Abstract
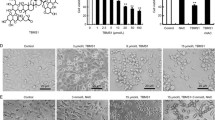
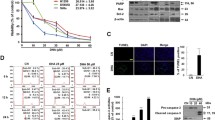
This study investigates the efficacy of carnosic acid (CA), a polyphenolic diterpene, isolated from the plant rosemary (Rosemarinus officinalis), on androgen-independent human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. CA induced anti-proliferative effects in PC-3 cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner, which was due to apoptotic induction as evident from flow-cytometry, DNA laddering and TUNEL assay. Apoptosis was associated with the activation of caspase-8, -9, -3 and -7, increase in Bax:Bcl-2 ratio, release of cytochrome-c and decrease in expression of inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family of proteins. Apoptosis was attenuated upon pretreatment with specific inhibitors of caspase-8 (Z-IETD-fmk) and caspase-9 (Z-LEHD-fmk) suggesting the involvement of both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic cascades. Further, apoptosis resulted from the inhibition of IKK/NF-κB pathway as evident from decreased DNA binding activity, nuclear translocation of p50 and p65 and IκBα phosphorylation. The down-regulation of IKK/NF-κB was associated with inhibition of Akt phosphorylation and its kinase activity with a concomitant increase in the serine/threonine protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activity. Pharmacologic inhibition of PP2A by okadaic acid and calyculin A, significantly reversed CA-mediated apoptotic events in PC-3 cells indicating that CA induced apoptosis by activation of PP2A through modulation of Akt/IKK/NF-κB pathway. In addition, CA induced apoptosis in another androgen refractory prostate cancer DU145 cells via intrinsic pathway as evidenced from the activation of caspase 3, cleavage of PARP, increase in Bax:Bcl-2 ratio and cytochrome-c release. Carnosic acid, therefore, may have the potential for use in the prevention and/or treatment of prostate cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Carnosic acid
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP)-ribose polymerase
- IAP:
-
Inhibitor of apoptosis
- IKK:
-
IκB kinase
- MTT:
-
(3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- PI3-K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PP2A:
-
Protein phosphatase 2A
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Cooperberg MR, Grossfeld GD, Lubeck DP, Carroll PR (2003) National practice patterns and time trends in androgen ablation for localized prostate cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 95:981–989
Feldman BJ, Feldman D (2001) The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 1:34–45
Hsing AW, Devesa SS (2001) Trends and patterns of prostate cancer: what do they suggest? Epidemiol Rev 23:3–13
Syed DN, Khan N, Afaq F, Mukhtar H (2007) Chemoprevention of prostate cancer through dietary agents: progress and promise. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16:2193–2203
Khan N, Afaq F, Mukhtar H (2008) Cancer chemoprevention through dietary antioxidants: progress and promise. Antioxid Redox Signal 10:475–510
Singletary KW, Nelshoppen JM (1991) Inhibition of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced mammary tumorigenesis and of in vivo formation of mammary DMBA-DNA adducts by rosemary extract. Cancer Lett 60:169–175
Singletary KW, Rokusek JT (1997) Tissue-specific enhancement of xenobiotic detoxification enzymes in mice by dietary rosemary extract. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 50:47–53
Pesakhov S, Khanin M, Studzinski GP, Danilenko M (2010) Distinct combinatorial effects of the plant polyphenols curcumin, carnosic acid, and silibinin on proliferation and apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Nutr Cancer 62:811–824
Yu YM, Lin CH, Chan HC, Tsai HD (2009) Carnosic acid reduces cytokine-induced adhesion molecules expression and monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells. Eur J Nutr 48:101–106
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X (1998) Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94:481–490
Delivani P, Martin SJ (2006) Mitochondrial membrane remodeling in apoptosis: an inside story. Cell Death Differ 13:2007–2010
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501
Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB: the enemy within. Cancer Cell 6:203–208
Pahl HL (1999) Activators and target genes of Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors. Oncogene 18:6853–6866
Sovak MA, Arsura M, Zanieski G, Kavanagh KT, Sonenshein GE (1999) The inhibitory effects of transforming growth factor beta1 on breast cancer cell proliferation are mediated through regulation of aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression. Cell Growth Differ 10:537–544
Lind DS, Hochwald SN, Malaty J et al (2001) Nuclear factor-kappa B is upregulated in colorectal cancer. Surgery 130:363–369
Koumakpayi IH, Le Page C, Mes-Masson AM, Saad F (2010) Hierarchical clustering of immunohistochemical analysis of the activated ErbB/PI3K/Akt/NF-kappaB signalling pathway and prognostic significance in prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 102:1163–1173
