Abstract
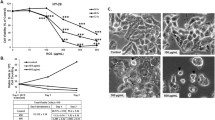
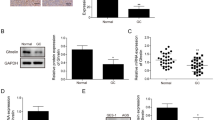
Ghrelin is a metabolism-regulating hormone recently investigated for its role in cancer survival and progression. Controversially, ghrelin may act as either anti-apoptotic or pro-apoptotic factor in different cancer cells, suggesting that the effects are cell type dependent. Limited data are currently available on the effects exerted by ghrelin on intracellular proteolytic pathways in cancer. Both the lysosomal and the proteasomal systems are fundamental in cellular proliferation and apoptosis regulation. With the aim of exploring if the proteasome and autophagy may be possible targets of ghrelin in cancer, we exposed human colorectal adenocarcinoma cells to ghrelin. Preliminary in vitro fluorimetric assays evidenced for the first time a direct inhibition of 20S proteasomes by ghrelin, particularly evident for the trypsin-like activity. Moreover, 1 μM ghrelin induced apoptosis in colorectal adenocarcinoma cells by inhibiting the ubiquitin–proteasome system and by activating autophagy, with p53 having an “interactive” role.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660
Tschop M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML (2000) Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature 407:908–913
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (2000) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin: two major forms of rat ghrelin peptide in gastrointestinal tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 279:909–913
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, Morris DG, McGee P, Fairclough P, Bhattacharya S, Carpenter R, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2002) The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2988
Baldanzi G, Filigheddu N, Cutrupi S, Catapano F, Bonissoni S, Fubini A, Malan D, Baj G, Granata R, Broglio F, Papotti M, Surico N, Bussolino F, Isgaard J, Deghenghi R, Sinigaglia F, Prat M, Muccioli G, Ghigo E, Graziani A (2002) Ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin inhibit cell death in cardiomyocytes and endothelial cells through ERK1/2 and PI 3-kinase/AKT. J Cell Biol 159:1029–1037
Bedendi I, Alloatti G, Marcantoni A, Malan D, Catapano F, Ghe C, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E, Muccioli G (2003) Cardiac effects of ghrelin and its endogenous derivatives des-octanoyl ghrelin and des-Gln14-ghrelin. Eur J Pharmacol 476:87–95
Cassoni P, Ghe C, Marrocco T, Tarabra E, Allia E, Catapano F, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E, Papotti M, Muccioli G (2004) Expression of ghrelin and biological activity of specific receptors for ghrelin and des-acyl ghrelin in human prostate neoplasms and related cell lines. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 150:173–184
Thompson NM, Gill DA, Davies R, Loveridge N, Houston PA, Robinson IC, Wells T (2004) Ghrelin and des-octanoyl ghrelin promote adipogenesis directly in vivo by a mechanism independent of the type 1a growth hormone secretagogue receptor. Endocrinology 145:234–242
Ekeblad S, Lejonklou MH, Grimfjard P, Johansson T, Eriksson B, Grimelius L, Stridsberg M, Stalberg P, Skogseid B (2007) Co-expression of ghrelin and its receptor in pancreatic endocrine tumours. Clin Endocrinol 66:115–122
Korbonits M, Bustin SA, Kojima M, Jordan S, Adams EF, Lowe DG, Kangawa K, Grossman AB (2001) The expression of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor ligand ghrelin in normal and abnormal human pituitary and other neuroendocrine tumors. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:881–887
Chopin L, Walpole C, Seim I, Cunningham P, Murray R, Whiteside E, Josh P, Herington A (2011) Ghrelin and cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 340:65–69
Jeffery PL, Herington AC, Chopin LK (2002) Expression and action of the growth hormone releasing peptide ghrelin and its receptor in prostate cancer cell lines. J Endocrinol 172:R7–11
Andreis PG, Malendowicz LK, Trejter M, Neri G, Spinazzi R, Rossi GP, Nussdorfer GG (2003) Ghrelin and growth hormone secretagogue receptor are expressed in the rat adrenal cortex: evidence that ghrelin stimulates the growth, but not the secretory activity of adrenal cells. FEBS Lett 536:173–179
