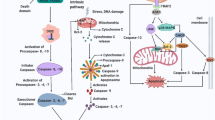
Abstract
Death associated protein 3 (DAP3) is known to be a highly conserved protein, and is responsible for regulating apoptosis induced by various stimuli. To understand the molecular mechanism of how DAP3 induces apoptosis, we performed yeast two-hybrid screening, and identified a novel DAP3-binding protein termed death ligand signal enhancer (DELE). In this report, we show that DELE actually binds to DAP3 in mammalian cells. We found that the cells stably expressing DELE are susceptible to apoptosis induction by the stimulation of TNF-α and TRAIL. In addition, knockdown of DELE expression rescued the HeLa cells from apoptosis induction by these stimuli. Moreover, activation of caspase-3, caspase-8 and caspase-9 induced by stimulation of TNF-α, anti-Fas or TRAIL was significantly inhibited by the knockdown of DELE expression. These results demonstrated the biological significance of DELE for apoptosis signal mediated by death receptors.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DAP3:
-
Death associated protein 3
- DELE:
-
Death ligand signal enhancer
- DR:
-
Death receptor
- TNF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor
- TRAIL:
-
TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand
- DD:
-
Death domain
- DED:
-
Death effector domain
- FADD:
-
Fas-associated death domain protein
- CARD:
-
Caspase-recruitment domain
- EGFP:
-
Enhanced green fluorescent protein
References
Hajra KM, Liu JR (2004) Apoptosome dysfunction in human cancer. Apoptosis 9:691–704
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR, Berneman ZN (2004) Apoptosis: mechanisms and relevance in cancer. Ann Hematol 84:627–639
Tanaka M, Miyake Y (2007) Apoptotic cell clearance and autoimmune disorder. Curr Med Chem 14:2892–2897
Krammer PH, Arnold R, Lavrik IN (2007) Life and death in peripheral T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 7:532–542
Opferman JT (2008) Apoptosis in the development of the immune system. Cell Death Differ 15:234–242
Abou-Sleiman PM, Muqit MM, Wood NW (2006) Expanding insights of mitochondrial dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:207–219
Nakamura T, Lipton SA (2009) Cell death: protein misfolding and neurodegenerative diseases. Apoptosis 14:455–468
Lorz C, Mehmet H (2009) The role of death receptors in neural injury. Front Biosci 14:583–595
Ashkenazi A, Herbst RS (2008) To kill a tumor cell: the potential of proapoptotic receptor agonists. J Clin Invest 118:1979–1990
Croft M (2009) The role of TNF superfamily members in T-cell function and diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 9:271–285
Karin M, Gallagher E (2009) TNFR signaling: ubiquitin-conjugated TRAFfic signals control stop-and-go for MAPK signaling complexes. Immunol Rev 228:225–240
Strasser A, Jost PJ, Nagata S (2009) The many roles of FAS receptor signaling in the immune system. Immunity 30:180–192
Wilson TR, Johnston PG, Longley DB (2009) Anti-apoptotic mechanisms of drug resistance in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 9:307–319
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Kissil JL, Deiss LP, Bayewitch M, Raveh T, Khaspekov G, Kimchi A (1995) Isolation of DAP3, a novel mediator of interferon-gamma-induced cell death. J Biol Chem 270:27932–27936
Miyazaki T, Reed JC (2001) A GTP-binding adapter protein couples TRAIL receptors to apoptosis-inducing proteins. Nat Immunol 2:493–500
Miyazaki T, Shen M, Fujikura D, Tosa N, Kim HR, Kon S, Uede T, Reed JC (2004) Functional role of death-associated protein 3 (DAP3) in anoikis. J Biol Chem 279:44667–44672
Li HM, Fujikura D, Harada T, Uehara J, Kawai T, Akira S, Reed JC, Iwai A, Miyazaki T (2009) IPS-1 is crucial for DAP3-mediated anoikis induction by caspase-8 activation. Cell Death Differ 16:1615–1621
Kim HR, Chae HJ, Thomas M, Miyazaki T, Monosov A, Monosov E, Krajewska M, Krajewski S, Reed JC (2007) Mammalian dap3 is an essential gene required for mitochondrial homeostasis in vivo and contributing to the extrinsic pathway for apoptosis. FASEB J 21:188–196
Kissil JL, Cohen O, Raveh T, Kimchi A (1999) Structure-function analysis of an evolutionary conserved protein, DAP3, which mediates TNF-alpha- and Fas-induced cell death. EMBO J 18:353–362
Berger T, Brigl M, Herrmann JM, Vielhauer V, Luckow B, Schlondorff D, Kretzler M (2000) The apoptosis mediator mDAP-3 is a novel member of a conserved family of mitochondrial proteins. J Cell Sci 113:3603–3612
