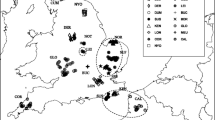
A population genetic analysis based on sequences of the mitochondrial control region in 110 red foxes from five sampling localities in northern Serbia was carried out. The analysis yielded nine different haplotypes. Neither haplotype phylogeny nor their distribution was in accordance with the geographic location of the populations. In particular, the data failed to detect an unequivocal influence of the two big rivers, the Danube and the Tisza, separating the populations studied. Population differentiation was altogether low, without any relationship to the rivers as possible migration barriers. Although the possibility of foxes crossing the rivers over bridges or by swimming, thus keeping up gene flow, cannot be ruled out, it is most probable that the control region sequences are not sensitive enough to resolve small-scale population relationships but rather show patterns determined by stochastic processes such as genetic drift or lineage sorting.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Avise, J. C. (2000). Phylogeography: The History and Formation of Species. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA.
Cirovic, D. (2000). Morphological variability and biogeographical status of the red fox (Vulpes vulpes) in Vojvodina. M.Sc. Thesis. University of Belgrade, Belgrade, Serbia.
Clement, M., Posada, D., and Crandall, K. A. (2000). TCS: A computer program to estimate gene genealogies. Mol. Ecol. 9:1657–1660.
Feulner, P. G. D., Bielfeldt, W., Zachos, F. E., Bradvarovic, J., Eckert, I., and Hartl, G. B. (2004). Mitochondrial DNA and microsatellite analyses of the genetic status of the presumed subspecies Cervus elaphus montanus (Carpathian red deer). Heredity 93:299–306.
Frati, F., Hartl, G. B., Lovari, S., Delibes, M., and Markov, G. (1998). Quaternary radiation and genetic structure of the red fox Vulpes vulpes in the Mediterranean Basin, as revealed by allozymes and mitochondrial DNA. J. Zool., London 245:43–51.
Frati, F., Lovari, S., and Hartl, G. B. (2000). Does protection from hunting favour genetic uniformity in the red fox? Z. Säugetierkunde 65:76–83.
Grobler, J. P., Pretorius, D. M., Botha, K., Kotze, A., Hallerman, E. M., and Van Vuuren, B. J. (2005). An exploratory analysis of geographic genetic variation in southern African nyala (Tragelaphus angasii). Mamm. Biol. 70:291–299.
Hall, T. A. (1999). BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. 41:95–98.
Hartl, G. B., Zachos, F. E., Nadlinger, K., Ratkiewicz, M., Klein, F., and Lang, G. (2005). Allozyme and mitochondrial DNA analysis of French red deer (Cervus elaphus) populations: Genetic structure and its implications for management and conservation. Mamm. Biol. 70:24–34.
Hmwe, S. S., Zachos, F. E., Eckert, I., Lorenzini, R., Fico, R., and Hartl, G. B. (2006). Conservation genetics of the endangered red deer from Sardinia and Mesola with further remarks on the phylogeography of Cervus elaphus corsicanus. Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 88:691–701.
Lade, J. A., Murray, N. D., Marks, C. A., and Robinson, N. A. (1996). Microsatellite differentiation between Phillip Island and mainland Australian populations of the red fox Vulpes vulpes. Mol. Ecol. 5:81–87.
Lebarbenchon, C., Poitevin, F., and Montgelard, C. (2006). Genetic variation of the weasel (Mustela nivalis) in Corsica based on mitochondrial control region sequences. Mamm. Biol. 71:164–171.
Lorenzini, R., Fico, R., and Mattioli, S. (2005). Mitochondrial DNA evidence for a genetic distinction of the native red deer of Mesola, northern Italy, from the Alpine populations and the Sardinian subspecies. Mamm. Biol. 70:187–198.
Mitchell-Jones, A. J., Amori, G., Bogdanowicz, W., Krystufek, B., Reijnders, P. J. H., Spitzenberger, F., Stubbe, M., Thissen, J. B. M., Vohralík, V., and Zima J. (1999). The Atlas of European Mammals. T&AD Poyser, London.
