Abstract
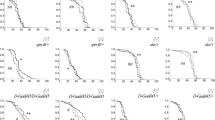
The research shows that unirradiated Drosophila lines with defects of DNA repair, antioxidant protection and apoptosis have higher speed of ageing, than wild type line. At the same time, depending on the line genotype, the irradiation results in change of life span. Mechanism of postponed effect of low dozes of ionizing radiation on the life span is elaborated. As cells with weakened protection will accumulate damages and will be exposed to ageing with the greater speed, than steady cells, their radio-induced elimination at early development stages will result in delay of age-dependent changes and will lower speed of ageing. In the subsequent irradiated generations the given somatic answer to stress (hormesis) may be replaced by negative genetic effects on the population level (shorter life span).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravind L, Dixit VM, Koonin EV (2001) Apoptotic molecular machinery: vastly increased complexity in vertebrates revealed by genome comparisons. Science 291:1279–1284
Ashburner M (1989) Drosophila: a laboratory handbook. Cold Spr Harb Lab Press, Newyork, p 1331
Le Bourg E, Minois N, Bullens P, Baret P (2000) A mild stress due to hypergravity exposure at young age increases longevity in Drosophila melanogaster males. Biogerontology 1:145–155
Rattan SI (2001) Hormesis in biogerontology. Crit rev toxicol 31:663–664
Sacher GA (1963) Effects of X-rays on the survival of Drosophila imagoes. Physiol Zool 36:295–311
Upton AC (2001) Radiation hormesis: data and interpretations. Crit rev toxicol 31:681–695
Vorobtsova IE (1963) Comparative studying of radiosensitivity of various lines of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc of Academy of Science of USSR 153:943–946
Zainullin VG, Moskalev AA, Shaposhnikov MV, Taskaev AI (1999) Current aspects of radiobiology of Drosophila melanogaster. Apoptosis and aging. Radiat biol Radioecol (RUSSIA) 39:49–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moskalev, A. Radiation-induced life span alteration of Drosophila lines with genotype differences. Biogerontology 8, 499–504 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9090-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-007-9090-x