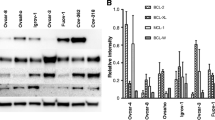
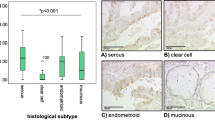
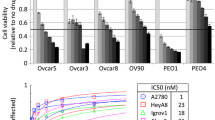
Abstract
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death from gynecological cancer. The anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-xL is frequently overexpressed in ovarian carcinoma which correlates with chemotherapy resistance. It has been demonstrated that Bcl-xL cooperates with another anti-apoptotic protein, Mcl-1, to protect ovarian cancer cells against apoptosis, and that their concomitant inhibition induces massive cell death. Here, we examined the interest of ABT-737, a potent BH3-mimetic molecule targeting Bcl-xL, both alone and in combination with Mcl-1 modulators, in ovarian cancer cell lines. As a single agent, ABT-737 was ineffective at promoting cell death in the four cell lines we tested in vitro. However, the specific inhibition of Mcl-1 by siRNA dramatically increased the sensitivity of chemoresistant cells to ABT-737. Platinum compounds also sensitize to ABT-737 by dose-dependently decreasing Mcl-1 expression or by increasing the expression of pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins Noxa and, to a lower extent, Bim. Furthermore, we demonstrated that Noxa accumulation was involved in apoptosis occurring in response to the combination of ABT-737 and platinum compounds, since cells were protected from apoptosis by its silencing. Moreover, the combination was also highly cytotoxic ex vivo in sliced SKOV3 tumor nodes. However we observed in these slices a strong basal expression of Noxa and apoptotic cell death in response to ABT-737 alone. Therefore, we have revealed that the modulation of the Mcl-1/Noxa axis by platinum compounds results in a strong sensitization of chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells to ABT-737, which could constitute a promising therapeutic in these cancers.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Carboplatin
- CDDP:
-
Cisplatin (cis-diammino-dichloro-platinum(II))
- CHX:
-
Cycloheximide
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribosyl) polymerase
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- HA14-1:
-
Ethyl [2-amino-6-bromo-4-(1-cyano-2-ethoxy-2-oxoethyl)]-4H-chromene-3-carboxylate
- HES:
-
Hematoxylin eosin safran
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Fesik SW (2005) Promoting apoptosis as a strategy for cancer drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer 5:876–885
Adams JM, Cory S (2007) The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 26:1324–1337
Williams J, Lucas PC, Griffith KA et al (2005) Expression of Bcl-xL in ovarian carcinoma is associated with chemoresistance and recurrent disease. Gynecol Oncol 96:287–295
Dodier P, Piche A (2006) Bcl-X(L) is functionally non-equivalent for the regulation of growth and survival in human ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol 100:254–263
Villedieu M, Louis MH, Dutoit S et al (2007) Absence of Bcl-xL down-regulation in response to cisplatin is associated with chemoresistance in ovarian carcinoma cells. Gynecol Oncol 105:31–44
Shigemasa K, Katoh O, Shiroyama Y et al (2002) Increased MCL-1 expression is associated with poor prognosis in ovarian carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 93:542–550
Brotin E, Meryet-Figuiere M, Simonin K et al (2010) Bcl-XL and MCL-1 constitute pertinent targets in ovarian carcinoma and their concomitant inhibition is sufficient to induce apoptosis. Int J Cancer 126:885–895
Varin E, Denoyelle C, Brotin E et al (2010) Downregulation of Bcl-xL and Mcl-1 is sufficient to induce cell death in mesothelioma cells highly refractory to conventional chemotherapy. Carcinogenesis 31:984–993
Trudel S, Li ZH, Rauw J, Tiedemann RE, Wen XY, Stewart AK (2007) Preclinical studies of the pan-Bcl inhibitor obatoclax (GX015-070) in multiple myeloma. Blood 109:5430–5438
Oliver L, Mahe B, Gree R, Vallette FM, Juin P (2007) HA14-1, a small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2, bypasses chemoresistance in leukaemia cells. Leuk Res 31:859–863
Arisan ED, Kutuk O, Tezil T, Bodur C, Telci D, Basaga H (2010) Small inhibitor of Bcl-2, HA14-1, selectively enhanced the apoptotic effect of cisplatin by modulating Bcl-2 family members in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119:271–281
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR et al (2005) An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435:677–681
Chauhan D, Velankar M, Brahmandam M et al (2007) A novel Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L)/Bcl-w inhibitor ABT-737 as therapy in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 26:2374–2380
Del GMV, Brown JR, Certo M, Love TM, Novina CD, Letai A (2007) Chronic lymphocytic leukemia requires BCL2 to sequester prodeath BIM, explaining sensitivity to BCL2 antagonist ABT-737. J Clin Investig 117:112–121