Nies, G., Zachos, F. E., and Hartl, G. B. (2005). The impact of female philopatry on population differentiation in the European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) as revealed by mitochondrial DNA and allozymes. Mamm. Biol. 70:130–134.
Nyström, V., Angerbjörn, A., and Dalén, L. (2006). Genetic consequences of a demographic bottleneck in the Scandinavian arctiv fox. Oikos 114:84–94.
Räikkönen, J., Bignert, A., Mortensen, P., and Fernholm, B. (2006). Congenital defects in a highly inbred wild wolf population (Canis lupus). Mamm. Biol. 71:65–73.
Rice, W. R. (1989). Analyzing tables of statistical tests. Evolution 43:223–225.
Robinson, N. A., and Marks, C. A. (2001). Genetic structure and dispersal of red foxes (Vulpes vulpes) in urban Melbourne. Aust. J. Zool. 49:589–601.
Rogers, A. R., and Harpending, H. (1992). Population growth makes waves in the distribution of pairwise genetic differences. Mol. Biol. Evol. 9:552–569.
Rozas, J., and Rozas, R. (1999). DNASP version 3: An integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174–175.
Schneider, S., Roessli, D., and Excoffier, L. (2000). Arlequin ver 2.000: A Software for Population Genetics Data Analysis. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland.
Simonsen, V. (1982). Electrophoretic variation in large mammals, 2: The red fox, Vulpes vulpes, the stoat, Mustela erminea, the weasel, Mustela nivalis, the pole cat, Mustela putorius, the pine marten, Martes martes, the beech marten, Martes foina, and the badger, Meles meles. Hereditas 96:299–305.
Simonsen, V., Pertoldi, C., Madsen, A. B., and Loeschcke, V. (2003). Genetic differentiation of foxes (Vulpes vulpes) analysed by means of craniometry and isozymes. J. Nat. Conserv. 11:109–116.
Swanson, B. J., Fuhrmann, R. T., and Crabtree, R. L. (2005). Elevational isolation of red fox populations in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. Conserv. Genet. 6:123–131.
Valière, N., Fumagalli, L., Gielly, L., Miquel, C., Lequette, B., Poulle, M.-L., Weber, J.-M., Arlettaz, R., and Taberlet, P. (2003). Long-distance wolf recolonization of France and Switzerland inferred from non-invasive genetic sampling over a period of 10 years. Anim. Conserv. 6:83–92.
Wandeler, A. I., and Lüps, P. (1993). Vulpes vulpes (Linnaeus, 1758)-Rotfuchs. In Stubbe, M., and Krapp, F. (eds.), Handbuch der Säugetiere Europas vol. 5/I Raubsäuger (vol. I). AULA-Verlag, Wiesbaden, Germany, pp. 139–193.
Wandeler, P., Funk, S. M., Largiadèr, C. R., Gloor, S., and Breitenmoser, U. (2003). The city-fox phenomenon: Genetic consequences of a recent colonization of urban habitat. Mol. Ecol. 12:647–656.
Zachos, F., Hartl, G. B., Apollonio, M., and Reutershan, T. (2003). On the phylogeographic origin of the Corsican red deer (Cervus elaphus corsicanus): Evidence from microsatellites and mitochondrial DNA. Mamm. Biol. 68:284–298.
Zachos, F. E., Hmwe, S. S., and Hartl, G. B. (2006). Biochemical and DNA markers yield strikingly different results regarding variability and differentiation of roe deer (Capreolus capreolus, Artiodactyla: Cervidae) populations from northern Germany. J. Zool. Syst. Evol. Res. 44:167–174.
Zachos, F. E., Cirovic, D., Rottgardt, I., Seiffert, B., Oeking, S., Eckert, I., and Hartl, G. B. (in press). Geographically large-scale genetic monomorphism in a highly successful introduced species: The case of the muskrat (Ondatra zibethicus) in Europe. Mamm. Biol.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirschning, J., Zachos, F.E., Cirovic, D. et al. Population Genetic Analysis of Serbian Red Foxes (Vulpes vulpes) by Means of Mitochondrial Control Region Sequences. Biochem Genet 45, 409–420 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-007-9082-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-007-9082-1