Abstract
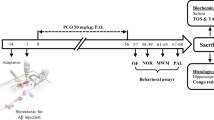
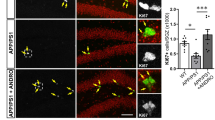
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder in the elderly. In the last years, abnormalities of lipid metabolism and in particular of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) have been recently linked with the development of the disease. According to the recent studies showing how hydroxylation of fatty acids enhances their biological activity, here we show that chronic treatment with a hydroxylated derivative of DHA, the 2-hydroxy-DHA (2OHDHA) in the 5XFAD transgenic mice model of AD improves performance in the radial arm maze test and restores cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus, with no changes in the presence of beta amyloid (Aβ) plaques. These results suggest that 2OHDHA induced restoration of cell proliferation can be regarded as a major component in memory recovery that is independent of Aβ load thus, setting the starting point for the development of a new drug for the treatment of AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrous DN, Koehl M, Le Moal M (2005) Adult neurogenesis: from precursors to network and physiology. Physiol Rev 85(2):523–569. doi:10.1152/physrev.00055.2003
Ashe KH (2001) Learning and memory in transgenic mice modeling Alzheimer’s disease. Learn Mem 8(6):301–308. doi:10.1101/lm.43701
Barceló-Coblijn G, Martin ML, de Almeida RF, Noguera-Salvà MA, Marcilla-Etxenike A, Guardiola-Serrano F, Lüth A, Kleuser B, Halver JE, Escribá PV (2011) Sphingomyelin and sphingomyelin synthase (SMS) in the malignant transformation of glioma cells and in 2-hydroxyoleic acid therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(49):19569–19574. doi:10.1073/pnas.1115484108
Bhatia HS, Agrawal R, Sharma S, Huo YX, Ying Z, Gomez-Pinilla F (2011) Omega-3 fatty acid deficiency during brain maturation reduces neuronal and behavioral plasticity in adulthood. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28451. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028451
Blondeau N, Nguemeni C, Debruyne DN, Piens M, Wu X, Pan H, Hu X, Gandin C, Lipsky RH, Plumier JC, Marini AM, Heurteaux C (2009) Subchronic alpha-linolenic acid treatment enhances brain plasticity and exerts an antidepressant effect: a versatile potential therapy for stroke. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(12):2548–2559. doi:10.1038/npp.2009.84
Calandria JM, Mukherjee PK, de Rivero Vaccari JC, Zhu M, Petasis NA, Bazan NG (2012) Ataxin-1 poly-Q-induced proteotoxic stress and apoptosis are attenuated in neural cells by docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.287078
Calon F, Lim GP, Yang F, Morihara T, Teter B, Ubeda O, Rostaing P, Triller A, Salem N, Ashe KH, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2004) Docosahexaenoic acid protects from dendritic pathology in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neuron 43(5):633–645. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.013
Demars M, Hu YS, Gadadhar A, Lazarov O (2010) Impaired neurogenesis is an early event in the etiology of familial Alzheimer’s disease in transgenic mice. J Neurosci Res 88(10):2103–2117. doi:10.1002/jnr.22387
Devi L, Ohno M (2012) 7,8-Dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule TrkB agonist, reverses memory deficits and BACE1 elevation in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(2):434–444. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.191
Dong H, Goico B, Martin M, Csernansky CA, Bertchume A, Csernansky JG (2004) Modulation of hippocampal cell proliferation, memory, and amyloid plaque deposition in APPsw (Tg2576) mutant mice by isolation stress. Neuroscience 127(3):601–609. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.05.040
Donovan MH, Yazdani U, Norris RD, Games D, German DC, Eisch AJ (2006) Decreased adult hippocampal neurogenesis in the PDAPP mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Comp Neurol 495(1):70–83. doi:10.1002/cne.20840
Dyall SC, Michael GJ, Michael-Titus AT (2010) Omega-3 fatty acids reverse age-related decreases in nuclear receptors and increase neurogenesis in old rats. J Neurosci Res 88(10):2091–2102. doi:10.1002/jnr.22390
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (2000) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem Res 25(9–10):1439–1451
Escribá PV (2006) Membrane-lipid therapy: a new approach in molecular medicine. Trends Mol Med 12(1):34–43. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2005.11.004
Freund-Levi Y, Eriksdotter-Jönhagen M, Cederholm T, Basun H, Faxén-Irving G, Garlind A, Vedin I, Vessby B, Wahlund LO, Palmblad J (2006) Omega-3 fatty acid treatment in 174 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease: OmegAD study: a randomized double-blind trial. Arch Neurol 63(10):1402–1408. doi:10.1001/archneur.63.10.1402
