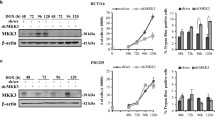
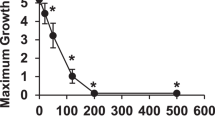
Abstract
Yeast-based functional screening of a human glioblastoma cDNA library identified ras-related nuclear protein (Ran) as a novel suppressor of Bcl-2-associated X protein (Bax), a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Yeast cells that expressed human Ran were resistant to Bax-induced cell death. In U373MG glioblastoma cells, stable overexpression of Ran significantly attenuated apoptotic cell death induced by the chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel. FACS analysis demonstrated that Ran is involved in paclitaxel-induced cell cycle arrest. Stable overexpression of Ran also markedly inhibited the phosphorylation of Bcl-2 by paclitaxel, and inhibited the translocation of Bax, the release of cytochrome c and activation of caspase-3. Paclitaxel-induced phosphorylation of c-JUN N-terminal kinase (JNK), but not p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt, was markedly suppressed in U373MG cells that stably expressed Ran. These results suggest that Ran suppresses paclitaxel-induced cell death through the downregulation of JNK-mediated signal pathways.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- JNK:
-
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal regulated kinase
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- NAC:
-
N-Acetyl-l-cysteine
References
Raff MC (1992) Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature 356:397–400. doi:10.1038/356397a0
Okada H, Mak TW (2004) Pathways of apoptotic and non-apoptotic death in tumour cells. Nat Rev Cancer 4:592–603. doi:10.1038/nrc1412
Elmore S (2007) Apoptosis: a review of programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol 35:495–516. doi:10.1080/01926230701320337
Hsu YT, Wolter KG, Youle RJ (1997) Cytosol-to-membrane redistribution of Bax and Bcl-xL during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:3668–3672. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.8.3668
Xu Q, Reed JC (1998) Bax inhibitor-1, a mammalian apoptosis suppressor identified by functional screening in yeast. Mol Cell 1:337–346. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80034-9
Sawada M, Sun W, Hayes P, Leskov K, Boothman DA, Matsuyama S (2003) Ku70 suppresses the apoptotic translocation of Bax to mitochondria. Nat Cell Biol 5:320–329. doi:10.1038/ncb950
Yang Z, Khoury C, Jean-Baptiste G, Greenwood MT (2006) Identification of mouse sphingomyelin synthase 1 as a suppressor of Bax-mediated cell death in yeast. FEMS Yeast Res 6:751–762. doi:10.1111/j.1567-1364.2006.00052.x
Moon H, Baek D, Lee B, Prasad DT, Lee SY, Cho MJ et al (2002) Soybean ascorbate peroxidase suppresses Bax-induced apoptosis in yeast by inhibiting oxygen radical generation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:457–462. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2001.6208
Kampranis SC, Damianova R, Atallah M, Toby G, Kondi G, Tsichlis PN et al (2000) A novel plant glutathione S-transferase/peroxidase suppresses Bax lethality in yeast. J Biol Chem 275:29207–29216. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002359200
Eisenhauer EA, Vermorken JB (1998) The taxoids. Comparative clinical pharmacology and therapeutic potential. Drugs 55:5–30. doi:10.2165/00003495-199855010-00002
Bokemeyer C, Hartmann JT, Kuczyk MA, Truss MC, Kollmannsberger C, Beyer J et al (1998) Recent strategies for the use of paclitaxel in the treatment of urological malignancies. World J Urol 16:155–162. doi:10.1007/s003450050044
Schiff PB, Fant J, Horwitz SB (1979) Promotion of microtubles assembly in vitro by taxol. Nature 277:665–667. doi:10.1038/277665a0
André N, Carré M, Brasseur G, Pourroy B, Kovacic H, Briand C et al (2002) Paclitaxel targets mitochondria upstream of caspase activation in intact human neuroblastoma cells. FEBS Lett 532:256–260. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03691-8
Wang YF, Chen CY, Chung SF, Chiou YH, Lo HR (2004) Involvement of oxidative stress and caspase activation in paclitaxel-induced apoptosis of primary effusion lymphoma cells. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 54:322–330. doi:10.1007/s00280-004-0831-0
