Abstract
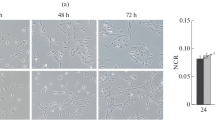
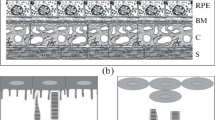
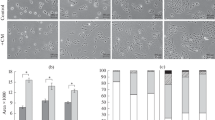
Changes in morphology and molecular genetic profile of human retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells in vitro were studied when exposed to the basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). The cell morphology was estimated by cell area and perimeter, spreading and polarization coefficients. It was demonstrated that the number of elongated (fibroblast-like) cells and the number of cells, which size was less than in the control increased in 48 h after adding the factor to the culture. At the same time, the cell proliferative activity decreased (according to MTT test). Immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated a decrease in the staining for connexin Cx43 and an increase in the intensity of staining for protein the Otx2 neuroepithelium protein. Simultaneously, the number of nestin-positive cells and βIII-tubulin positive cells increased. Using quantitative real-time PCR method, an increase in mRNA expression of the KLF4, OCT4, NANOG, OTX2, and NES and decrease in mRNA expression of the MITF and KRT18 were detected in RPE cells treated with bFGF; this indicates enhancement of cell dedifferentiation. These data are confirmed by a decrease in the COL1A1 mRNA expression indicating a decrease in synthetic cell activity. The results indicate that single (short-time) effect by bFGF is sufficient to activate the mechanism, which decreases the cell differentiation level toward neuroepithelium.








Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Al-Hussaini, H., Kam, J.H., Vugler, A., Semo, M., anad Jeffery, G., Mature retinal pigment epithelium cells are retained in the cell cycle and proliferate in vivo, Mol. Vis., 2008, vol. 14, pp. 1784–1791.
Baldwin, A.K., Cain, S.A., Lennon, R., Godwin, A., Merry, C.L.R., and Kielty, C.M., Epithelial–mesenchymal status influences how cells deposit fibrillin microfibrils, J. Cell Sci., 2014, vol. 127, no. 1, pp. 158–171. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.134270
Beckmann, A., Schubert, M., Hainz, N., Haase, A., Martin, U., Tschernig, T., and Meier, C., Ultrastructural demonstration of Cx43 gap junctions in induced pluripotent stem cells from human cord blood, Histochem. Cell Biol., 2016, vol. 146, no. 5, pp. 529–537.
Burke, J.M. and Hjelmeland, L.M., Mosaicism of the retinal pigment epithelium: seeing the small picture, Mol. Interv., 2005, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 241–249. https://doi.org/10.1124/mi.5.4.7
Chen, X., Xiao, W., Liu, X., Zeng, M., Luo, L., Wu, M., Ye, S., and Liu, Y., Blockade of Jagged/Notch pathway abrogates transforming growth factor β2-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition in human retinal pigment epithelium cells, Curr. Mol. Med., 2014, vol. 14, no. 4, pp. 523–534.
Chiba, C., The retinal pigment epithelium: an important player of retinal disorders and regeneration, Exp. Eye Res. 2014, vol. 123, pp. 107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2013.07.009
Ezati, R., Etemadzadeh, A., Soheili, Z., Samiei, S., Pirmardan, E.R., Davari, M., and Najafabadi, H.S., The influence of RAAV2-mediated SOX2 delivery into neonatal and adult human RPE cells: a comparative study, J. Cell. Physiol, 2018, vol. 233, no. 2, pp. 1222–1235.
Ferguson, L.R., Balaiya, S., Mynampati, B.K., Sambhav, K., and Chalam, K.V., Deprivation of bFGF promotes spontaneous differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into retinal pigment epithelial cells, J. Stem Cells, 2015, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 159–170.
Fuhrmann, S., Zou, C., and Levine, E.M., Retinal pigment epithelium development, plasticity, and tissue homeostasis, Exp. Eye Res., 2014, vol. 123, pp. 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2013.09.003
Grigoryan, E.N., Markitantova, Y.V., Avdonin, P.P., and Radugina, E.A., Study of regeneration in amphibians in age of molecular-genetic approaches and methods, Russ. J. Genet., 2013, vol. 49, pp. 46–62.
Huang, X., Wei, Y., Ma, H., and Zhang, S., Vitreous-induced cytoskeletal rearrangements via the Rac1 GTPase-dependent signaling pathway in human retinal pigment epithelial cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2012, vol. 419, no. 2, pp. 395–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.033
Islam, M.R., Nakamura, K., Casco-Robles, M.M., Kunahong, A., Inami, W., Toyama, F., Maruo, F., and Chiba, C., The newt reprograms mature RPE cells into a unique multipotent state for retinal regeneration, Sci. Rep., 2014, vol. 4, p. 6043. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep06043
Koike, C., Nishida, A., Ueno, S., Saito, H., Sanuki, R., Sato, S., Furukawa, A., Aizawa, S., Matsuo, I., Suzuki, N., Kondo, M., and Furukawa, T., Functional roles of Otx2 transcription factor in postnatal mouse retinal development, Mol. Cell. Biol., 2007, vol. 27, no. 23, pp. 8318–8329.
