Abstract
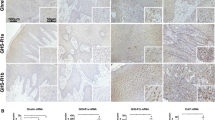
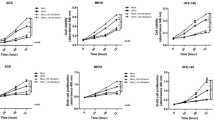
As the endogenous ligand for the GH secretagogue receptor (GHSR), Ghrelin is aberrant expressed in multiple malignant carcinoma, and involved in regulating a number of progression of cancer, especially in metastasis and proliferation. However, the precise role of Ghrelin in tumorigenesis of gastric cancer (GC) is still poorly understood. In this study, we extensively investigated the roles and mechanisms of Ghrelin in human gastric cancer. Ghrelin levels in cancer tissues and cell lines were analyzed by immunohistochemistry, qRT-PCR, and Western blot. Functional studies were performed after Ghrelin overexpressed or knockdown in AGS cell line. Cell proliferation was evaluated in by MTT and clone formation assays. The wound healing and Transwell system were used to assess the cell migration and invasive ability of GC cells. Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry, and metabolic assays were performed to reveal the function of Warburg effect in the process. Ghrelin was lowly expressed in gastric cancer tissues and cell lines. Overexpression of Ghrelin inhibited gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and promoted apoptosis by activating the AMPK pathway, while d-[lys3]-GHRP-6 (a GHSR agonist) treatment relieved the effect, promoting tumorigenesis. Ghrelin knockdown increased the glucose uptake and lactic acid release, suggesting that Ghrelin elicited an anti-Warburg effect via AMPK pathway to inhibit gastric tumorigenesis. Ghrelin inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by eliciting an anti-Warburg effect via AMPK signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bai RX et al (2016) Ghrelin attenuates the growth of HO-8910 ovarian cancer cells through the ERK pathway. Braz J Med Biol Res 49(3):e5043
Baniak N et al (2016) Gastric biomarkers: a global review. World J Surg Oncol 14(1):212
Bayliss JA et al (2016) Ghrelin-AMPK signaling mediates the neuroprotective effects of calorie restriction in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 36(10):3049–3063
Bray F et al (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Carling D (2017) AMPK signalling in health and disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol 45:31–37
Chang HR et al (2016) HNF4alpha is a therapeutic target that links AMPK to WNT signalling in early-stage gastric cancer. Gut 65(1):19–32
Charalampakis N et al (2018) Medical management of gastric cancer: a 2017 update. Cancer Med 7(1):123–133
Chen JH et al (2011) Ghrelin induces cell migration through GHS-R, CaMKII, AMPK, and NF-kappaB signaling pathway in glioma cells. J Cell Biochem 112(10):2931–2941
Chen X et al (2013) Ghrelin induces cell migration through GHSR1a-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS/NO signaling pathway in endothelial progenitor cells. Metabolism 62(5):743–752
Choi YY, Noh SH, An JY (2017) A randomized controlled trial of Roux-en-Y gastrojejunostomy vs. gastroduodenostomy with respect to the improvement of type 2 diabetes mellitus after distal gastrectomy in gastric cancer patients. PLoS One 12(12):e0188904
Chopin L et al (2011) Ghrelin and cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 340(1):65–69
Faubert B et al (2013) AMPK is a negative regulator of the Warburg effect and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Cell Metab 17(1):113–124
Gao M, Dang F, Deng C (2019) beta-Cryptoxanthin induced anti-proliferation and apoptosis by G0/G1 arrest and AMPK signal inactivation in gastric cancer. Eur J Pharmacol 859:172528
Gray SM, Page LC, Tong J (2019) Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. J Neuroendocrinol 31(7):e12705
Hardie DG, Alessi DR (2013) LKB1 and AMPK and the cancer-metabolism link—ten years after. BMC Biol 11:36
Hart PC et al (2015) MnSOD upregulation sustains the Warburg effect via mitochondrial ROS and AMPK-dependent signalling in cancer. Nat Commun 6:6053
Huang H, Yang XJ, Gao R (2016a) Research advances in the mechanisms of gastric cancer multidrug resistance. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 38(6):739–745
Huang D et al (2016b) Negative regulation of Bmi-1 by AMPK and implication in cancer progression. Oncotarget 7(5):6188–6200
Kraus D et al (2016) Ghrelin promotes oral tumor cell proliferation by modifying GLUT1 expression. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(6):1287–1299
Li Z, Zhang H (2016) Reprogramming of glucose, fatty acid and amino acid metabolism for cancer progression. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(2):377–392
Li W et al (2015) Targeting AMPK for cancer prevention and treatment. Oncotarget 6(10):7365–7378
Li W et al (2018) CAB39L elicited an anti-Warburg effect via a LKB1-AMPK-PGC1alpha axis to inhibit gastric tumorigenesis. Oncogene 37(50):6383–6398
Liberti MV, Locasale JW (2016) The Warburg effect: how does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci 41(3):211–218