Maccarinelli G, Sibilia V, Torsello A, Raimondo F, Pitto M, Giustina A, Netti C, Cocchi D (2005) Ghrelin regulates proliferation and differentiation of osteoblastic cells. J Endocrinol 184:249–256
Nanzer AM, Khalaf S, Mozid AM, Fowkes RC, Patel MV, Burrin JM, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2004) Ghrelin exerts a proliferative effect on a rat pituitary somatotroph cell line via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Eur J Endocrinol/Eur Fed Endocr Soc 151:233–240
Pettersson I, Muccioli G, Granata R, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E, Ohlsson C, Isgaard J (2002) Natural (ghrelin) and synthetic (hexarelin) GH secretagogues stimulate H9c2 cardiomyocyte cell proliferation. J Endocrinol 175:201–209
Wang DH, Hu YS, Du JJ, Hu YY, Zhong WD, Qin WJ (2009) Ghrelin stimulates proliferation of human osteoblastic TE85 cells via NO/cGMP signaling pathway. Endocrine 35:112–117
Xia Q, Pang W, Pan H, Zheng Y, Kang JS, Zhu SG (2004) Effects of ghrelin on the proliferation and secretion of splenic T lymphocytes in mice. Regul Pept 122:173–178
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Jeffery PL, Herington AC, Chopin LK (2003) The potential autocrine/paracrine roles of ghrelin and its receptor in hormone-dependent cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 14:113–122
Soares JB, Leite-Moreira AF (2008) Ghrelin, des-acyl ghrelin and obestatin: three pieces of the same puzzle. Peptides 29:1255–1270
Waseem T, Javaid Ur R, Ahmad F, Azam M, Qureshi MA (2008) Role of ghrelin axis in colorectal cancer: a novel association. Peptides 29:1369–1376
Tian PY, Fan XM (2012) The proliferative effects of ghrelin on human gastric cancer AGS cells. J Dig Dis 13:453–458
Jeffery PL, Murray RE, Yeh AH, McNamara JF, Duncan RP, Francis GD, Herington AC, Chopin LK (2005) Expression and function of the ghrelin axis, including a novel preproghrelin isoform, in human breast cancer tissues and cell lines. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:839–850
Fung JN, Seim I, Wang D, Obermair A, Chopin LK, Chen C (2010) Expression and in vitro functions of the ghrelin axis in endometrial cancer. Horm Cancer 1:245–255
Sirotkin AV, Grossmann R, Maria-Peon MT, Roa J, Tena-Sempere M, Klein S (2006) Novel expression and functional role of ghrelin in chicken ovary. Mol Cell Endocrinol 257–258:15–25
Ammori JB, Zhang WZ, Li JY, Chai BX, Mulholland MW (2008) Effects of ghrelin on neuronal survival in cells derived from dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. Surgery 144:159–167
Cassoni P, Papotti M, Ghe C, Catapano F, Sapino A, Graziani A, Deghenghi R, Reissmann T, Ghigo E, Muccioli G (2001) Identification, characterization, and biological activity of specific receptors for natural (ghrelin) and synthetic growth hormone secretagogues and analogs in human breast carcinomas and cell lines. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:1738–1745
Ghe C, Cassoni P, Catapano F, Marrocco T, Deghenghi R, Ghigo E, Muccioli G, Papotti M (2002) The antiproliferative effect of synthetic peptidyl GH secretagogues in human CALU-1 lung carcinoma cells. Endocrinology 143:484–491
Granado M, Priego T, Martin AI, Villanua MA, Lopez-Calderon A (2005) Ghrelin receptor agonist GHRP-2 prevents arthritis-induced increase in E3 ubiquitin-ligating enzymes MuRF1 and MAFbx gene expression in skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 289:E1007–E1014
Balasubramaniam A, Joshi R, Su C, Friend LA, Sheriff S, Kagan RJ, James JH (2009) Ghrelin inhibits skeletal muscle protein breakdown in rats with thermal injury through normalizing elevated expression of E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R893–R901
Ciechanover A (2005) Intracellular protein degradation: from a vague idea thru the lysosome and the ubiquitin-proteasome system and onto human diseases and drug targeting. Cell Death Differ 12:1178–1190
Orlowski M (1990) The multicatalytic proteinase complex, a major extralysosomal proteolytic system. Biochemistry 29:10289–10297