Saveanu C, Fromont-Racine M, Harington A, Ricard F, Namane A, Jacquier A (2001) Identification of 12 new yeast mitochondrial ribosomal proteins including 6 that have no prokaryotic homologues. J Biol Chem 276:15861–15867
Madeo F, Herker E, Maldener C, Wissing S, Lächelt S, Herlan M, Fehr M, Lauber K, Sigrist SJ, Wesselborg S, Fröhlich KU (2002) A caspase-related protease regulates apoptosis in yeast. Mol Cell 9:911–917
Takeda S, Iwai A, Nakashima M, Fujikura D, Chiba S, Li HM, Uehara J, Kawaguchi S, Kaya M, Nagoya S, Wada T, Yuan J, Rayter S, Ashworth A, Reed JC, Yamashita T, Uede T, Miyazaki T (2007) LKB1 is crucial for TRAIL-mediated apoptosis induction in osteosarcoma. Anticancer Res 27:761–768
Lamb JR, Tugendreich S, Hieter P (1995) Tetratrico peptide repeat interactions: to TPR or not to TPR? Trends Biochem Sci 20:257–259
Das AK, Cohen PW, Barford D (1998) The structure of the tetratricopeptide repeats of protein phosphatase 5: implications for TPR-mediated protein-protein interactions. EMBO J 17:1192–1199
D’Andrea LD, Regan L (2003) TPR proteins: the versatile helix. Trends Biochem Sci 28:655–662
Murata Y, Wakoh T, Uekawa N, Sugimoto M, Asai A, Miyazaki T, Maruyama M (2006) Death-associated protein 3 regulates cellular senescence through oxidative stress response. FEBS Lett 580:6093–6099
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1999) Apoptosis control by death and decoy receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:255–260
Guicciardi ME, Gores GJ (2009) Life and death by death receptors. FASEB J 23:1625–1637
Kroemer G, Martin SJ (2005) Caspase-independent cell death. Nat Med 11:725–730
Thorburn A (2004) Death receptor-induced cell killing. Cell Signal 16:139–144
Chinnaiyan AM, O’Rourke K, Tewari M, Dixit VM (1995) FADD, a novel death domain-containing protein, interacts with the death domain of Fas and initiates apoptosis. Cell 81:505–512
Garrido C, Galluzzi L, Brunet M, Puig PE, Didelot C, Kroemer G (2006) Mechanisms of cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 13:1423–1433
Hofmann K, Bucher P, Tschopp J (1997) The CARD domain: a new apoptotic signalling motif. Trends Biochem Sci 22:155–156
Weber CH, Vincenz C (2001) The death domain superfamily: a tale of two interfaces? Trends Biochem Sci 26:475–481
Reed JC, Doctor KS, Godzik A (2004) The domains of apoptosis: a genomics perspective. Sci STKE 239:re9
Rechsteiner M, Rogers SW (1996) PEST sequences and regulation by proteolysis. Trends Biochem Sci 21:267–271
Nagase T, Seki N, Ishikawa K, Tanaka A, Nomura N (1996) Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. V. The coding sequences of 40 new genes (KIAA0161-KIAA0200) deduced by analysis of cDNA clones from human cell line KG-1 (supplement). DNA Res 3:43–53
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3, RESEARCH0034.1-0034.11
Acknowledgment
We would like to thank Prof. Toshimitsu Uede (Department of Molecular Immunology, Institute for Genetic Medicine, Hokkaido University) whose consultations helped us in our research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10495_2010_519_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 1. Induction of apoptosis to the HeLa cells by transiently overexpressing DELE. HeLa cells were seeded onto 6-well plate, and subsequently the cells were transfected with 4 μg of control vector or expression vector of DELE after 48 h, the cells were observed using phase-contrast microscope (Eclipse TE200-U; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan). (TIFF 14937 kb)
10495_2010_519_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplemental Fig. 2. Rescue of the HeLa cells from the TRAIL induced apoptosis by knockdown of DELE. The HeLa cells were transfected with DELE specific siRNA or control siRNA. After 48 h, cells were stimulated with TRAIL at the series of concentrations indicated in the figure. After a 24 h post-stimulation incubation period, the cells were observed using phase-contrast microscope (Eclipse TE200-U; Nikon). (TIFF 29674 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harada, T., Iwai, A. & Miyazaki, T. Identification of DELE, a novel DAP3-binding protein which is crucial for death receptor-mediated apoptosis induction. Apoptosis 15, 1247–1255 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0519-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0519-3