Abstract
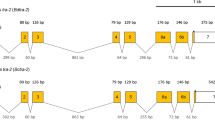
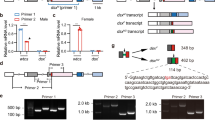
Characterization and expression analyses are essential to gain insight into sex-determination pathways in members of the Acari. Little is known about sex determination at the molecular level in the western orchard predatory mite Metaseiulus occidentalis (Arthropoda: Chelicerata: Arachnida: Acari: Phytoseiidae), a parahaploid species. In this study, eight genes previously identified as putative homologs to genes involved in the sex-determination pathway in Drosophila melanogaster were evaluated for sex-specific alternative splicing and sex-biased expression using reverse-transcriptase PCR and quantitative real-time PCR techniques, respectively. The homologs evaluated in M. occidentalis included two doublesex-like genes (Moccdsx1 and Moccdsx2), transformer-2 (Mocctra-2), intersex (Moccix), two fruitless-like genes (MoccBTB1 and MoccBTB2), as well as two vitellogenin-like genes (Moccvg1 and Moccvg2). Single transcripts of equal size were detected in males and females for Moccdsx1, Moccdsx2, Mocctra-2, Moccix, and MoccBTB2, suggesting that their pre-mRNAs do not undergo alternative splicing in a sex-specific manner. Three genes, Moccdsx1, Moccdsx2 and MoccBTB2, displayed male-biased expression relative to females. One gene, Moccix, displayed female-biased expression relative to males. Two genes, Mocctra-2 and MoccBTB1, did not display detectable differences in transcript abundance in males and females. Expression of Moccvg1 and Moccvg2 were detected in females only, and transcript levels were up-regulated in mated females relative to unmated females. To our knowledge, this represents the first attempt to elucidate expression patterns of putative sex-determination genes in an acarine. This study is an initial step towards understanding the sex-determination pathway in the parahaploid M. occidentalis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amrein H, Maniatis T, Nothiger R (1990) Alternatively spliced transcripts of the sex-determining gene tra-2 of Drosophila encode functional proteins of different size. EMBO J 9:3619–3629
Anand A, Villella A, Ryner LC, Carlo T, Goodwin SF, Song HJ, Gailey DA, Morales A, Hall JC, Baker BS, Taylor BJ (2001) Molecular genetic dissection of the sex-specific and vital functions of the Drosophila melanogaster sex determination gene fruitless. Genetics 158:1569–1595
Bachtrog D, Mank JE, Peichel CL, Kirkpatrick M, Otto SP, Ashman T, Hahn MW, Kitano J, Mayrose I, Ming R, Perrin N, Ross L, Valenzuela N, Vamosi JC (2014) Sex determination: why so many ways of doing it? PLoS Biol 12:e1001899
Baker BS, Ridge KA (1980) Sex and the single cell. I. On the action of major loci affecting sex determination in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 94:383–423
Bell LR, Maine EM, Schedl P, Cline TW (1988) Sex-lethal, a Drosophila sex determination switch gene, exhibits sex-specific RNA splicing and sequence similarity to RNA binding proteins. Cell 55:1037–1046
Bellefroid EJ, Leclere L, Saulnier A, Keruzore M, Sirakov M, Vervoort M, De Clercq S (2013) Expanding roles for the evolutionarily conserved Dmrt sex transcriptional regulators during embryogenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:3829–3845
Boerjan B, Tobback J, De Loof A, Schoofs L, Huybrechts R (2011) Fruitless RNAi knockdown in males interferes with copulation success in Schistocerca gregaria. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 41:340–347
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of sex determining mechanisms. Benjamin Cummings Publishing, Menlo Park
Burghardt G, Hediger M, Siegenthaler C, Moser M, Dubendorfer A, Bopp D (2005) The transformer2 gene in Musca domestica is required for selecting and maintaining the female pathway of development. Dev Genes Evol 215:165–176
Burtis KC, Baker BS (1989) Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. Cell 56:997–1010
Cabrera Cordon AR, Shirk PD, Duehl AJ et al (2013) Variable induction of vitellogenin genes in the varroa mite, Varroa destructor (Anderson & Trueman), by the honeybee, Apis mellifera L, host and its environment. Insect Mol Biol 22:88–103
Chase BA, Baker BS (1995) A genetic analysis of intersex, a gene regulating sexual differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster females. Genetics 139:1649–1661