Kojima, A., Nakahama, K.-I., Ohno-Matsui, K., Shimada, N., Mori, K., Iseki, S., Sato, T., Mochizuki, M., and Morita, I., Connexin 43 contributes to differentiation of retinal pigment epithelial cells via cyclic AMP signaling, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2008, vol. 366, no. 2, pp. 532–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.11.159
Kuz’minykh, E.V. and Petrov, Y.P., A simple model for the study of effects of the extracellular matrix on the cell morphology in vitro, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2004, vol. 1671, nos. 1–3, pp. 18–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2004.01.001
Kuznetsova, A.V. and Aleksandrova, M.A., Heterogeneity of retinal pigment epithelial cells from adult human eye in different culturing systems, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2017, vol. 162, pp. 569–577.
Kuznetsova, A.V., Grigoryan, E.N., and Aleksandrova, M.A., Human adult retinal pigment epithelial cells as potential cell source for retina recovery, Cell Tissue Biol., 2011, vol. 5, no. 5, pp. 495–502.
Kuznetsova, A.V., Kurinov, A.M., and Aleksandrova, M.A., Cell models to study regulation of cell transformation in pathologies of retinal pigment epithelium, J. Ophthalmol., 2014, pp. 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/801787
Kuznetsova, A.V., Aleksandrova, M.A., Kurinov, A.M., Chentsova, E.V., and Makarov, P.V., Plasticity of adult human retinal pigment epithelial cells, Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med., 2016, vol. 9, no. 11, pp. 20892–20906. http://ijcem.com/files/ijcem0033105.pdf .
Liu, W., Jin, G., Long, C., Zhou, X., Tang, Y., Huang, S., Kuang, X., Wu, L., Zhang, Q., and Shen, H., Blockage of Notch signaling inhibits the migration and proliferation of retinal pigment epithelial cells, Sci. World J., 2013, p. 178708. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/178708
Lotz, S., Goderie, S., Tokas, N., Hirsch, S.E., Ahmad, F., Corneo, B., Le, S., Banerjee, A., Kane, R.S., Stern, J.H., Temple, S., and Fasano, C.A., Sustained levels of FGF2 maintain undifferentiated stem cell cultures with biweekly feeding, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 2. e56289. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0056289
Luz-Madrigal, A., Grajales-Esquivel, E., McCorkle, A., DiLorenzo, A.M., Barbosa-Sabanero, K., Tsonis, P.A., and Del Rio-Tsonis, K., Reprogramming of the chick retinal pigmented epithelium after retinal injury, BMC Biol., 2014, vol. 12, no. 1, p. 28. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-12-28
Martínez-Morales, J.R., Signore, M., Acampora, D., Simeone, A., and Bovolenta, P., Otx genes are required for tissue specification in the developing eye, Development, 2001, vol. 128, no. 11, pp. 2019–2030.
Martínez-Morales, J., Dolez, V., Rodrigo, I., Zaccarini, R., Leconte, L., Bovolenta, P., and Saule, S., OTX2 activates the molecular network underlying retina pigment epithelium differentiation, J. Biol. Chem., 2003, vol. 278, no. 24, pp. 21721–21731.
Milyushina, L.A., Kuznetsova, A. V., Grigoryan, E.N., and Aleksandrova, M.A., Phenotypic plasticity of retinal pigment epithelial cells from adult human eye in vitro, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2011, vol. 151, no. 4, pp. 506–511.
Milyushina, L.A., Verdiev, B.I., Kuznetsova, A. V., and Aleksandrova, M.A., Expression of multipotent and retinal markers in pigment epithelium of adult human in vitro, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2012, vol. 153, no. 1, pp. 157–162.
Murrell, W., Palmero, E., Bianco, J., Stangeland, B., Joel, M., Paulson, L., Thiede, B., Grieg, Z., Ramsnes, I., Skjellegrind, H.K., Nygård, S., Brandal, P., Sandberg, C., Vik-Mo, E., Palmero, S., and Langmoen, I.A., Expansion of multipotent stem cells from the adult human brain, PLoS One, 2013, vol. 8, no. 8. e71334. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0071334
Petrov, Y.P., Kukhareva, L.V., and Krylova, T.A., The effect of type I collagen and fibronectin on the morphology of human mesenchymal stromal cells in culture, Cell Tissue Biol., 2013, vol. 7, no. 6, pp. 545–555.
Pittack, C., Jones, M., and Reh, T.A., Basic fibroblast growth factor induces retinal pigment epithelium to generate neural retina in vitro, Development, 1991, vol. 113, no. 2, pp. 577–588.
Reyes-Aguirre, L.I. and Lamas, M., Oct4 methylation-mediated silencing as an epigenetic barrier preventing Müller glia dedifferentiation in a murine model of retinal injury, Front. Neurosci., 2016, vol. 10, p. 523. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00523
Sakaguchi, D.S., Janick, L.M., and Reh, T.A., Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) induced transdifferentiation of retinal pigment epithelium: generation of retinal neurons and glia, Dev. Dyn., 1997, vol. 209, no. 4, pp. 387–398.