Kuroda J, Kimura S, Andreeff M et al (2008) ABT-737 is a useful component of combinatory chemotherapies for chronic myeloid leukaemias with diverse drug-resistance mechanisms. Br J Haematol 140:181–190
Wesarg E, Hoffarth S, Wiewrodt R et al (2007) Targeting BCL-2 family proteins to overcome drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer 121:2387–2394
Tahir SK, Yang X, Anderson MG et al (2007) Influence of Bcl-2 family members on the cellular response of small-cell lung cancer cell lines to ABT-737. Cancer Res 67:1176–1183
Tagscherer KE, Fassl A, Campos B et al (2008) Apoptosis-based treatment of glioblastomas with ABT-737, a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins. Oncogene 27:6646–6656
Bray K, Chen HY, Karp CM et al (2009) Bcl-2 modulation to activate apoptosis in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer Res 7:1487–1496
Chen S, Dai Y, Harada H, Dent P, Grant S (2007) Mcl-1 down-regulation potentiates ABT-737 lethality by cooperatively inducing Bak activation and Bax translocation. Cancer Res 67:782–791
Konopleva M, Contractor R, Tsao T et al (2006) Mechanisms of apoptosis sensitivity and resistance to the BH3-mimetic ABT-737 in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 10:375–388
Kang MH, Wan Z, Kang YH, Sposto R, Reynolds CP (2008) Mechanism of synergy of N-(4-hydroxyphenyl)retinamide and ABT-737 in acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines: Mcl-1 inactivation. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:580–595
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G et al (2005) Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 19:1294–1305
Simonin K, Brotin E, Dufort S et al (2009) Mcl-1 is an important determinant of the apoptotic response to the BH3-mimetic molecule HA14-1 in cisplatin-resistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 8:3162–3170
Poulain L, Lincet H, Duigou F et al (1998) Acquisition of chemoresistance in a human ovarian carcinoma cell is linked to a defect in cell cycle control. Int.J. Cancer 78:454–463
Ke N, Wang X, Xu X, Abassi YA (2011) The xCELLigence system for real-time and label-free monitoring of cell viability. Methods Mol Biol 740:33–43
Hauck P, Chao BH, Litz J, Krystal GW (2009) Alterations in the Noxa/Mcl-1 axis determine sensitivity of small cell lung cancer to the BH3-mimetic ABT-737. Mol Cancer Ther 8:883–892
Kutuk O, Letai A (2008) Alteration of the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway is key to acquired paclitaxel resistance and can be reversed by ABT-737. Cancer Res 68:7985–7994
Cragg MS, Jansen ES, Cook M, Harris C, Strasser A, Scott CL (2008) Treatment of B-RAF mutant human tumor cells with a MEK inhibitor requires Bim and is enhanced by a BH3-mimetic. J Clin Investig 118:3651–3659
Kline MP, Rajkumar SV, Timm MM et al (2007) ABT-737, an inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins, is a potent inducer of apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 21:1549–1560
van Delft MF, Wei AH, Mason KD et al (2006) The BH3-mimetic ABT-737 targets selective Bcl-2 proteins and efficiently induces apoptosis via Bak/Bax if Mcl-1 is neutralized. Cancer Cell 10:389–399
Yin S, Dong Y, Li J et al (2012) Methylseleninic acid potentiates multiple types of cancer cells to ABT-737-induced apoptosis by targeting Mcl-1 and Bad. Apoptosis 17:388–399
Yecies D, Carlson NE, Deng J, Letai A (2010) Acquired resistance to ABT-737 in lymphoma cells that up-regulate MCL-1 and BFL-1. Blood 115:3304–3313
Nijhawan D, Fang M, Traer E et al (2003) Elimination of Mcl-1 is required for the initiation of apoptosis following ultraviolet irradiation. Genes Dev 17:1475–1486
Ding Q, He X, Hsu JM et al (2007) Degradation of Mcl-1 by beta-TrCP mediates glycogen synthase kinase 3-induced tumor suppression and chemosensitization. Mol Cell Biol 27:4006–4017
Weng C, Li Y, Xu D, Shi Y, Tang H (2005) Specific cleavage of Mcl-1 by caspase-3 in tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis in Jurkat leukemia T cells. J Biol Chem 280:10491–10500
Clohessy JG, Zhuang J, Brady HJ (2004) Characterisation of Mcl-1 cleavage during apoptosis of haematopoietic cells. Br J Haematol 125:655–665
Hikita H, Takehara T, Shimizu S et al (2010) The Bcl-xL inhibitor, ABT-737, efficiently induces apoptosis and suppresses growth of hepatoma cells in combination with sorafenib. Hepatology 52:1310–1321
Schwickart M, Huang X, Lill JR et al (2010) Deubiquitinase USP9X stabilizes MCL1 and promotes tumour cell survival. Nature 463:103–107
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA (1995) Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378:785–789
Warr MR, Acoca S, Liu Z et al (2005) BH3-ligand regulates access of MCL-1 to its E3 ligase. FEBS Lett 579:5603–5608
