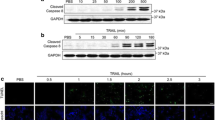
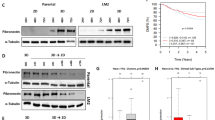
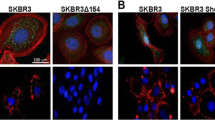
Abstract
Fibronectin (FN) is an endogenous ligand of integrins, which plays a critical role in cell adhesion and growth. Here, we converted globular FN (G-FN) into a fibrillar form (F-FN) and found that, even though both G-FN and F-FN interacted with integrin α5β1, G-FN induced cellular proliferation, whereas F-FN resulted in apoptosis that was associated with deactivation of Akt/GSK-3β and phosphorylation of SHP-2. SHP-2 inhibitor and anti-sense oligodeoxynucleotide decreased SHP-2 level and reversed the F-FN mediated apoptosis. F-FN also induced stress fiber formation associated with activation of RhoA, Rho kinase (ROCK), and filamin. Inhibition of ROCK by ROCK inhibitor or dominant negative plasmid treatment modulated F-FN mediated apoptosis. Pharmacological studies revealed that F-FN was effective in inhibiting the survival of SKOV-3 and MCF-7 cancer cells. These findings thus demonstrate that unlike G-FN, F-FN exhibits fibrillar structure to induce cell apoptosis that is associated with phosphorylation of SHP-2, activation of RhoA/ROCK and formation of stress fibers as well as deactivation of Akt/GSK-3β.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pankov R, Yamada KM (2002) Fibronectin at a glance. J Cell Sci 115:3861–3863
Peters DM, Portz LM, Fullenwider J, Mosher DF (1990) Co-assembly of plasma and cellular fibronectins into fibrils in human fibroblast cultures. J Cell Biol 111:249–256
Tamkun JW, Hynes RO (1983) Plasma fibronectin is synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 258:4641–4647
Ruoslahti E, Pierschbacher MD (1987) New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science 238:491–497
Danen EH (2005) Integrins: regulators of tissue function and cancer progression. Curr Pharm Des 11:881–891
Morgan MR, Humphries MJ, Bass MD (2007) Synergistic control of cell adhesion by integrins and syndecans. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:957–969
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110:673–687
Plow EF, Haas TA, Zhang L, Loftus J, Smith JW (2000) Ligand binding to integrins. J Biol Chem 275:21785–21788
Feng GS, Pawson T (1994) Phosphotyrosine phosphatases with SH2 domains: regulators of signal transduction. Trends Genet 10:54–58
Ling Y, Maile LA, Clemmons DR (2003) Tyrosine phosphorylation of the beta3-subunit of the alphaVbeta3 integrin is required for embrane association of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 and its further recruitment to the insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Mol Endocrinol 17:1824–1833
Lacalle RA, Mira E, Gomez-Mouton C, Jimenez-Baranda S, Martinez AC, Manes S (2002) Specific SHP-2 partitioning in raft domains triggers integrin-mediated signaling via Rho activation. J Cell Biol 157:277–289
Ueda K, Ohta Y, Hosoya H (2003) The carboxy-terminal pleckstrin homology domain of ROCK interacts with filamin-A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 301:886–890
Somanath PR, Razorenova OV, Chen J, Byzova TV (2006) Akt1 in endothelial cell and angiogenesis. Cell Cycle 5:512–518
Bucciantini M, Giannoni E, Chiti F et al (2002) Inherent toxicity of aggregates implies a common mechanism for protein misfolding diseases. Nature 416:507–511
Huang CY, Liang CM, Chu CL, Liang SM (2009) Albumin fibrillization induces apoptosis via integrin/FAK/Akt pathway. BMC Biotechnol 9:2
LeVine H III (1999) Quantification of beta-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T. Methods Enzymol 309:274–284
Ishizaki T, Naito M, Fujisawa K et al (1997) p160ROCK, a Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein kinase, works downstream of Rho and induces focal adhesions. FEBS Lett 404:118–124
Mannell H, Hellwig N, Gloe T et al (2008) Inhibition of the tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2 suppresses angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo. J Vasc Res 45:153–163
Tooney NM, Mosesson MW, Amrani DL, Hainfeld JF, Wall JS (1983) Solution and surface effects on plasma fibronectin structure. J Cell Biol 97:1686–1692
Toker A (2000) Protein kinases as mediators of phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling. Mol Pharmacol 57:652–658
Luo HR, Hattori H, Hossain MA et al (2003) Akt as a mediator of cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:11712–11717
DeMali KA, Wennerberg K, Burridge K (2003) Integrin signaling to the actin cytoskeleton. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:572–582
Arthur WT, Noren NK, Burridge K (2002) Regulation of Rho family GTPases by cell-cell and cell-matrix adhesion. Biol Res 35:239–246
Glabe CG (2008) Structural classification of toxic amyloid oligomers. J Biol Chem 283:29639–29643
Chow MK, Ellisdon AM, Cabrita LD, Bottomley SP (2006) Purification of polyglutamine proteins. Methods Enzymol 413:1–19
Pellenc D, Berry H, Gallet O (2006) Adsorption-induced fibronectin aggregation and fibrillogenesis. J Colloid Interface Sci 298:132–144
Kreplak L, Aebi U (2006) From the polymorphism of amyloid fibrils to their assembly mechanism and cytotoxicity. Adv Protein Chem 73:217–233
