Abstract
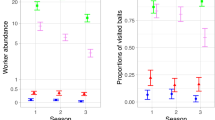
The two spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch, is an important herbivore pest of apple trees in Northwest China. This spider mite and another less damaging spider mite, Eotetranychus pruni Oudemans, are attacked by a common and often effective phytoseiid predator, Euseius finlandicus (Oudemans). Functional relationships were studied in the field to evaluate the impact of E. pruni and E. finlandicus on T. urticae. The results from this study showed that the predator-mediated apparent competition strongly affected the population dynamics of T. urticae. The addition of the apparent competitor E. pruni alone had little impact on T. urticae densities. Although the release of the predator E. finlandicus alone could result in reduction in T. urticae densities, the greatest reduction in T. urticae densities occurred in plots where both the predator E. finlandicus and apparent competitor E. pruni were released. In apple orchards, the early introduction of both the apparent competitor E. pruni and predator E. finlandicus would evidently increase the population size of the predator E. finlandicus and consequently significantly enhance the control of T. urticae populations. It is concluded from the study that the predator and apparent competitor release might be an appropriate control for the target species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergesson E. and Messina F.J. (1997). Resource-versus enemy-mediated interactions between cereal aphids (Homoptera. Aphididae) on a common host plant. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 90: 425–432
Bonsall M.B and Hassell M.P. (1997). Apparent competition structures ecological assemblages. Nature 388: 371–373
Bonsall M.B. and Hassell M.P. (1998). Population dynamics of apparent competition in a host-parasitoid assemblage. J. Anim. Ecol. 67: 918–929
Boykin L.S. and Campbell W.V. (1982). Rate of Population increase of the two spotted spider mite (Acari.Tetranychidae) on peanut leaves treated with pesticides. J. Econ. Entomol. 75: 966–971
Chaneton E.J. and Bonsall M.B. (2000). Enemy-mediated apparent competition. empirical patterns and the evidence. Oikos 88: 380–394
Collyer E. (1964). The effect of an alternative food supply on the relationship between two Typhlodromus species and Panonychus ulmi (Koch) (Acarina). Entomol. Exp. Appl. 7: 120–124
Hanna R., Wilson L.T., Zalom F.G. and Flaherty D.L. (1997). Effects of predation and competition on the population dynamics of Tetranychus pacificus. J. Appl. Ecol. 34: 878–888
He C.G. and Liu C.Z. (1990). Construction and analysis on the experimental population life table of Eotetranychus pruni (Oudemans). Journal of Gansu Agricultural University 25: 401–404
He D.H., Zhao X.P. and Jin Q.H. (2001). Dispersion of two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch, and its selection of host plants on farmland in Ningxia. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology 7: 447–451
Holt R.D. (1977). Predation, apparent competition and the structure of prey communities. Theor. Popul. Biol. 11: 197–229
Holt R.D. (1984). Spatial heterogeneity, indirect interactions and the coexistence of prey species. Am. Nat. 124: 377–406
Holt R.D. and Kotler B.P. (1987). Short-term apparent competition. Am. Nat. 130: 412–430
Holt R.D. and Lawton J.H. (1993). Apparent competition and enemy-free space in insect host-parasitoid communities. Am. Nat. 142: 623–645
Holt R.D. and Lawton J.H. (1994). The ecological consequences of shared natural enemies. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 25: 495–520
Holt R.D., Grover J. and Tilman D. (1994). Simple rules of interspecific dominance in systems with exploitative and apparent competition. Am. Nat 144: 741–777
Huang C. and Sih A. (1990). Experimental studies on behaviorally mediated, indirect interactions through a shared predator. Ecology 71: 1515–1522
Karban R., Hougen-Eitzman D. and English-Loeb G.M. (1994). Predator-mediated apparent competition between two herbivores that feed on grapevines. Oecologia 97: 508–511
Langer A. and Hance T. (2004). Enhancing parasitism of wheat aphids through apparent competition. A tool for biological control. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 102: 205–212
Liu C.Z. and He C.G. (1994). Analysis on the experimental population parameters of three species of fruit tree spider miters. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica 21: 176–178
Liu C.Z., Wang G., Wang W.X. and Zhou S.R. (2002). Spatial pattern of Tetranychus urticae koch population in apple tree. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 13: 993–996
Luczynski A., Isman M.B. and Raworth D.A. (1990). Chemical and morphological factors of resistance against the two spotted spider mite in beach strawberry. J. Econ. Entomol. 83: 564–569
Maggi V.L. and Leigh T.F. (1983). Fecundity response of the two spotted spider mite to cotton treated with methyl parathion or phosphoric acid. J. Econ. Entomol. 76: 20–25
Morris R.J., Müller C.B. and Godfray H.C.J. (2001). Field experiments testing for apparent competition between primary parasitoids mediated by secondary parasitoids. J. Anim. Ecol. 70: 301–309
Morris R.J., Lewis O.T. and Godfray H.C.J. (2004). Experimental evidence for apparent competition in a tropical forest food web. Nature 428: 310–313
Müller C.B. and Godfray H.C.J. (1997). Apparent competition between two aphid species. J. Anim. Ecol. 66: 57–64
Rott A.S., Müller C.B. and Godfray H.C.J. (1998). Indirect population interaction between two aphid species. Ecol. Lett. 1: 99–103
Schmitt R.J. (1987). Indirect interactions between prey. apparent competition, predator aggregation and habitat segregation. Ecology 68: 1887–1897
Settle W.H. and Wilson L.T. (1990). Invasion by the variegated leafhopper and biotic interaction. parasitism, competition and apparent competition. Ecology 71: 1461–1470
Shen H.M. and Zhang X.H. (2002a). Studies on influence of life-force and fecundity of cyhalothrin and fenpropathrin to Tetranychus urticae Koch. Acta Phytophylacica Sinica 29: 183–187
Shen H.M. and Zhang X.H. (2002b). Studies on the induction, decline and recovery of Tetranychus urticae resistance to fenpropathrin, omethoate and clofentezine. Acta Entomologica Sinica 45: 341–345
Sih A., Crowley P., McPeek M., Petranka J. and Stohmeier K. (1985). Predation, competition, and prey communities. a review of field experiments. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 16: 269–311
Sonneveld T., Wainwright H. and Labuschagne L. (1996). Development of two spotted spider mite (Acari.Tetranychidae) populations on strawberry and raspberry cultivars. Annu. Appl. Biol. 129: 405–413
Tang Q.Y. and Feng M.G. (2002). Data Processing System for Practical Statistics. Science Press, Beijing
Zar J.H. (1984). Biostatistical Analysis. Edition Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, U.S.A
Zhang X.H. (1993). A preliminary report on predatory process of Euseius finlandicus (Oudemans). Journal of Gansu Agricultural University 28: 287–289
Zhang X.H. and Liu C.Z. (1993). The population intrinsic increase capacity of Euseius finlandicus (Oudemans). Journal of Gansu Agricultural University 28: 158–161
Zhang X.H. and Liu C.Z. (2000). Study of biological character of Euseius finlandicus (Oudemans). Journal of Gansu Agricultural University 35: 388–394
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Cz., Yan, L., Li, Hr. et al. Effects of predator-mediated apparent competition on the population dynamics of Tetranychus urticae on apples. Biocontrol 51, 453–463 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-005-4363-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-005-4363-z