Orlowski M, Cardozo C, Michaud C (1993) Evidence for the presence of five distinct proteolytic components in the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Properties of two components cleaving bonds on the carboxyl side of branched chain and small neutral amino acids. Biochemistry 32:1563–1572
Kloetzel PM, Soza A, Stohwasser R (1999) The role of the proteasome system and the proteasome activator PA28 complex in the cellular immune response. Biological chemistry 380:293–297
Cecarini V, Cuccioloni M, Mozzicafreddo M, Bonfili L, Angeletti M, Eleuteri AM (2011) Targeting proteasomes with natural occurring compounds in cancer treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 11:307–324
Bonfili L, Amici M, Cecarini V, Cuccioloni M, Tacconi R, Angeletti M, Fioretti E, Keller JN, Eleuteri AM (2009) Wheat sprout extract-induced apoptosis in human cancer cells by proteasomes modulation. Biochimie 91:1131–1144
Fujishima Y, Nishiumi S, Masuda A, Inoue J, Nguyen NM, Irino Y, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Kutsumi H, Azuma T, Yoshida M (2011) Autophagy in the intestinal epithelium reduces endotoxin-induced inflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-kappaB activation. Arch Biochem Biophys 506:223–235
Reggiori F, Klionsky DJ (2002) Autophagy in the eukaryotic cell. Eukaryot Cell 1:11–21
Klionsky DJ, Cregg JM, Dunn WA Jr, Emr SD, Sakai Y, Sandoval IV, Sibirny A, Subramani S, Thumm M, Veenhuis M, Ohsumi Y (2003) A unified nomenclature for yeast autophagy-related genes. Dev Cell 5:539–545
Wang CW, Klionsky DJ (2003) The molecular mechanism of autophagy. Mol Med 9:65–76
Itakura E, Mizushima N (2011) p62 Targeting to the autophagosome formation site requires self-oligomerization but not LC3 binding. J Cell Biol 192:17–27
Yu L, McPhee CK, Zheng L, Mardones GA, Rong Y, Peng J, Mi N, Zhao Y, Liu Z, Wan F, Hailey DW, Oorschot V, Klumperman J, Baehrecke EH, Lenardo MJ (2010) Termination of autophagy and reformation of lysosomes regulated by mTOR. Nature 465:942–946
Gozuacik D, Kimchi A (2004) Autophagy as a cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene 23:2891–2906
Shintani T, Klionsky DJ (2004) Autophagy in health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science 306:990–995
Paglin S, Hollister T, Delohery T, Hackett N, McMahill M, Sphicas E, Domingo D, Yahalom J (2001) A novel response of cancer cells to radiation involves autophagy and formation of acidic vesicles. Cancer Res 61:439–444
Ogier-Denis E, Codogno P (2003) Autophagy: a barrier or an adaptive response to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1603:113–128
Eleuteri AM, Angeletti M, Lupidi G, Tacconi R, Bini L, Fioretti E (2000) Isolation and characterization of bovine thymus multicatalytic proteinase complex. Protein Expr Purif 18:160–168
Amici M, Lupidi G, Angeletti M, Fioretti E, Eleuteri AM (2003) Peroxynitrite-induced oxidation and its effects on isolated proteasomal systems. Free Radical Biol Med 34:987–996
Eleuteri AM, Kohanski RA, Cardozo C, Orlowski M (1997) Bovine spleen multicatalytic proteinase complex (proteasome). Replacement of X, Y, and Z subunits by LMP7, LMP2, and MECL1 and changes in properties and specificity. J Biol Chem 272:11824–11831
Duxbury MS, Waseem T, Ito H, Robinson MK, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW, Whang EE (2003) Ghrelin promotes pancreatic adenocarcinoma cellular proliferation and invasiveness. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 309:464–468
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Amici M, Bonfili L, Spina M, Cecarini V, Calzuola I, Marsili V, Angeletti M, Fioretti E, Tacconi R, Gianfranceschi GL, Eleuteri AM (2008) Wheat sprout extract induces changes on 20S proteasomes functionality. Biochimie 90:790–801
Biederbick A, Kern HF, Elsasser HP (1995) Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol 66:3–14
Buonanno F, Quassinti L, Bramucci M, Amantini C, Lucciarini R, Santoni G, Iio H, Ortenzi C (2008) The protozoan toxin climacostol inhibits growth and induces apoptosis of human tumor cell lines. Chem Biol Interact 176:151–164
Pagano M, Tam SW, Theodoras AM, Beer-Romero P, Del Sal G, Chau V, Yew PR, Draetta GF, Rolfe M (1995) Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in regulating abundance of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27. Science 269:682–685