Chong T, Collins JJ, Brudacher JL, Zarkower D, Newmark PA (2013) A sex-specific transcription factor controls male identity in a simultaneous hermaphrodite. Nat Commun 4:1814
Clynen E, Ciudad L, Belles X, Piulachs MD (2011) Conservation of fruitless’ role as master regulator of male courtship behavior from cockroaches to flies. Dev Genes Evol 221:43–48
Donohue KV, Khalil SMS, Soneshine DE, Roe RM (2009) Heme-binding storage proteins in the Chelicerata. J Insect Physiol 55:287–296
Garrett-Engele CM, Siegal ML, Manoli DS, Williams BC, Li H, Baker BS (2002) intersex, a gene required for female sexual development in Drosophila, is expressed in both sexes and functions together with doublesex to regulate terminal differentiation. Development 129:4661–4675
Hasselman M, Gempe T, Schiott M, Nunes-Silva CG, Otte M, Beye M (2008) Evidence for the evolutionary nascence of a novel sex determination pathway in honeybees. Nature 454:519–522
Helle W, Bolland HR, van Arendonk R, De Boer R, Schulten GM (1978) Genetic evidence for biparental males in haplo-diploid predator mites (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Genetica 49:165–171
Hodgkin J (2002) The remarkable ubiquity of DM domain factors as regulators of sexual phenotype: ancestry or aptitude? Genes Dev 16:2322–2326
Hoy MA (1979) Parahaploidy of the “arrhenotokous” predator, Metaseiulus occidentalis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae), demonstrated by x-irradiation of males. Entomol Exp Appl 26:97–104
Hoy MA (1982) Genetics and genetic improvement of the Phytoseiidae. In: Hoy MA (ed) Recent advances in knowledge of the Phytoseiidae. Univ. Calif. Pub. No. 3284, Berkeley, pp 72–89
Hoy MA, Standow KA (1982) Inheritance of resistance to sulfur in the spider mite predator Metaseiulus occidentalis. Entomol Exp Appl 31:316–323
Hoy MA, Yu F, Meyer JM, Tarazona OA, Jeyaprakash A, Wu K (2013) Transcriptome sequencing and annotation of the predatory mite Metaseiulus occidentalis (Acari: Phytoseiidae): a cautionary tale about possible contamination by prey sequences. Exp Appl Acarol 59:283–296
Huffaker CB, van de Vrie M, McMurtry JA (1970) Ecology of tetranychid mites and their natural enemies: a review. II. Tetranychid populations and their possible control by predators: an evaluation. Hilgardia 40:391–458
Kato Y, Kobayashi K, Oda S, Tatarazako N, Watanabe H, Iguchi T (2010) Sequence divergence and expression of a transformer gene in the branchiopod crustacean, Daphnia magna. Genomics 95:160–165
Kato Y, Kobayashi K, Watanabe H, Iguchi T (2011) Environmental sex determination in the branchiopod crustacean Daphnia magna: deep conservation of a doublesex gene in the sex-determining pathway. PLoS Genet 7:e1001345
Kettlewell JR, Raymond CS, Zarkower D (2000) Temperature-dependent expression of turtle Dmrt1 prior to sexual differentiation. Genesis 26:174–178
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
MacDougall C, Harbison D, Bownes M (1995) The developmental consequences of alternative splicing in sex determination and differentiation in Drosophila. Dev Biol 172:353–376
Mank JE, Wedell N, Hosken DJ (2013) Polyandry and sex-specific gene expression. Philos Trans R Soc B 368:20120047
Matson CK, Murphy MW, Groswold MD, Yoshida S, Bardwell VJ, Zarkower D (2010) The mammalian doublesex homolog DMRT1 is a transcriptional gatekeeper that controls mitosis versus meiosis decisions in male germ cells. Dev Cell 19:612–624
Matsuda M, Nagahama Y, Shinomiya A, Sato T, Matsuda C, Kobayashi T, Morrey CE, Shibita N, Asakawa S, Shimizu N, Hri H, Hamaguchi S, Sakaizumi M (2002) DMY is a Y-specific DM-domain gene required for male development in the medaka fish. Nature 417:559–563
Mattox W, Baker BS (1991) Autoregulation of the splicing of transcripts from the transformer-2 gene of Drosophila. Genes Dev 5:786–796
McMurtry JA, Croft BA (1997) Life-styles of phytoseiid mites and their role in biological control. Annu Rev Entomol 42:291–321
Morandin C, Havukainen H, Kulmuni J, Dhaygude K, Trontti K, Helantera H (2014) Not only for egg yolk—functional and evolutionary insights from expression, selection and structural analyses of Formica ant vitellogenins. Mol Biol Evol 31:2181–2193
Nagoshi RN, McKeown M, Burtis KC, Belote JM, Baker BS (1988) The control of alternative splicing at genes regulating sexual differentiation in D. melanogaster. Cell 53:229–236
Naimi A, Martinez A, Specq M, Mrac A, Diss B, Mathieu M, Sourdaine P (2009) Identification and expression of a factor of the DM family in the oyster Crassostrea gigas. Comp Biohem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol 152:189–196