Pushkarev VM, Starenki DV, Saenko VA, Namba H, Kurebayashi J, Tronko MD et al (2004) Molecular mechanisms of the effects of low concentrations of taxol in anaplastic thyroid cancer cells. Endocrinology 145:3143–3152. doi:10.1210/en.2004-0127
Bischoff FR, Ponstingl H (1991) Mitotic regulator protein RCC1 is complexed with a nuclear ras-related polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10830–10834. doi:10.1073/pnas.88.23.10830
Sweet DJ, Gerace L (1996) A GTPase distinct from Ran is involved in nuclear protein import. J Cell Biol 133:971–983. doi:10.1083/jcb.133.5.971
Bischoff FR, Ponstingl H (1995) Catalysis of guanine nucleotide exchange of Ran by RCC1 and stimulation of hydrolysis of Ran-bound GTP by Ran-GAP1. Meth Enzymol 257:135–144. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(95)57019-5
Kalab P, Pu RT, Dasso M (1999) The Ran GTPase regulates mitotic spindle assembly. Curr Biol 9:481–484. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(99)80213-9
Joseph J (2006) Ran at a glance. J Cell Sci 119:3481–3484. doi:10.1242/jcs.03071
Rush MG, Drivas G, D’Eustachio P (1996) The small nuclear GTPase Ran: how much does it run? Bioessays 18:103–112. doi:10.1002/bies.950180206
Azuma K, Sasada T, Takedatsu H, Shomura H, Koga M, Maeda Y et al (2004) Ran, a small GTPase gene, encodes cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) epitopes capable of inducing HLA-A33 restricted and tumor-reactive CTLs in cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 10:6695–6702. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0818
Hill J, Ian KA, Donald G, Griffiths DE (1991) DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 19:5791. doi:10.1093/nar/19.20.5791
Kang ES, Woo IS, Kim HJ, Eun SY, Paek KS, Kim HJ et al (2007) Up-regulation of aldose reductase expression mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and Nrf2 is involved in the protective effect of curcumin against oxidative damage. Free Radic Biol Med 43:535–545. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2007.05.006
Brezniceanu ML, Volp K, Bosser S, Solbach C, Lichter P, Joos S et al (2003) HMGB1 inhibits cell death in yeast and mammalian cells and is abundantly expressed in human breast carcinoma. FASEB J 17:1295–1297
Lee LF, Li G, Templeton DJ, Ting JP (1998) Paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced gene expression and cell death are both mediated by the activation of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK). J Biol Chem 273:28253–28260. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.43.28253
Tsuruta F, Sunayama J, Mori Y, Hattori S, Shimizu S, Tsujimoto U et al (2004) JNK promotes Bax translocation to mitochondria through phosphorylation of 14-3-3 proteins. EMBO J 23:1889–1899. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600194
Briches L, Cazettes G, Valette A (2004) JNK is associated with Bcl-2 and PP1 in mitochondria. Cell Cycle 3:e47–e54
Tudor G, Aguilera A, Halverson DO, Laing ND, Sausville EA (2000) Susceptibility to drug-induced apoptosis correlates with differential modulation of Bad, Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL protein levels. Cell Death Differ 7:574–586. doi:10.1038/sj.cdd.4400688
Varbiro G, Veres B, Gallyas F Jr, Sumegi B (2001) Direct effect of taxol on free radical formation and mitochondrial permeability transition. Free Radic Biol Med 31:548–558. doi:10.1016/S0891-5849(01)00616-5
Park SJ, Wu CH, Gordon JD, Zhong X, Emami A, Safa AR (2004) Taxol induces caspase-10-dependent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 279:51057–51067. doi:10.1074/jbc.M406543200
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Korean Science and Engineering Foundation grant R13-2005-012-02001-0, which is funded by the Korean government and a grant (2007040103403301) from BioGreen 21 Program, RDA, Republic of Korea. I.S.W. is a recipient of the Korea Research Foundation Grant (KRF-2006-005-J04202).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Im Sun Woo and Han-Su Jang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, I.S., Jang, HS., Eun, S.Y. et al. Ran suppresses paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human glioblastoma cells. Apoptosis 13, 1223–1231 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0247-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0247-0