Gamoh S, Hashimoto M, Sugioka K, Shahdat Hossain M, Hata N, Misawa Y, Masumura S (1999) Chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid improves reference memory-related learning ability in young rats. Neuroscience 93(1):237–241
Gamoh S, Hashimoto M, Hossain S, Masumura S (2001) Chronic administration of docosahexaenoic acid improves the performance of radial arm maze task in aged rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 28(4):266–270
Gordon JA (2011) Oscillations and hippocampal-prefrontal synchrony. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21(3):486–491. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2011.02.012
Green KN, Martinez-Coria H, Khashwji H, Hall EB, Yurko-Mauro KA, Ellis L, LaFerla FM (2007) Dietary docosahexaenoic acid and docosapentaenoic acid ameliorate amyloid-beta and tau pathology via a mechanism involving presenilin 1 levels. J Neurosci 27(16):4385–4395. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0055-07.2007
Grimm MO, Kuchenbecker J, Grösgen S, Burg VK, Hundsdörfer B, Rothhaar TL, Friess P, de Wilde MC, Broersen LM, Penke B, Péter M, Vígh L, Grimm HS, Hartmann T (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid beta production via multiple pleiotropic mechanisms. J Biol Chem 286(16):14028–14039. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.182329
Hartmann T, Kuchenbecker J, Grimm MO (2007) Alzheimer’s disease: the lipid connection. J Neurochem 103(Suppl 1):159–170. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04715.x
Hashimoto M, Tozawa R, Katakura M, Shahdat H, Haque AM, Tanabe Y, Gamoh S, Shido O (2011) Protective effects of prescription n-3 fatty acids against impairment of spatial cognitive learning ability in amyloid β-infused rats. Food Funct 2(7):386–394. doi:10.1039/c1fo00002k
Hasselmo ME, Eichenbaum H (2005) Hippocampal mechanisms for the context-dependent retrieval of episodes. Neural Netw 18(9):1172–1190. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2005.08.007
Haughey NJ, Nath A, Chan SL, Borchard AC, Rao MS, Mattson MP (2002) Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid beta-peptide, and perturbed neural progenitor cell homeostasis, in models of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 83(6):1509–1524
He C, Qu X, Cui L, Wang J, Kang JX (2009) Improved spatial learning performance of fat-1 mice is associated with enhanced neurogenesis and neuritogenesis by docosahexaenoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(27):11370–11375. doi:10.1073/pnas.0904835106
Jin K, Galvan V, Xie L, Mao XO, Gorostiza OF, Bredesen DE, Greenberg DA (2004a) Enhanced neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic (PDGF-APPSw, Ind) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(36):13363–13367. doi:10.1073/pnas.0403678101
Jin K, Peel AL, Mao XO, Xie L, Cottrell BA, Henshall DC, Greenberg DA (2004b) Increased hippocampal neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(1):343–347. doi:10.1073/pnas.2634794100
Johnson EJ, Schaefer EJ (2006) Potential role of dietary n-3 fatty acids in the prevention of dementia and macular degeneration. Am J Clin Nutr 83(6 Suppl):1494S–1498S
Kalmijn S, Launer LJ, Ott A, Witteman JC, Hofman A, Breteler MM (1997) Dietary fat intake and the risk of incident dementia in the Rotterdam Study. Ann Neurol 42(5):776–782. doi:10.1002/ana.410420514
Katsuki H, Kurimoto E, Takemori S, Kurauchi Y, Hisatsune A, Isohama Y, Izumi Y, Kume T, Shudo K, Akaike A (2009) Retinoic acid receptor stimulation protects midbrain dopaminergic neurons from inflammatory degeneration via BDNF-mediated signaling. J Neurochem 110(2):707–718. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06171.x
Kawakita E, Hashimoto M, Shido O (2006) Docosahexaenoic acid promotes neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 139(3):991–997. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.01.021
Kimura R, Ohno M (2009) Impairments in remote memory stabilization precede hippocampal synaptic and cognitive failures in 5XFAD Alzheimer mouse model. Neurobiol Dis 33(2):229–235. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2008.10.006
Krishnamoorthy T, Chen X, Govin J, Cheung WL, Dorsey J, Schindler K, Winter E, Allis CD, Guacci V, Khochbin S, Fuller MT, Berger SL (2006) Phosphorylation of histone H4 Ser1 regulates sporulation in yeast and is conserved in fly and mouse spermatogenesis. Genes Dev 20(18):2580–2592. doi:10.1101/gad.1457006
Lim GP, Calon F, Morihara T, Yang F, Teter B, Ubeda O, Salem N, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2005) A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged Alzheimer mouse model. J Neurosci 25(12):3032–3040. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4225-04.2005
Llado V, Gutierrez A, Martínez J, Casas J, Terés S, Higuera M, Galmés A, Saus C, Besalduch J, Busquets X, Escribá PV (2010) Minerval induces apoptosis in Jurkat and other cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 14(3):659–670. doi:10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00625.x
