of glucagons like peptide-1 by human plasma in vitro yields an N-terminally truncated peptide that is a major endogenous metabolite in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 80:952–957
Deacon CF, Knudsen LB, Madsen K, Wiberg FC, Jacobsen O, Holst JJ (1998) Dipeptidyl peptidase IV resistant analogues of glucagon-like peptide-1 which have extended metabolic stability and improved biological activity. Diabetologia 41:271–278
Drucker DJ, Philippe J, Mojsov S, Chick WL, Habener JF (1987) Glucagon-like peptide-1 stimulates insulin gene expression and increases cyclic AMP levels in rat islet cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:3434–3438
Fridolf T, Ahrén B (1991) GLP-1(7–36) amide stimulates insulin secretion in rat islets: studies on the mode of action. Diabetes Res 16:185–191
Fridolf T, Bottcher G, Sundler F, Ahrén B (1991) GLP-1 and GLP-1(7–36) amide: Influences on basal and stimulated insulin and glucagon secretion in the mouse. Pancreas 6:208–215
Frokjaer S, Otzen DE (2005) Protein drug stability: a formulation challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:298–306
Gutniak M, Orskov C, Holst JJ, Ahrén B, Efendic S (1992) Antidiabetogenic effect of glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36) amide in normal subjects and patients with diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 326:1316–1322
Hamman JH, Enslin GM, Kotze AF (2005) Oral delivery of peptide drugs: barriers and development. BioDrugs 19:165–177
Hidari KI, Horie N, Murata T, Miyamoto D, Suzuki T, Usui T, Suzuki Y (2005) Purification and characterization of a soluble recombinant human ST6Gal I functionally expressed in Escherichia coli. Glycoconj J 22:1–11
Holst JJ (1997) Enteroglucagon. Annu Rev Physiol 57:257–271
Holst JJ, Orskov C, Nielsen OV, Schwartz TW (1987) Truncated glucagon-like peptide I, an insulin-releasing hormone from the distal gut. FEBS Lett 211:169–174
Juhl CB, Hollingdal M, Sturis J, Jakobsen G, Agerso H, Veldhuis J, Porksen N, Schmitz O (2002) Bedtime administration of NN2211, a long-acting GLP-1 derivative, substantially reduces fasting and postprandial glycemia in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 51:424–429
Kagawa N, Cao Q, Kusano K (2003). Expression of human aromatase (CYP19) in Escherichia coli by N-terminal replacement and induction of cold stress response. Steroids 68:205–209
Kolterman OG, Buse JB, Fineman MS, Gaines E, Heintz S, Bicsak TA, Taylor K, Kim D, Aisporna M, Wang Y, Baron AD (2003) Synthetic exendin-4 (Exenatide) significantly reduces postprandial and fasting plasma glucose in subjects with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3082–3089
Kreyman B, Ghatei MA, Williams G, Bloom SR (1987) Glucagon like peptide-1 7–36: a physiological incretin in man. Lancet 2:1300–1303
Lawrence B, Dreyfus J, Wen S, Guicarc’h P, Drucker D, Castaigne JP (2003) CJC-ll31, a long acting GLP-1 derivative, exhibits an extended pharmacokinetic profile in healthy human volunteers (Abstract). Diabetes 52(suppl. 1):A125
Ma Z, Lim TM, Lim LY (2005) Pharmacological activity of peroral chitosan-insulin nanoparticles in diabetic rats. Int J Pharm 293:271–280
Mahato RI, Narang AS, Thoma L, Miller DD (2003) Emerging trends in oral delivery of peptide and proteins. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 20:153–214
Morishita M, Morishita I, Takayama K, Machida Y, Nagai T (1993) Site-dependent effect of aprotinin, sodium caprate, Na2EDTA and sodium glycocholate on intestinal absorption of insulin. Biol Pharm Bull 16:68–72
Pan Y, Li YJ, Zhao HY, Zheng JM, Xu H, Wei G, Hao JS, Cui FD (2002) Bioadhesive polysaccharide in protein delivery system: chitosan nanoparticles improve the intestinal absorption of insulin in vivo. Int J Pharm 249:139–147
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Shah RB, Ahsan F, Khan MA (2002) Oral delivery of proteins: Progress and prognostication. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 19:135–169
Studier FW, Moffatt BA (1986) Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol 189:113–130
Tang-Christensen M, Larsen PJ, Goke R, Fink-Jensen A, Jessop DS, Moller M, Sheikh SP (1996) Central administration of GLP-1-(7–36) amide inhibits food and water intake in rats. Am J Physiol 271:R848–R856
Torchilin VP, Lukyanov AN (2003) Peptide and protein drug delivery to and into tumors: challenges and solutions. Drug Discov Today 8:259–266
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Tozaki H, Odoriba T, Iseki T, Taniguchi T, Fujita T, Murakami M, Muranishi S, Yamamoto A (1998) Use of protease inhibitors to improve calcitonin absorption from the small and large intestine in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 50:913–920
Turton MD, O’Shea D, Gunn I, Beak SA, Edwards CM, Meeran K, Choi SJ, Taylor GM, Heath MM, Lambert PD, Wilding JP, Smith DM, Ghatei MA, Herbert J, Bloom SR (1996) A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 379:69–72
Van Dijk G, Lindskog S, Holst JJ, Steffens AB, Ahrén B (1996) Effects of glucagon- like peptide-1 on glucose turnover in rats. Am J Physiol 270:E1015–E1021
Weickert MJ, Pagratis M, Curry SR, Blackmore R (1997) Stabilization of apoglobin by low temperature increases yield of soluble recombinant hemoglobin in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4313–4320
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by 863 Project funds (No. 2002AA213061) in P. R. China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. H. Hou and R. X. Yan contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Yan, R., Ding, D. et al. Oral administration of a fusion protein containing eight GLP-1 analogues produced in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biotechnol Lett 29, 1439–1446 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9427-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9427-1