Lien GS et al (2016) Ghrelin induces colon cancer cell proliferation through the GHS-R, Ras, PI3K, Akt, and mTOR signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 776:124–131
Lin SC, Hardie DG (2018) AMPK: sensing glucose as well as cellular energy status. Cell Metab 27(2):299–313
Lin TC et al (2015) Ghrelin promotes renal cell carcinoma metastasis via Snail activation and is associated with poor prognosis. J Pathol 237(1):50–61
Lin TC et al (2019) Ghrelin upregulates oncogenic aurora A to promote renal cell carcinoma invasion. Cancers (Basel) 11(3):303
Liu J et al (2016) A new mechanism of trastuzumab resistance in gastric cancer: MACC1 promotes the Warburg effect via activation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. J Hematol Oncol 9(1):76
Ngo DC et al (2015) Introduction to the molecular basis of cancer metabolism and the Warburg effect. Mol Biol Rep 42(4):819–823
Pereira J, da Silva FC, de Moraes-Vieira PMM (2017) The impact of ghrelin in metabolic diseases: an immune perspective. J Diabetes Res 2017:4527980
Poher AL, Tschop MH, Muller TD (2018) Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. Peptides 100:236–242
Pradhan G, Samson SL, Sun Y (2013) Ghrelin: much more than a hunger hormone. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 16(6):619–624
Pritchett NR et al (2020) Serum ghrelin and esophageal and gastric cancer in two cohorts in China. Int J Cancer 146(10):2728–2735
Schwartz L, Supuran CT, Alfarouk KO (2017) The Warburg effect and the hallmarks of cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem 17(2):164–170
Sever S, White DL, Garcia JM (2016) Is there an effect of ghrelin/ghrelin analogs on cancer? A systematic review. Endocr Relat Cancer 23(9):R393–R409
Shen M et al (2019a) The long-term population impact of endoscopic screening programmes on disease burdens of gastric cancer in China: a mathematical modelling study. J Theor Biol 484:109996
Shen Y et al (2019b) ARHGAP4 mediates the Warburg effect in pancreatic cancer through the mTOR and HIF-1alpha signaling pathways. Onco Targets Ther 12:5003–5012
Soleyman-Jahi S et al (2017) Prognostic significance of preoperative and postoperative plasma levels of ghrelin in gastric cancer: 3-year survival study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 8(1):e209
Song Z et al (2017) Progress in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 39(7):1010428317714626
Takaya K et al (2000) Ghrelin strongly stimulates growth hormone release in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(12):4908–4911
Tennakoon JB et al (2014) Androgens regulate prostate cancer cell growth via an AMPK-PGC-1alpha-mediated metabolic switch. Oncogene 33(45):5251–5261
Tian C et al (2013) Ghrelin induces gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through GHS-R/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 382(1–2):163–172
Wu Y et al (2016) AMPK activator AICAR promotes 5-FU-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 411(1–2):299–305
Xiao S, Zhou L (2017) Gastric cancer: metabolic and metabolomics perspectives (Review). Int J Oncol 51(1):5–17
Xu Y et al (2013) Ghrelin inhibits ovarian epithelial carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro. Oncol Rep 30(5):2063–2070
Xu DH et al (2018) Transmembrane protein GRINA modulates aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor progression in gastric cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37(1):308
Youn GJ, Chung WC (2017) Micrometastasis in gastric cancer. Korean J Gastroenterol 69(5):270–277
Zub-Pokrowiecka A et al (2011) Ghrelin and gastrin in advanced gastric cancer before and after gastrectomy. World J Gastroenterol 17(4):449–458
Funding
The present study was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of Southwest University (Grant No. XDJK2018C083); Associative Medical Research Project of Health and Science in Chongqing in 2019 (Grant No. 2019ZDXM032).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
(1) Conception and design: ZHW, XLH, and JW. (2) Administrative support: ZHW, XLH, and CHH. (3) Provision of study materials or patients: CHH and JW. (4) Collection and assembly of data: YJZ, XYH, and LY. (5) Data analysis and interpretation: LY and WJH. (6) Manuscript writing: All authors. (7) Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The present study has obtained the patient’s informed consent and has been approved by Ethics Committee of Southwest University Hospital.
Consent for Publication
The informed consent was obtained from study participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, XL., Zhu, YJ., Hu, CH. et al. Ghrelin Affects Gastric Cancer Progression by Activating AMPK Signaling Pathway. Biochem Genet 59, 652–667 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-10022-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-020-10022-x