Le Page C, Koumakpayi IH, Lessard L, Saad F, Mes-Masson AM (2005) Independent role of phosphoinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) and casein kinase II (CK-2) in EGFR and Her-2-mediated constitutive NF-kappaB activation in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 65:306–315
Cohen PT (1997) Novel protein serine/threonine phosphatases: variety is the spice of life. Trends Biochem Sci 22:245–251
Van Kanegan MJ, Adams DG, Wadzinski BE, Strack S (2005) Distinct protein phosphatase 2A heterotrimers modulate growth factor signaling to extracellular signal-regulated kinases and Akt. J Biol Chem 280:36029–36036
Yu S, Shen G, Khor TO, Kim JH, Kong AN (2008) Curcumin inhibits Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling through protein phosphatase-dependent mechanism. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2609–2620
Matsuoka Y, Nagahara Y, Ikekita M, Shinomiya T (2003) A novel immunosuppressive agent FTY720 induced Akt dephosphorylation in leukemia cells. Br J Pharmacol 138:1303–1312
Yesil-Celiktas O, Sevimli C, Bedir E, Vardar-Sukan F (2010) Inhibitory effects of rosemary extracts, carnosic acid and rosmarinic acid on the growth of various human cancer cell lines. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 65:158–163
Ukil A, Biswas A, Das T, Das PK (2005) 18 Beta-glycyrrhetinic acid triggers curative Th1 response and nitric oxide up-regulation in experimental visceral leishmaniasis associated with the activation of NF-kappa B. J Immunol 175:1161–1169
Deveraux QL, Reed JC (1999) IAP family proteins—suppressors of apoptosis. Genes Dev 13:239–252
Chendil D, Das A, Dey S, Mohiuddin M, Ahmed MM (2002) Par-4, a pro-apoptotic gene, inhibits radiation-induced NF kappa B activity and Bcl-2 expression leading to induction of radiosensitivity in human prostate cancer cells PC-3. Cancer Biol Ther 1:152–160
Vermeulen L, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G (2006) Regulation of NF-kappaB transcriptional activity. Cancer Treat Res 130:89–102
Vlietstra RJ, van Alewijk DC, Hermans KG, van Steenbrugge GJ, Trapman J (1998) Frequent inactivation of PTEN in prostate cancer cell lines and xenografts. Cancer Res 58:2720–2723
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2006) Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25:4798–4811
Hyer ML, Shi R, Krajewska M et al (2008) Apoptotic activity and mechanism of 2-cyano-3,12-dioxoolean-1,9-dien-28-oic-acid and related synthetic triterpenoids in prostate cancer. Cancer Res 68:2927–2933
Baron A, Mancini M, Caldwell E, Cabrelle A, Bernardi P, Pagano F (2009) Serenoa repens extract targets mitochondria and activates the intrinsic apoptotic pathway in human prostate cancer cells. BJU Int 103:1275–1283
Singh AV, Xiao D, Lew KL, Dhir R, Singh SV (2004) Sulforaphane induces caspasemediated apoptosis in cultured PC-3 human prostate cancer cells and retards growth of PC-3 xenografts in vivo. Carcinogenesis 25:83–90
Gasparian AV, Yao YJ, Kowalczyk D et al (2002) The role of IKK in constitutive activation of NF-kappaB transcription factor in prostate carcinoma cells. J Cell Sci 115:141–151
Ross JS, Jennings TA, Nazeer T et al (2003) Prognostic factors in prostate cancer. Am J Clin Pathol 120(Suppl):S85–S100
Fradet V, Lessard L, Begin LR, Karakiewicz P, Masson AM, Saad F (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB nuclear localization is predictive of biochemical recurrence in patients with positive margin prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:8460–8464
Suh J, Payvandi F, Edelstein LC et al (2002) Mechanisms of constitutive NF-kappaB activation in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate 52:183–200
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY, Baldwin AS Jr (2001) Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol Chem 276:18934–18940
Wellwood CRL, Cole RA (2004) Relevance of carnosic acid concentrations to the selection of Rosemary, Rosmarinus officinalis (L.), accessions for optimization of antioxidant yield. J Agric Food Chem 52:6101–6107
Yan H, Wang L, Li X et al (2009) High-performance liquid chromatography method for determination of carnosic acid in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study. Biomed Chromatogr 23:776–781
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Network Project (NWP 0038) and Supra Institutional Project (SIP 007) grant of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India.
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Susanta Kar and Shreyasi Palit contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kar, S., Palit, S., Ball, W.B. et al. Carnosic acid modulates Akt/IKK/NF-κB signaling by PP2A and induces intrinsic and extrinsic pathway mediated apoptosis in human prostate carcinoma PC-3 cells. Apoptosis 17, 735–747 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0715-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0715-4