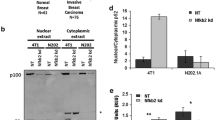
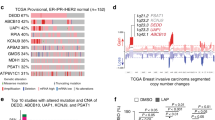
Abstract
Anoikis-resistance of tumor cells is critical for anchorage-independent growth and metastasis. The inflammatory-response transcription factor NF-κB contributes to anoikis-resistance and tumor progression through mechanisms that are understood incompletely. Deleted in breast cancer-1 (DBC1) protein (KIAA1967) is over-expressed in several tumor types, and correlates with a poorer prognosis in some cases. We report here that DBC1 suppressed anoikis in normal epithelial and breast cancer cell lines. DBC1 interacted with IKK-β, stimulating its kinase activity, promoting NF-κB transcriptional activity through the phosphorylation of relA serine-536 and enhancing the expression of the NF-κB target genes, c-FLIP and bcl-xl. Our results indicate that DBC1 is an important co-factor for the control of the IKK-β-NF-κB signaling pathway that regulates anoikis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frisch SM, Francis H (1994) Disruption of epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 124:619–626
Guadamillas MC, Cerezo A, Del Pozo MA (2011) Overcoming anoikis—pathways to anchorage-independent growth in cancer. J Cell Sci 124:3189–3197
Frisch SM, Schaller M, Cieply B (2013) Mechanisms that link the oncogenic epithelial-mesenchymal transition to suppression of anoikis. J Cell Sci 126(pt 1):21–29
Simpson CD, Anyiwe K, Schimmer AD (2008) Anoikis resistance and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett 272:177–185
Baldwin AS (2012) Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-kappaB: critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol Rev 246:327–345
Aggarwal BB, Sung B (2011) NF-kappaB in cancer: a matter of life and death. Cancer Discov 1:469–471
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F, Karin M (2012) NF-kappaB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev 246:379–400
Toruner M, Fernandez-Zapico M, Sha JJ, Pham L, Urrutia R et al (2006) Antianoikis effect of nuclear factor-kappaB through up-regulated expression of osteoprotegerin, BCL-2, and IAP-1. J Biol Chem 281:8686–8696
Liu Z, Li H, Wu X, Yoo BH, Yan SR et al (2006) Detachment-induced upregulation of XIAP and cIAP2 delays anoikis of intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 25:7680–7690
Mehrotra S, Languino LR, Raskett CM, Mercurio AM, Dohi T et al (2010) IAP regulation of metastasis. Cancer Cell 17:53–64
Mawji IA, Simpson CD, Hurren R, Gronda M, Williams MA et al (2007) Critical role for Fas-associated death domain-like interleukin-1-converting enzyme-like inhibitory protein in anoikis resistance and distant tumor formation. J Natl Cancer Inst 99:811–822
Yan SR, Joseph RR, Rosen K, Reginato MJ, Jackson A et al (2005) Activation of NF-kappaB following detachment delays apoptosis in intestinal epithelial cells. Oncogene 24:6482–6491
Lin DC, Zhang Y, Pan QJ, Yang H, Shi ZZ et al (2011) PLK1 Is transcriptionally activated by NF-kappaB during cell detachment and enhances anoikis resistance through inhibiting beta-catenin degradation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 17:4285–4295
Howe EN, Cochrane DR, Cittelly DM, Richer JK (2012) miR-200c targets a NF-kappaB up-regulated TrkB/NTF3 autocrine signaling loop to enhance anoikis sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer. PLoS One 7:e49987
Calao M, Burny A, Quivy V, Dekoninck A, Van Lint C (2008) A pervasive role of histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases in an NF-kappaB-signaling code. Trends Biochem Sci 33:339–349
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2011) Crosstalk in NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Nat Immunol 12:695–708
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Park HU, Brady JN (2005) A novel NF-kappaB pathway involving IKKbeta and p65/RelA Ser-536 phosphorylation results in p53 inhibition in the absence of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. J Biol Chem 280:10326–10332
Sakurai H, Chiba H, Miyoshi H, Sugita T, Toriumi W (1999) IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 274:30353–30356
Yang F, Tang E, Guan K, Wang CY (2003) IKK beta plays an essential role in the phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 536 induced by lipopolysaccharide. J Immunol 170:5630–5635
Adli M, Merkhofer E, Cogswell P, Baldwin AS (2010) IKKalpha and IKKbeta each function to regulate NF-kappaB activation in the TNF-induced/canonical pathway. PLoS One 5:e9428
Zannini L, Buscemi G, Kim JE, Fontanella E, Delia D (2012) DBC1 phosphorylation by ATM/ATR inhibits SIRT1 deacetylase in response to DNA damage. J Mol Cell Biol 4:294–303
Hiraike H, Wada-Hiraike O, Nakagawa S, Saji S, Maeda D et al (2011) Expression of DBC1 is associated with nuclear grade and HER2 expression in breast cancer. Exp Ther Med 2:1105–1109
Lee H, Kim KR, Noh SJ, Park HS, Kwon KS et al (2011) Expression of DBC1 and SIRT1 is associated with poor prognosis for breast carcinoma. Hum Pathol 42:204–213
Kim SH, Kim JH, Yu EJ, Lee KW, Park CK (2012) The overexpression of DBC1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma correlates with poor prognosis. Histol Histopathol 27:49–58