Sun J, Nam S, Lee CS, Li B, Coppola D, Hamilton AD, Dou QP, Sebti SM (2001) CEP1612, a dipeptidyl proteasome inhibitor, induces p21WAF1 and p27KIP1 expression and apoptosis and inhibits the growth of the human lung adenocarcinoma A-549 in nude mice. Cancer Res 61:1280–1284
Roff M, Thompson J, Rodriguez MS, Jacque JM, Baleux F, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Hay RT (1996) Role of IkappaBalpha ubiquitination in signal-induced activation of NFkappaB in vivo. J Biol Chem 271:7844–7850
Steele RJ, Thompson AM, Hall PA, Lane DP (1998) The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Br J Surg 85:1460–1467
Korolchuk VI, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2009) A novel link between autophagy and the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Autophagy 5:862–863
Zhu BS, Xing CG, Lin F, Fan XQ, Zhao K, Qin ZH (2011) Blocking NF-kappaB nuclear translocation leads to p53-related autophagy activation and cell apoptosis. World J gastroenterol WJG 17:478–487
Zheng Q, Li J, Wang X (2009) Interplay between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in proteinopathies. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol 1:127–142
Cecarini V, Bonfili L, Cuccioloni M, Mozzicafreddo M, Rossi G, Buizza L, Uberti D, Angeletti M, Eleuteri AM (2012) Crosstalk between the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy in a human cellular model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:1741–1751
Yogalingam G, Pendergast AM (2008) Abl kinases regulate autophagy by promoting the trafficking and function of lysosomal components. J Biol Chem 283:35941–35953
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A, Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y, Yoshimori T (2000) LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J 19:5720–5728
Porter AG, Janicke RU (1999) Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 6:99–104
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 7:321–328
Affar EB, Germain M, Winstall E, Vodenicharov M, Shah RG, Salvesen GS, Poirier GG (2001) Caspase-3-mediated processing of poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase during apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:2935–2942
Lazebnik YA, Kaufmann SH, Desnoyers S, Poirier GG, Earnshaw WC (1994) Cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase by a proteinase with properties like ICE. Nature 371:346–347
Salvesen GS, Duckett CS (2002) IAP proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:401–410
Ciechanover A, Orian A, Schwartz AL (2000) The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway: mode of action and clinical implications. J Cell Biochem Suppl 34:40–51
Levine B, Kroemer G (2008) Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 132:27–42
McCray BA, Taylor JP (2008) The role of autophagy in age-related neurodegeneration. Neurosignals 16:75–84
Kojima M, Kangawa K (2005) Ghrelin: structure and function. Physiol Rev 85:495–522
Garber K (2006) Energy deregulation: licensing tumors to grow. Science 312:1158–1159
Lawnicka H, Melen-Mucha G, Motylewska E, Mucha S, Stepien H (2012) Modulation of ghrelin axis influences the growth of colonic and prostatic cancer cells in vitro. Pharmacol Rep 64:951–959
Du Y, Yang D, Li L, Luo G, Li T, Fan X, Wang Q, Zhang X, Wang Y, Le W (2009) An insight into the mechanistic role of p53-mediated autophagy induction in response to proteasomal inhibition-induced neurotoxicity. Autophagy 5:663–675
Rikiishi H (2012) Novel Insights into the Interplay between Apoptosis and Autophagy. Int J Cell Biol 2012:317645
Hosoda H, Doi K, Nagaya N, Okumura H, Nakagawa E, Enomoto M, Ono F, Kangawa K (2004) Optimum collection and storage conditions for ghrelin measurements: octanoyl modification of ghrelin is rapidly hydrolyzed to desacyl ghrelin in blood samples. Clin Chem 50:1077–1080
Acknowledgments
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonfili, L., Cuccioloni, M., Cecarini, V. et al. Ghrelin induces apoptosis in colon adenocarcinoma cells via proteasome inhibition and autophagy induction. Apoptosis 18, 1188–1200 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0856-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0856-0