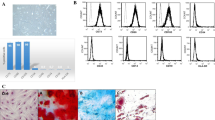
We studied immunosuppressive properties of skin fibroblasts and mesenchymal stromal cells against NK cells. In vitro experiments showed that mesenchymal stromal cells isolated from human umbilical cord and human skin fibroblasts can considerably attenuate cytotoxic activity of NK cells against Jurkat cells sensitive to NK-mediated lysis. NK cells cultured in lymphocyte population exhibited higher cytotoxic activity than isolated NK cells. Mesenchymal stromal cells or fibroblasts added 1:1 to lymphocyte culture almost completely suppressed NK cell cytotoxicity. This suggests that fibroblast-like cells can suppress not only isolated NK cells, but also NK cells in natural cell microenvironment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abakushina EV, Kuzmina EG, Kovalenko EI. The main characteristics of human natural killer cells. Immunologiya. 2012;33(4):220-224. Russian.
Vdovin AS, Lupatov AY, Kholodenko IV, Yarygin KN. Comparison of the efficiency of viral transduction and episomal transfection in human fibroblast reprogramming. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015;160(1):123-128.
Lupatov AY, Vdovin AS, Vakhrushev IV, Poltavtseva RA, Yarygin KN. Comparative analysis of the expression of surface markers on fibroblasts and fibroblast-like cells isolated from different human tissues. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2015;158(4):537-543.
Lupatov AY, Karalkin PA, Suzdal’tseva YG, Burunova VV, Yarygin VN, Yarygin KN. Cytofluorometric analysis of phenotypes of human bone marrow and umbilical fibroblast-like cells. 2006;142(4):521-526.
Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105(4):1815-1822.
Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, Ferrer K, McIntosh K, Patil S, Hardy W, Devine S, Ucker D, Deans R, Moseley A, Hoffman R. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp. Hematol. 2002;30(1):42-48.
Blasi A, Martino C, Balducci L, Saldarelli M, Soleti A, Navone S.E, Canzi L, Cristini S, Invernici G, Parati E.A, Alessandri G. Dermal fibroblasts display similar phenotypic and differentiation capacity to fat-derived mesenchymal stem cells, but differ in anti-inflammatory and angiogenic potential. Vasc. Cell. 2011;3(1):5. doi: 10.1186/2045-824X-3-5.
Chen L, Tredget EE, Wu PY, Wu Y. Paracrine factors of mesenchymal stem cells recruit macrophages and endothelial lineage cells and enhance wound healing. PLoS One. 2008;3(4):e1886.
Chen L, Zhang W, Yue H, Han Q, Chen B, Shi M, Li J, Li B, You S, Shi Y, Zhao R.C. Effects of human mesenchymal stem cells on the differentiation of dendritic cells from CD34+ cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2007;16(5):719-731.
Chen Y, Perussia B, Campbell KS. Prostaglandin D2 suppresses human NK cell function via signaling through D prostanoid receptor. J. Immunol. 2007;179(5):2766-2773.
DelaRosa O, Sánchez-Correa B, Morgado S, Ramírez C, del Río B, Menta R, Lombardo E, Tarazona R, Casado JG. Human adipose-derived stem cells impair natural killer cell function and exhibit low susceptibility to natural killer-mediated lysis. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;21(8):1333-1343.
Ghannam S, Pène J, Moquet-Torcy G, Jorgensen C, Yssel H. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit human Th17 cell differentia-tion and function and induce a T regulatory cell phenotype. J. Immunol. 2010;185(1):302-312.
Götherström C, Lundqvist A, Duprez IR, Childs R, Berg L, le Blanc K. Fetal and adult multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells are killed by different pathways. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(3):269-278.
Jorgensen C, Djouad F, Apparailly F, Noël D. Engineering mesenchymal stem cells for immunotherapy. Gene Ther. 2003;10(10):928-931.
Krampera M, Cosmi L, Angeli R, Pasini A, Liotta F, Andreini A, Santarlasci V, Mazzinghi B, Pizzolo G, Vinante F, Romagnani P, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F. Role for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(2):386-398.
Le Blanc K. Immunomodulatory effects of fetal and adult mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotherapy 2003;5(6):485-489.
Poggi A, Prevosto C, Massaro A.M, Negrini S, Urbani S, Pierri I, Saccardi R, Gobbi M, Zocchi M.R. Interaction between human NK cells and bone marrow stromal cells induces NK cell triggering: role of NKp30 and NKG2D receptors. J. Immunol. 2005;175(10):6352-6360.
Rasmusson I, Le Blanc K, Sundberg B, Ringdén O. Mesenchymal stem cells stimulate antibody secretion in human B cells. Scand. J. Immunol. 2007;65(4):336-343.
Rasmusson I, Uhlin M, Le Blanc K, Levitsky V. Mesenchymal stem cells fail to trigger effector functions of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007;82(4):887-893.
Ryan JM, Barry F, Murphy JM, Mahon BP. Interferon-gamma does not break, but promotes the immunosuppressive capacity of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2007;149(2):353-363.
Sotiropoulou PA, Perez SA, Gritzapis AD, Baxevanis CN, Papamichail M. Interactions between human mesenchymal stem cells and natural killer cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(1):74-85.
Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, Moretta L. MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2009;113(26):6576-6583.
Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, Mingari MC, Moretta L. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2008;111(3):1327-1333.
Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S, Mingari MC, Moretta L. Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell interactions: evidence that activated NK cells are capable of killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK cell proliferation. Blood. 2006;107(4):1484-1490.
Thomas H, Jäger M, Mauel K, Brandau S, Lask S, Flohé S.B. Interaction with mesenchymal stem cells provokes natural killer cells for enhanced IL-12/IL-18-induced interferon-gamma secretion. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014. ID 143463. doi: 10.1155/2014/143463. http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/143463.
Tu Z, Li Q, Bu H, Lin F. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit complement activation by secreting factor H. Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(11):1803-1809.
Vallera DA, Felices M, McElmurry R, McCullar V, Zhou X, Schmohl JU, Zhang B, Lenvik AJ, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Verneris MR, Tolar J, Cooley S, Weisdorf DJ, Blazar BR, Miller JS. IL15 trispecific killer engagers (TriKE) make natural killer cells specific to CD33+ targets while also inducing persistence, in vivo expansion, and enhanced function. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22(14):3440-3450.
Zamai L, Ahmad M, Bennett IM, Azzoni L, Alnemri ES, Perussia B. Natural killer (NK) cell-mediated cytotoxicity: differential use of TRAIL and Fas ligand by immature and mature primary human NK cells. J. Exp. Med. 1998;188(12):2375-2380.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tekhnologii v Biologii i Meditsine, No. 4, pp. 241-244, October, 2016
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lupatov, A.Y., Kim, Y.S., Bystrykh, O.A. et al. Effect of Fibroblast-Like Cells of Mesenchymal Origin of Cytotoxic Activity of Lymphocytes against NK-Sensitive Target Cells. Bull Exp Biol Med 162, 552–557 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3658-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3658-5