Zhang Y, Gu Y, Sha S, Kong X, Zhu H, et al (2013) DBC1 is over-expressed and associated with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. doi:10.1007/s10147-012-0506-5
Kim JE, Chen J, Lou Z (2009) p30 DBC is a potential regulator of tumorigenesis. Cell Cycle 8(18):2932–2935
Escande C, Chini CC, Nin V, Dykhouse KM, Novak CM et al (2010) Deleted in breast cancer-1 regulates SIRT1 activity and contributes to high-fat diet-induced liver steatosis in mice. J Clin Invest 120:545–558
Debnath J, Muthuswamy SK, Brugge JS (2003) Morphogenesis and oncogenesis of MCF-10A mammary epithelial acini grown in three-dimensional basement membrane cultures. Methods 30:256–268
Shehzad A, Khan S, Sup Lee Y (2012) Curcumin molecular targets in obesity and obesity-related cancers. Future Oncol 8:179–190
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, Yamasaki Y, Tsukasaki K et al (2002) Bay 11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell leukemia cells. Blood 100:1828–1834
Woronicz JD, Gao X, Cao Z, Rothe M, Goeddel DV (1997) IkappaB kinase-beta: NF-kappaB activation and complex formation with IkappaB kinase-alpha and NIK. Science 278:866–869
Boehm JS, Zhao JJ, Yao J, Kim SY, Firestein R et al (2007) Integrative genomic approaches identify IKBKE as a breast cancer oncogene. Cell 129:1065–1079
Zhao W, Kruse JP, Tang Y, Jung SY, Qin J et al (2008) Negative regulation of the deacetylase SIRT1 by DBC1. Nature 451:587–590
Kim JE, Chen J, Lou Z (2008) DBC1 is a negative regulator of SIRT1. Nature 451:583–586
Bouwmeester T, Bauch A, Ruffner H, Angrand PO, Bergamini G et al (2004) A physical and functional map of the human TNF-alpha/NF-kappa B signal transduction pathway. Nat Cell Biol 6:97–105
Sakamoto K, Hikiba Y, Nakagawa H, Hirata Y, Hayakawa Y et al (2013) Promotion of DNA repair by nuclear IKKbeta phosphorylation of ATM in response to genotoxic stimuli. Oncogene 32(14):1854–1862
Alfano D, Iaccarino I, Stoppelli MP (2006) Urokinase signaling through its receptor protects against anoikis by increasing BCL-xL expression levels. J Biol Chem 281:17758–17767
Mawji IA, Simpson CD, Gronda M, Williams MA, Hurren R et al (2007) A chemical screen identifies anisomycin as an anoikis sensitizer that functions by decreasing FLIP protein synthesis. Cancer Res 67:8307–8315
Adli M, Baldwin AS (2006) IKK-i/IKKepsilon controls constitutive, cancer cell-associated NF-kappaB activity via regulation of Ser-536 p65/RelA phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 281:26976–26984
Tsuchiya Y, Asano T, Nakayama K, Kato T Jr, Karin M et al (2010) Nuclear IKKbeta is an adaptor protein for IkappaBalpha ubiquitination and degradation in UV-induced NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell 39:570–582
Lewander A, Gao J, Carstensen J, Arbman G, Zhang H et al (2012) NF-kappaB p65 phosphorylated at serine-536 is an independent prognostic factor in Swedish colorectal cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis 27:447–452
Bae HJ, Chang YG, Noh JH, Kim JK, Eun JW et al (2012) DBC1 does not function as a negative regulator of SIRT1 in liver cancer. Oncol Lett 4:873–877
Yu EJ, Kim SH, Heo K, Ou CY, Stallcup MR et al (2011) Reciprocal roles of DBC1 and SIRT1 in regulating estrogen receptor alpha activity and co-activator synergy. Nucleic Acids Res 39:6932–6943
Li Z, Chen L, Kabra N, Wang C, Fang J et al (2009) Inhibition of SUV39H1 methyltransferase activity by DBC1. J Biol Chem 284:10361–10366
Chini CC, Escande C, Nin V, Chini EN (2010) HDAC3 is negatively regulated by the nuclear protein DBC1. J Biol Chem 285:40830–40837
Hiraike H, Wada-Hiraike O, Nakagawa S, Koyama S, Miyamoto Y et al (2010) Identification of DBC1 as a transcriptional repressor for BRCA1. Br J Cancer 102:1061–1067
Trauernicht AM, Kim SJ, Kim NH, Boyer TG (2007) Modulation of estrogen receptor alpha protein level and survival function by DBC-1. Mol Endocrinol 21:1526–1536
Fu J, Jiang J, Li J, Wang S, Shi G et al (2009) Deleted in breast cancer 1, a novel androgen receptor (AR) coactivator that promotes AR DNA-binding activity. J Biol Chem 284:6832–6840
Close P, East P, Dirac-Svejstrup AB, Hartmann H, Heron M et al (2012) DBIRD complex integrates alternative mRNA splicing with RNA polymerase II transcript elongation. Nature 484:386–389
Nin V, Escande C, Chini CC, Giri S, Camacho-Pereira J et al (2012) Role of deleted in breast cancer 1 (DBC1) protein in SIRT1 deacetylase activation induced by protein kinase A and AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 287:23489–23501
Acknowledgments
S.M. Frisch was supported by NIH Grant R01CA123359. The flow cytometry core facility (Mary Babb Randolph Cancer Center) was supported by NIH Grants RR020866 and P20 RR16440 and we thank Kathy Brundage for performing the flow-sorting. We also wish to thank Zenkun Lou, Eduardo Chini for the DBC1-knockout cells, Alexey Ivanov, Elena Pugacheva, Jurg Tschopp, Russ Carstens, Yon Rojanasakul and Sierra Talbott for constructs; we also thank the Biochemistry Protein Core for assistance with recombinant protein production.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.