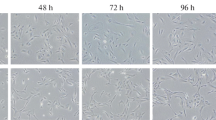
Multipotent characteristics of human fetal (9-11.5 weeks) pigmented epithelial retinal cells and capacity to transdifferentiation in neuronal direction were studied in vitro under different culturing conditions. The cultures were analyzed using a wide spectrum of antibodies. It was found that pigmented epithelium of human eye is a heterogeneous cell population with three subtypes differing by adhesion characteristics, migration, transdifferentiation potential, and reaction to microenvironmental factors. Subtype 1 cells steadily retain their epithelial characteristics, subtype 2 cells change their morphotype and produce neuroblast and photoreceptor cell proteins, and subtype 3 cells form free fl oating spheres and are capable to multipotent differentiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Aleksandrova, O. V. Podgornyi, and M. V. Marei, Kletochn. Tekhnol. Biol. Med., No. 1, 13-19 (2005).
K. Amemiya, M. Haruta, and M. Takahashi, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 316, No. 1, 1-5 (2004).
N. Asuma, K. Tadokoro, A. Asaka, et al., Hum. Mol. Genet., 14, No. 8, 1059-1068 (2005).
J. M. Burke and L. M. Hjelmeland, Mol. Interv., 5, No. 4, 241-249 (2005).
Ch. Chiba and V. Mitashov, Strategies for Retinal Tissue Repair and Regeneration in Vertebrates: from Fish to Human, Ed. Ch. Chiba, India: Trivandrum Res. Singpost (2008).
B. L. Coles, B. Angenieux, T. Inoue, et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, No. 44, 15,772-15,777 (2004).
M. Engelhardt, N. Bogdahn, and L. Aigner, Brain Res., 1040, Nos. 1-2, 98-111 (2005).
H. Klassen, D. S. Sakaguchi, and M. J. Young, Prog. Retin. Eye Res., 23, No. 2, 149-181 (2004).
A. Kojima, K. Nakahama, K. Ohno-Matsui, et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 366, No. 2, 532-538 (2008).
T. Marquardt, R. Ashery-Padan, N. Andrejewski, et al., Cell, 105, No. 1, 43-55 (2001).
J. R. Martinez-Morales, I. Rodrigo, and P. Bovolenta, Bioessays, 26, No. 7, 766-777 (2004).
F. T. Merkle and A. Alvarez-Buylla, Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol., 18, No. 6, 704-709 (2006).
V. I. Mitashov, Int. J. Develop. Biol., 41, No. 6, 893-905 (1997).
M. C. Moe, R. S. Kolberg, and C. Sandberg, Exp. Eye Res., 88, No. 1, 30-38 (2009).
N. Osumi, H. Shinohara, K. Numayama-Tsuruta, and M. Maekawa, Stem Cells, 26, No. 7, 1663-1672 (2008).
B. Raji, A. Dansault, J. Leemput, et al., Mol. Vis., 13, 1412-1427 (2007).
J. S. Schwegler, M. C. Knorz, I. Akkoyun, and H. Liesenhoff, Ibid., 3, 10 (1997).
O. Strauss, Physiol. Rev., 85, No. 3, 845-881 (2005).
O. G. Stroeva and V. I. Mitashov, Int. Rev. Cytol., 83, 221-293 (1983).
K. Susaki, J. Kaneko, Y. Yamano, et al., Exp. Eye Res., 88, No. 3, 347-355 (2009).
A. D. Tramontin, J. M. Garcia-Verdugo, D. A. Lim, and A. Anarez-Buylla, Cereb. Cortex, 13, No. 6, 580-587 (2003).
V. Tropepe, B. L. Coles, B. J. Chiasson, et al., Science, 287, No. 5460, 2032-2036 (2000).
U. Vielkind and B. J. Crawford, Develop. Growth, 30, No. 6, 727-736 (1988).
H. Xu, D. D. Sta Iglesia, J. L. Kielczewski, et al., Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 48, No. 4, 1674-1682 (2007).
F. Yan, Y. N. Hui, Y. Li, et al., Ophthalmologica, 221, No. 4, 244-250 (2007).
Y. Yanagi, Y. Inoue, Y. Kawase, et al., Exp. Eye Res., 82, No. 3, 471-478 (2006).
S. Zhao, L. J. Rizzolo, and C. J. Barnstable, Int. Rev. Cytol., 171, 225-266 (1997).
S. Zhao, S. C. Thornquist, and C. J. Barnstable, Brain Res., 677, No. 2, 300-310 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Kletochnye Tehnologii v Biologii i Medicine, No. 3, pp. 128-135, July, 2009
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milyushina, L.A., Poltavtseva, R.A., Marei, M.V. et al. In Vitro Phenotypic Modifi cation of Pigmented Epithelium Cells from Human Eye at Early Stages of Development. Bull Exp Biol Med 148, 113–119 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0657-1
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-009-0657-1