Salero, E., Blenkinsop, T.A., Corneo, B., Harris, A., Rabin, D., Stern, J.H., and Temple, S., Adult human RPE can be activated into a multipotent stem cell that produces mesenchymal derivatives, Cell Stem Cell., 2012, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 88–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2011.11.018
Sandberg, C.J., Vik-Mo, E.O., Behnan, J., Helseth, E., and Langmoen, I.A., Transcriptional profiling of adult neural stem-like cells from the human brain, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 12. e114739. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114739
Schwegler, J.S., Knorz, M.C., Akkoyun, I., and Liesenhoff, H., Basic, not acidic fibroblast growth factor stimulates proliferation of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells, Mol. Vis., 1997, vol. 3, p. 10. http://www.molvis.org/molvis/v3/a10/schwegler.pdf.
Shafei, E.V., Kurinov, A.M., Kuznetsova, A.V., and Aleksandrova, M.A., Reprogramming of human retinal pigment epithelial cells under the effect of bFGF in vitro, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2017, vol. 163, no. 4, pp. 574–582.
Spence, J.R., Madhavan, M., Aycinena, J.C., and Del, Rio-Tsonis, K., Retina regeneration in the chick embryo is not induced by spontaneous Mitf downregulation but requires FGF/FGFR/MEK/Erk dependent upregulation of Pax6, Mol. Vis., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 57–65.
Theofilas, P., Steinh?user, C., Theis, M., and Derouiche, A., Morphological study of a connexin 43-GFP reporter mouse highlights glial heterogeneity, amacrine cells, and olfactory ensheathing cells, J. Neurosci. Res., 2017, vol. 95, no. 11, pp. 2182–2194.
Tian, J., Ishibashi, K., Honda, S., Boylan, S.A., Hjelmeland, L.M., and Handa, J.T., The expression of native and cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells grown in different culture conditions, Br. J. Ophthalmol., 2005, vol. 89, no. 11, pp. 1510–1517. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjo.2005.072108
Vincent, P.H., Benedikz, E., Uhlén, P., Hovatta, O., and undström, E., Expression of pluripotency markers in nonpluripotent human neural stem and progenitor cells, Stem Cells Dev., 2017, vol. 26, no. 12, pp. 876–887.
Wang, S.-Z., Ma, W., Yan, R.-T., and Mao, W., Generating retinal neurons by reprogramming retinal pigment epithelial cells, Expert Opin. Biol. Ther., 2010, vol. 10, no. 8, pp. 1227–1239.
Westenskow, P.D., McKean, J.B., Kubo, F., Nakagawa, S., and Fuhrmann, S., Ectopic Mitf in the embryonic chick retina by co-transfection of β-catenin and Otx2, Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci., 2010, vol. 51, no. 10, pp. 5328–5335.
Woodbury, M.E. and Ikezu, T., Fibroblast growth factor-2 signaling in neurogenesis and neurodegeneration, J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol., 2014, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 92–101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-013-9501-5
Xiao, W., Chen, X., Liu, X., Luo, L., Ye, S., and Liu, Y., Trichostatin A, a histone deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and epithelial–mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelium cells, J. Cell. Mol. Med., 2014, vol. 18, no. 4, pp. 646–655. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.12212
Zhao, S., Thornquist, S.C., and Barnstable, C.J., In vitro transdifferentiation of embryonic rat retinal pigment epithelium to neural retina, Brain Res., 1995, vol. 677, no. 2, pp. 300–310.
Zhu, J., Nguyen, D., Ouyang, H., Zhang, X.-H., Chen, X.M., and Zhang, K., Inhibition of RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway suppresses the expression of extracellular matrix induced by CTGF or TGF-β in ARPE-19, Int. J. Ophthalmol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 8–14. https://doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.01.02
Zhu, J., Luz-Madrigal, A., Haynes, T., Zavada, J., Burke, A.K., and Del Rio-Tsonis, K., β-Catenin inactivation is a pre-requisite for chick retina regeneration, PLoS One, 2014, vol. 9, no. 7. e101748. https://doi.org/10.3980/j.issn.2222-3959.2013.01.02
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was performed within part of a state order of the Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, on topic no. 0108-2018-0004 using the equipment of the Center for Collective Use of the Koltzov Institute of Developmental Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of compliance with standards of research involving humans as subjects. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Additional information
Translated by A. Barkhash
Abbreviations: ICC—immunocytochemistry, IPSC—induced pluripotent stem cells, qPCR—quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction, bFGF—basic fibroblast growth factor, RPE—retinal pigment epithelium.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsova, A.V., Kurinov, A.M., Rzhanova, L.A. et al. Mechanisms of Dedifferentiation of Adult Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells in vitro. Morphological and Molecular Genetic Analysis. Cell Tiss. Biol. 13, 107–119 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X19020068
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1990519X19020068