Glabe CG (2006) Common mechanisms of amyloid oligomer pathogenesis in degenerative disease. Neurobiol Aging 27:570–575
Engel MF, Khemtemourian L, Kleijer CC et al (2008) Membrane damage by human islet amyloid polypeptide through fibril growth at the membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6033–6038
Martin D, Salinas M, Lopez-Valdaliso R, Serrano E, Recuero M, Cuadrado A (2001) Effect of the Alzheimer amyloid fragment Abeta(25–35) on Akt/PKB kinase and survival of PC12 cells. J Neurochem 78:1000–1008
Petratos S, Li QX, George AJ et al (2008) The beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer’s disease increases neuronal CRMP-2 phosphorylation by a Rho-GTP mechanism. Brain 131:90–108
Seyb KI, Ansar S, Bean J, Michaelis ML (2006) beta-Amyloid and endoplasmic reticulum stress responses in primary neurons: effects of drugs that interact with the cytoskeleton. J Mol Neurosci 28:111–123
Yan SD, Shi Y, Zhu A et al (1999) Role of ERAB/L-3-hydroxyacyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase type II activity in Abeta-induced cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem 274:2145–2156
Shea TB, Ortiz D (2003) 17 beta-estradiol alleviates synergistic oxidative stress resulting from folate deprivation and amyloid-beta treatment. J Alzheimers Dis 5:323–327
Morla A, Zhang Z, Ruoslahti E (1994) Superfibronectin is a functionally distinct form of fibronectin. Nature 367:193–196
Yi M, Ruoslahti E (2001) A fibronectin fragment inhibits tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:620–624
Tellier MC, Greco G, Klotman M et al (2000) Superfibronectin, a multimeric form of fibronectin, increases HIV infection of primary CD4+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol 164:3236–3245
Ambesi A, Klein RM, Pumiglia KM, McKeown-Longo PJ (2005) Anastellin, a fragment of the first type III repeat of fibronectin, inhibits extracellular signal-regulated kinase and causes G(1) arrest in human microvessel endothelial cells. Cancer Res 65:148–156
Kuwada SK, Li X (2000) Integrin alpha5/beta1 mediates fibronectin-dependent epithelial cell proliferation through epidermal growth factor receptor activation. Mol Biol Cell 11:2485–2496
Wright S, Malinin NL, Powell KA, Yednock T, Rydel RE, Griswold-Prenner I (2007) Alpha2beta1 and alphaVbeta1 integrin signaling pathways mediate amyloid-beta-induced neurotoxicity. Neurobiol Aging 28:226–237
Chen HC, Appeddu PA, Parsons JT, Hildebrand JD, Schaller MD, Guan JL (1995) Interaction of focal adhesion kinase with cytoskeletal protein talin. J Biol Chem 270:16995–16999
Lewis JM, Schwartz MA (1995) Mapping in vivo associations of cytoplasmic proteins with integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain mutants. Mol Biol Cell 6:151–160
Miyamoto S, Akiyama SK, Yamada KM (1995) Synergistic roles for receptor occupancy and aggregation in integrin transmembrane function. Science 267:883–885
Schaller MD, Otey CA, Hildebrand JD, Parsons JT (1995) Focal adhesion kinase and paxillin bind to peptides mimicking beta integrin cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Biol 130:1181–1187
Yu DH, Qu CK, Henegariu O, Lu X, Feng GS (1998) Protein-tyrosine phosphatase Shp-2 regulates cell spreading, migration, and focal adhesion. J Biol Chem 273:21125–21131
Kamarajan P, Kapila YL (2007) An altered fibronectin matrix induces anoikis of human squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing integrin alpha v levels and phosphorylation of FAK and ERK. Apoptosis 12:2221–2231
Kapila YL, Kapila S, Johnson PW (1996) Fibronectin and fibronectin fragments modulate the expression of proteinases and proteinase inhibitors in human periodontal ligament cells. Matrix Biol 15:251–261
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the following members of Academia Sinica, Taiwan for their assistance: Dr. Chia-Seng Chang and Wei-Chiao Lai of the Institute of Physics for assistance in scanning electron microscopy analyses; Shu-Chen Shen of the Scientific Instrument Center for assistance in confocal microscopy analyses; and Tai-Lang Lin and the Core Facility of the Institute of Cellular and Organismic Biology for assistance in transmission electron microscopy analyses. The authors wish to thank Miranda Loney for editing the manuscript. This work was supported by grant NSC 96-2313-B-001-002 to SML from the National Science Council, Taiwan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10495_2010_500_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary Fig. S1: The effect of G-FN on the proliferative activity of BHK-21 cells. BHK-21 cells were treated with various concentrations of G-FN, and cell proliferative activity was measured by MTT. Values represent means ± SD from two separate experiments. (TIFF 7569 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CY., Liang, CM., Chu, CL. et al. A fibrillar form of fibronectin induces apoptosis by activating SHP-2 and stress fiber formation. Apoptosis 15, 915–926 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0500-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0500-1