Ding Q, Huo L, Yang JY et al (2008) Down-regulation of myeloid cell leukemia-1 through inhibiting Erk/Pin 1 pathway by sorafenib facilitates chemosensitization in breast cancer. Cancer Res 68:6109–6117
Mazumder S, Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Almasan A (2012) Mcl-1 phosphorylation defines ABT-737 resistance that can be overcome by increased Noxa expression in leukemic B cells. Cancer Res 72:3069–3079
Li R, Zang Y, Li C, Patel NS, Grandis JR, Johnson DE (2009) ABT-737 synergizes with chemotherapy to kill head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells via a Noxa-mediated pathway. Mol Pharmacol 75:1231–1239
Lucas KM, Mohana-Kumaran N, Lau D et al (2012) Modulation of Noxa and MCL-1 as a strategy for sensitizing melanoma cells to the BH3-mimetic ABT-737. Clin Cancer Res 18:783–795
Albershardt TC, Salerni BL, Soderquist RS et al (2011) Multiple BH3-mimetics antagonize antiapoptotic MCL1 protein by inducing the endoplasmic reticulum stress response and up-regulating BH3-only protein Noxa. J Biol Chem 286:24882–24895
Yang C, Kaushal V, Shah SV, Kaushal GP (2007) Mcl-1 is downregulated in cisplatin-induced apoptosis, and proteasome inhibitors restore Mcl-1 and promote survival in renal tubular epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F1710–F1717
Chatelut E (2011) Pharmacology of platinum compounds: differences between the three molecules and factors of interpatient variability. Bull Cancer 98:1253–1261
Braddock PD, Connors TA, Jones M, Khokhar AR, Melzack DH, Tobe ML (1975) Structure and activity relationships of platinum complexes with anti-tumour activity. Chem Biol Interact 11:145–161
Goodisman J, Hagrman D, Tacka KA, Souid AK (2006) Analysis of cytotoxicities of platinum compounds. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 57:257–267
Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE et al (2003) Phase III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol 21:3194–3200
Jain HV, Meyer-Hermann M (2011) The molecular basis of synergism between carboplatin and ABT-737 therapy targeting ovarian carcinomas. Cancer Res 71:705–715
Witham J, Valenti MR, De-Haven-Brandon AK et al (2007) The Bcl-2/Bcl-XL family inhibitor ABT-737 sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to carboplatin. Clin Cancer Res 13:7191–7198
Zall H, Weber A, Besch R, Zantl N, Hacker G (2010) Chemotherapeutic drugs sensitize human renal cell carcinoma cells to ABT-737 by a mechanism involving the Noxa-dependent inactivation of Mcl-1 or A1. Mol Cancer 9:164
Tromp JM, Geest CR, Breij EC et al (2012) Tipping the Noxa/Mcl-1 balance overcomes ABT-737 resistance in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 18:487–498
Kim JY, Ahn HJ, Ryu JH, Suk K, Park JH (2004) BH3-only protein Noxa is a mediator of hypoxic cell death induced by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. J Exp Med 199:113–124
Hetschko H, Voss V, Senft C, Seifert V, Prehn JH, Kogel D (2008) BH3-mimetics reactivate autophagic cell death in anoxia-resistant malignant glioma cells. Neoplasia 10:873–885
Mammen A, Kubin J, Greeley WJ et al (2011) Effect of hypoxia on expression of selected proteins involved in regulation of apoptotic activity in striatum of newborn piglets. Neurochem Res 36:746–753
Harrison LR, Micha D, Brandenburg M et al (2011) Hypoxic human cancer cells are sensitized to BH3-mimetic-induced apoptosis via downregulation of the Bcl-2 protein Mcl-1. J Clin Investig 121:1075–1087
High LM, Szymanska B, Wilczynska-Kalak U et al (2010) The Bcl-2 homology domain 3 mimetic ABT-737 targets the apoptotic machinery in acute lymphoblastic leukemia resulting in synergistic in vitro and in vivo interactions with established drugs. Mol Pharmacol 77:483–494
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Edwige Lemoisson, Marie-Hélène Louis (BioTICLA Unit) and Maryline Duval (Flow cytometry accommodation, SF 4206 ICORE, University of Caen) for their helpful technical support and ABBOTT Laboratories for providing us with ABT-737. We also acknowledge AngloScribe society for English language editing. This work was supported by the “Ligue Contre le Cancer” (Calvados and Manche’s committee), the “Conseil Régional de Basse–Normandie” and the French State. KS was the recipient of a doctoral fellowship from the “Ligue Contre le Cancer” (Calvados’s Committee). Acquisition of the xCELLigence real-time activity measurement system has been supported by European Community (FEDER) and Comprehensive Cancer Center F. Baclesse.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Karin Simonin and Monique N’Diaye contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simonin, K., N’Diaye, M., Lheureux, S. et al. Platinum compounds sensitize ovarian carcinoma cells to ABT-737 by modulation of the Mcl-1/Noxa axis. Apoptosis 18, 492–508 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0799-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0799-x