Lladó V, Terés S, Higuera M, Alvarez R, Noguera-Salva MA, Halver JE, Escribá PV, Busquets X (2009) Pivotal role of dihydrofolate reductase knockdown in the anticancer activity of 2-hydroxyoleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(33):13754–13758. doi:10.1073/pnas.0907300106
López-Toledano MA, Shelanski ML (2007) Increased neurogenesis in young transgenic mice overexpressing human APP(Sw, Ind). J Alzheimers Dis 12(3):229–240
Lu Y, Christian K, Lu B (2008) BDNF: A key regulator for protein synthesis-dependent LTP and long-term memory? Neurobiol Learn Mem 89(3):312–323. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2007.08.018
Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2008) Docosahexaenoic acid and the aging brain. J Nutr 138(12):2510–2514. doi:10.3945/jn.108.096016
Lukiw WJ, Cui JG, Marcheselli VL, Bodker M, Botkjaer A, Gotlinger K, Serhan CN, Bazan NG (2005) A role for docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 in neural cell survival and Alzheimer disease. J Clin Invest 115(10):2774–2783. doi:10.1172/JCI25420
Martin SJ, Clark RE (2007) The rodent hippocampus and spatial memory: from synapses to systems. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(4):401–431. doi:10.1007/s00018-007-6336-3
Morley JE, Banks WA (2010) Lipids and cognition. J Alzheimers Dis 20(3):737–747. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-091576
Morris MC, Evans DA, Bienias JL, Tangney CC, Bennett DA, Wilson RS, Aggarwal N, Schneider J (2003) Consumption of fish and n-3 fatty acids and risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 60(7):940–946. doi:10.1001/archneur.60.7.940
Mu Y, Gage FH (2011) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and its role in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener 6:85. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-6-85
Noristani HN, Olabarria M, Verkhratsky A, Rodríguez JJ (2010) Serotonin fibre sprouting and increase in serotonin transporter immunoreactivity in the CA1 area of hippocampus in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 32(1):71–79. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07274.x
Oakley H, Cole SL, Logan S, Maus E, Shao P, Craft J, Guillozet-Bongaarts A, Ohno M, Disterhoft J, Van Eldik L, Berry R, Vassar R (2006) Intraneuronal beta-amyloid aggregates, neurodegeneration, and neuron loss in transgenic mice with five familial Alzheimer’s disease mutations: potential factors in amyloid plaque formation. J Neurosci 26(40):10129–10140. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1202-06.2006
Oddo S, Caccamo A, Shepherd JD, Murphy MP, Golde TE, Kayed R, Metherate R, Mattson MP, Akbari Y, LaFerla FM (2003) Triple-transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease with plaques and tangles: intracellular Abeta and synaptic dysfunction. Neuron 39(3):409–421
Ohno M (2009) Failures to reconsolidate memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Learn Mem 92(3):455–459. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2009.05.001
Ohno M, Chang L, Tseng W, Oakley H, Citron M, Klein WL, Vassar R, Disterhoft JF (2006) Temporal memory deficits in Alzheimer’s mouse models: rescue by genetic deletion of BACE1. Eur J Neurosci 23(1):251–260. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.04551.x
Ohno M, Cole SL, Yasvoina M, Zhao J, Citron M, Berry R, Disterhoft JF, Vassar R (2007) BACE1 gene deletion prevents neuron loss and memory deficits in 5XFAD APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Neurobiol Dis 26(1):134–145. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2006.12.008
Pang PT, Lu B (2004) Regulation of late-phase LTP and long-term memory in normal and aging hippocampus: role of secreted proteins tPA and BDNF. Ageing Res Rev 3(4):407–430. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2004.07.002
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2004) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, London
Peng S, Wuu J, Mufson EJ, Fahnestock M (2005) Precursor form of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor are decreased in the pre-clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 93(6):1412–1421. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03135.x
Quinn JF, Raman R, Thomas RG, Yurko-Mauro K, Nelson EB, Van Dyck C, Galvin JE, Emond J, Jack CR, Weiner M, Shinto L, Aisen PS (2010) Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation and cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease: a randomized trial. JAMA 304(17):1903–1911. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1510
Rodríguez JJ, Verkhratsky A (2011) Neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease. J Anat 219(1):78–89. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2011.01343.x
Rodríguez JJ, Jones VC, Tabuchi M, Allan SM, Knight EM, LaFerla FM, Oddo S, Verkhratsky A (2008) Impaired adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS ONE 3(8):e2935. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002935
