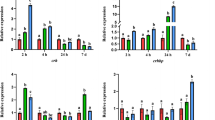
We studied histophysiology of the adrenal medulla in adult (70-day-old) male Wistar rats developmentally exposed to low doses of endocrine disruptor DDT. It was found that exposure to DDT during the prenatal and postnatal ontogeny decelerated the development of the adrenal medulla and reduced the synthesis of tyrosine hydroxylase, the rate-liming enzyme of catecholamine synthesis, in chromaffin cells, which led to a decrease in epinephrine secretion into the blood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Customs Union Technical Regulations TR CU 021/2011 “On Safety of Food Products”. St. Petersburg, 2015. Russian.
Yaglova NV, Tsomartova DA, Yaglov VV. Effect of Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Low Doses of DDT on Catecholamine Secretion in Rats in Different Period of Ontogeny. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017;163(4):422-424. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3819-6
Yaglova NV, Tsomartova DA, Yaglov VV, Obernikhin SS, Nazimova SV. Altered secretion of adrenomedullary a-cells in rats after developmental exposure to low-dose dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Klin. Eksp. Morfol. 2018;(3):30-34.
Bachman MJ, Keller JM, West KL, Jensen BA. Persistent organic pollutant concentrations in blubber of 16 species of cetaceans stranded in the Pacific Islands from 1997 through 2011. Sci. Total Environ. 2014;488-489:115-123.
Gore AC, Chappell VA, Fenton SE, Flaws JA, Nadal A, Prins G.S, Toppari J, Zoeller RT. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society’s Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 2015;36(6):E1-E150.
Hatcher JM, Delea KC, Richardson JR, Pennell KD, Miller GW. Disruption of dopamine transport by DDT and its metabolites. Neurotoxicology. 2008;29(4):682-690.
Kvetnansky R, Sabban EL, Palkovits M. Catecholaminergic systems in stress: structural and molecular genetic approaches. Physiol. Rev. 2009;89(2):535-606.
Pignatelli D, Xiao F, Gouveia AM, Ferreira JG, Vinson GP. Adrenarche in the rat. J. Endocrinol. 2006;191(1):301-308.
State of the Science of Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals — 2012. Bergman Å, Heindel JJ, Jobling S, Kidd KA, Zoeller RT, eds. WHO, 2012.
Tekin I, Roskoski R Jr, Carkaci-Salli N, Vrana KE. Complex molecular regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna). 2014;121(12):1451-1481.
Zala SM, Penn DJ. Abnormal behaviours induced by chemical pollution: a review of the evidence and new challenges. Anim. Behav. 2004;68:649-664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anbehav.2004.01.005
Zoeller RT, Rovet J. Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: clinical observations and experimental findings. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2004;16(10):809-818.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 3, pp. 372-375, March, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaglova, N.V., Timokhina, E.P., Yaglov, V.V. et al. Changes in Histophysiology of the Adrenal Medulla in Rats after Prenatal and Postnatal Exposure to Endocrine Disruptor DDT. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 398–400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04895-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04895-6