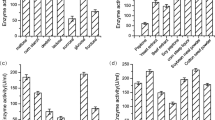
Abstract
A newly isolated strain, Penicillium sp. S-22, was used to produce an enzyme that hydrolyses raw yam starch [raw yam starch digesting enzyme (RYSDE)]. The enzyme activity and overall enzyme productivity were respectively 16 U/ml and 0.19 U/ml h in the batch culture. The enzyme activity increased to 85 U/ml by feeding of partially hydrolyzed raw yam starch. When a mixture containing partially hydrolyzed raw yam starch and peptone was fed by a pH-stat strategy, the enzyme activity reached 366 U/ml, 23-fold of that obtained in the batch culture, and the overall productivity reached 3.4 U/ml h, which was 18-fold of that in the batch culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goyal N, Gupta JK, Soni SK (2005) A novel raw starch digesting thermostable α-amylase from Bacillus sp. I-3 and its use in the direct hydrolysis of raw potato starch. Enzyme Microbial Technol 37:723–734
MarlidaY, Saari N, Hassan Z, Radu S (2000) Improvement in raw sago starch degrading enzyme production from Acremonium sp. endophytic fungus using carbon and nitrogen sources. Enzyme Microbial Technol 27:511–515
Morita H, Fujio Y (2000) Effect of organic nitrogen sources on raw starch-digesting glucoamylase production of Rhizopus sp. MKU 40. Starch 52:18–21
Nagasaka Y, Kurosawa, Yakota A, Tomita F (1998) Purification and properties of the raw-starch-digesting glucoamylase from Corticium rolfsii. Appl Microbiol Biot 50:323–330
Nigam P, Singh D (1995) Enzyme and microbial systems involved in starch processing. Enzyme Microbial Technol 17:770–778
Rajoka MI, Yasmeen A (2005) Induction, and production studies of a novel glucoamylase of Aspergillus Niger. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:179–187
Roy I, Gupta MN (2004) Hydrolysis of starch by a mixture of glucoamylase and pullulanase entrapped individually in calcium alginate beads. Enzyme Microbial Technol 34:26–32
Wang WJ, Powell AD, Oates CG (1996) Starch as a biomass source: raw sago starch hydrolysis by commercial enzymes. Bioresource Technol 55:55–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, HY., Ge, XY. & Zhang, WG. Improved production of an enzyme that hydrolyses raw yam starch by Penicillium sp. S-22 using fed-batch fermentation. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1719–1723 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9151-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9151-2