Rodríguez JJ, Jones VC, Verkhratsky A (2009) Impaired cell proliferation in the subventricular zone in an Alzheimer’s disease model. NeuroReport 20(10):907–912. doi:10.1097/WNR.0b013e32832be77d
Rodríguez JJ, Noristani HN, Olabarria M, Fletcher J, Somerville TD, Yeh CY, Verkhratsky A (2011) Voluntary running and environmental enrichment restores impaired hippocampal neurogenesis in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 8(7):707–717
Salem N, Litman B, Kim HY, Gawrisch K (2001) Mechanisms of action of docosahexaenoic acid in the nervous system. Lipids 36(9):945–959
Schaeffer EL, Figueiro M, Gattaz WF (2011) Insights into Alzheimer disease pathogenesis from studies in transgenic animal models. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 66(Suppl 1):45–54
Su HM (2010) Mechanisms of n-3 fatty acid-mediated development and maintenance of learning memory performance. J Nutr Biochem 21(5):364–373. doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.003
Sydenham E, Dangour AD, Lim WS (2012) Omega 3 fatty acid for the prevention of cognitive decline and dementia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 6:CD005379. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005379.pub3
Terés S, Lladó V, Higuera M, Barceló-Coblijn G, Martin ML, Noguera-Salvà MA, Marcilla-Etxenike A, García-Verdugo JM, Soriano-Navarro M, Saus C, Gómez-Pinedo U, Busquets X, Escribá PV (2012) 2-Hydroxyoleate, a nontoxic membrane binding anticancer drug, induces glioma cell differentiation and autophagy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. doi:10.1073/pnas.1118349109
Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, De Zubicaray GI, Janke AL, Rose SE, Semple J, Hong MS, Herman DH, Gravano D, Doddrell DM, Toga AW (2004) Mapping hippocampal and ventricular change in Alzheimer disease. Neuroimage 22(4):1754–1766. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.03.040
Uauy R, Dangour AD (2006) Nutrition in brain development and aging: role of essential fatty acids. Nutr Rev 64(5 Pt 2):S24–S33 (discussion S72–91)
Vertes RP, Hoover WB, Szigeti-Buck K, Leranth C (2007) Nucleus reuniens of the midline thalamus: link between the medial prefrontal cortex and the hippocampus. Brain Res Bull 71(6):601–609. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2006.12.002
Wen PH, Shao X, Shao Z, Hof PR, Wisniewski T, Kelley K, Friedrich VL, Ho L, Pasinetti GM, Shioi J, Robakis NK, Elder GA (2002) Overexpression of wild type but not an FAD mutant presenilin-1 promotes neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neurobiol Dis 10(1):8–19. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2002.0490
Wirsching BA, Beninger RJ, Jhamandas K, Boegman RJ, El-Defrawy SR (1984) Differential effects of scopolamine on working and reference memory of rats in the radial maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20(5):659–662
Yamin G (2009) NMDA receptor-dependent signaling pathways that underlie amyloid beta-protein disruption of LTP in the hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 87(8):1729–1736. doi:10.1002/jnr.21998
Zhang C, McNeil E, Dressler L, Siman R (2007) Long-lasting impairment in hippocampal neurogenesis associated with amyloid deposition in a knock-in mouse model of familial Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol 204(1):77–87. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2006.09.018
Zhao Y, Calon F, Julien C, Winkler JW, Petasis NA, Lukiw WJ, Bazan NG (2011) Docosahexaenoic acid-derived neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival via secretase- and PPARgamma-mediated mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease models. PLoS ONE 6(1):e15816. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015816
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Spanish Government: TRACE [grant number PET2008/0172-01 (to X.B.)]; INNPACTO [grant number IPT-010000-2010–16 (to X.B.)]; Plan Nacional de I+D+I 2008–2011 and ISCIII-Subdirección General de Evaluación y Fomento de la investigación co-financed by FEDER [grant number PI10/02738 (to J.J.R. and A.V.)]; and the Government of the Basque Country grants [grant numbers AE-2010-1-28, AEGV10/16 and GV-2011111020 (to J.J.R.)]; as well as by [BIO2010-21132 from the MICINN (to P.E.)]. M.A.F-dR was supported by a fellowship from the Govern de les Illes Balears (Conselleria d’Educació, Cultura i Universitats) operational program co-funded by the European Social Fund. M.A.F-dR and M.T. were also recipients of an IPT-Spanish government fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiol-deRoque, M.A., Gutierrez-Lanza, R., Terés, S. et al. Cognitive recovery and restoration of cell proliferation in the dentate gyrus in the 5XFAD transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease following 2-hydroxy-DHA treatment. Biogerontology 14, 763–775 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9461-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-013-9461-4