Abstract
Introduction
The NF-κB transcription factor protein family has diverse cellular and biological functions, and posttranslational modification is important to regulate these functions. An important site of phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 subunit is at serine-536 (phospho-Ser536-p65), and this phosphorylation is involved in regulation of transcriptional activity, nuclear localization, and protein stability.
Patients and Methods
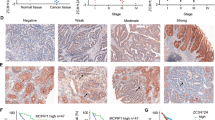
In this study, we investigated expression of phospho-Ser536-p65 in colorectal cancers and its relationships with clinicopathological factors. The expression of phospho-Ser536-p65 was examined by immunohistochemistry in 203 primary colorectal cancers, 156 normal mucosa specimens, and 18 metastases in the lymph nodes.
Results
The expression of phospho-Ser536-p65 increased from normal mucosa to primary tumor (p < 0.0001). Further, the increased expression of phospho-Ser536-p65 in the cytoplasm of the primary tumors correlated with worse survival of the patients independently of gender, age, tumor location, stage, and differentiation (p = 0.04; hazard ratio, 1.89; 95% CI 1.03–3.47).
Conclusion
The NF-κB p65 subunit phosphorylated at serine-536 is an independent prognostic factor in colorectal cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chee CE, Sinicrope FA (2010) Targeted therapeutic agents for colorectal cancer. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 39:601–613
Sun X-F, Zhang H (2007) NFKB and NFKBI polymorphisms in relation to susceptibility of tumour and other diseases. Histol Histopathol 22:1387–1398
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V, Chariot A (2005) Phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and IkappaB proteins: implications in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci 30:43–52
Moynagh PN (2005) The NF-kappaB pathway. J Cell Sci 118:4589–4592
Sakurai H, Chiba H, Miyoshi H, Sugita T, Toriumi W (1999) IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 274:30353–30356
Sizemore N, Lerner N, Dombrowski N, Sakurai H, Stark GR (2002) Distinct roles of the IκB kinase α and β subunits in liberating nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) from IκB and in phorphorylating the p65 subunit of NF-κB. J Biol Chem 277:3863–3869
Buss H, Dörrie A, Schmitz ML, Hoffmann E, Resch K, Kracht M (2004) Constitutive and interleukin-1-inducible phosphorylation of p65 NF-κB at serine 536 is mediated by multiple protein kinases including IκB kinase (IKK)-α, IKKβ, IKKε, TRAF family member-associated (TANK)-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), and an unknown kinase and couples p65 to TATA-binding protein-associated factor II31-mediated interleukin-8 transcription. J Biol Chem 279:55633–55643
Lawrence T, Bebien M, Liu GY, Nizet V, Karin M (2005) IKKα limits macrophage NF-κB activation and contributes to the resolution of inflammation. Nature 434:1138–1143
Berenson JR, Ma HM, Vescio R (2001) The role of nuclear factor-kappaB in the biology and treatment of multiple myeloma. Semin Oncol 28:626–633
Beinke S, Ley SC (2004) Functions of NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 in immune cell biology. Biochem J 382:393–409
Yu Y, Wan Y, Huang C (2009) The biological functions of NF-kappaB1 (p50) and its potential as an anti-cancer target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:566–571
Lind DS, Hochwald SN, Malaty J, Rekkas S, Hebig P, Mishra G, Moldawer LL, Copeland EM 3rd, Mackay S (2001) Nuclear factor-κB is upregulated in colorectal cancer. Surgery 130:363–369
Yu HG, Yu LL, Yang Y, Luo HS, Yu JP, Meier JJ, Schrader H, Bastian A, Schmidt WE, Schmitz F (2003) Increased expression of RelA/nuclear factor-kappa B protein correlates with colorectal tumorigenesis. Oncology 65:37–45
Wang W, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Larry L, Cleary KR, Chiao PJ (1999) The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 5:119–127
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van Antwerp D, Miyamoto S (1995) Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev 9:2723–2735
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Helen Richard, Cecilia Bergenwald, Gertrud Stridh, Gunnel Lindell, and Kerstin Ingels, Department of Pathology, Linköping Hospital, Sweden, for kindly preparing tissue sections, and Dr. David Hinselwood (a Scottish doctor) at the Division of Oncology, Linköping University, Sweden, for revising this paper.
Conflicts of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study was supported by grants from the Swedish Cancer Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, and the Health Research Council in the Southeast of Sweden.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewander, A., Gao, J., Carstensen, J. et al. NF-κB p65 phosphorylated at serine-536 is an independent prognostic factor in Swedish colorectal cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis 27, 447–452 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1356-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00384-011-1356-8