Nelson-Rees WA, Hoy MA, Roush RT (1980) Heterochromatization, chromatin elimination and haploidization in the parahaploid mite Metaseiulus occidentalis (Nesbitt) (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Chromosoma 77:263–276
Nissen I, Muller M, Beye M (2012) The Am-tra2 gene is an essential regulator of female splice regulation at two levels of the sex determination hierarchy of the honeybee. Genetics 192:1015–1026
Oliver JH (1971) Parthenogenesis in mites and ticks (Arachnida: Acari). Am Zool 11:283–299
Oliver JH (1983) Chromosomes, genetic variance and reproductive strategies among mites and ticks. Bull Entomol Soc Am 29:8–17
Pomerantz AF, Hoy MA, Kawahara A (2014) Molecular characterization and evolutionary insights into potential sex-determination genes in the western orchard predatory mite Metaseiulus occidentalis (Chelicerata: Arachnida: Acari: Phytoseiidae). J Biomol Struc Dyn. Epub ahead of print. doi:10.1080/07391102.2014.941402
Rota-Stabelli O, Daley AC, Pisani D (2013) Molecular time trees reveal a Cambrian colonization of land and a new scenario of Ecdysozoan evolution. Curr Biol 23:392–398
Roush RT, Hoy MA (1981) Laboratory, glasshouse, and field studies of artificially selected carbaryl resistance in Metaseiulus occidentalis. J Econ Entomol 74:142–147
Roush RT, Plapp FW (1982) Biochemical genetics of resistance to aryl carbamate insecticides in the predaceous mite Metaseiulus occidentalis. J Econ Entomol 75:304–307
Salz HK (2011) Sex determination in insects: a binary decision based on alternative splicing. Curr Opin Genet Dev 4:395–400
Sanchez L (2008) Sex-determining mechanisms in insects. Int J Dev Biol 52:837–856
Shukla JN, Nagaraju J (2010) Doublesex: a conserved downstream gene controlled by diverse upstream regulators. J Genet 89:341–356
Shukla JN, Palli SR (2012) Doublesex target genes in the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum. Sci Rep 2:948
Shukla JN, Palli SR (2013) Tribolium castaneum transformer-2 regulates sex-determination and development in both males and females. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 43:1125–1132
Soller M, Bownes M, Kubli E (1997) Mating and sex peptide stimulate the accumulation of yolk in oocytes of Drosophila melanogaster. Eur J Biochem 243:732–738
Tian M, Maniatis T (1993) A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell 74:105–114
Toyoshima S, Amano H (2012) Presumed paternal genome loss during embryogenesis of predatory phytoseiid mites. In: Dr. Sato K-I (ed) Embryogenesis, ISBN: 978-953-51-0466-7, InTech. doi: 10.5772/37477
Toyota K, Kato Y, Sato M, Sugiura N, Miyagawa S, Miyakawa H, Watanabe H, Oda S, Ogino Y, Hiruta C, Mizutani T, Tatarazako N, Paland S, Jackson C, Colbourne JK, Iguchi T (2013) Molecular cloning of doublesex genes of four cladocera (water flea) species. BMC Genomics 14:239
Ubeda-Manzanaro M, Merlo MA, Ortiz-Delgado JB, Rebordinos L, Sarasquete C (2014) Expression profiling of the sex-related gene Dmrt1 in adults of the Lusitanian toadfish Halobatrachus didactylus (Bloch and Schneider, 1801). Gene 535:255–265
Usui-Aoki K, Ito H, Ui K, Takahashi K, Lukacsovich T, Awano W, Nakata H, Piao ZF, Nilsson EE, Tomida J, Yamamoto D (2000) Formation of the male-specific muscle in female Drosophila by ectopic fruitless expression. Nat Cell Biol 2:500–506
van Doorn GS (2014) Evolutionary transitions between sex-determining mechanisms: a review of theory. Sex Dev 8:7–19
Verhulst EC, van de Zande L (2014) Insect sex determination: a cascade of mechanisms. Sex Dev 8:5–6
Villella A, Gailey DA, Berwald B, Oshima S, Barnes PT, Hall JC (1997) Extended reproductive roles of the fruitless gene in Drosophila melanogaster revealed by behavioral analysis of new fru mutations. Genetics 147:1107–1130
Wilkins AS (1995) Moving up the hierarchy: a hypothesis on the evolution of a genetic sex determination pathway. BioEssays 17:71–77
Yi W, Zarkower D (1999) Similarity of a DNA binding and transcriptional regulation by Caenorhabditis elegans MAB-3 and Drosophila melanogaster DSX suggests conservation of sex determining mechanisms. Development 126:873–881
Zhang E, Qiu G (2010) A novel Dmrt gene is specifically expressed in the testis of Chinese mitten crab, Eriocheir sinensis. Dev Genes Evol 220:151–159
Zhao Y, Dunsong L, Zhang M, Chen W, Zhang G (2014) Food source affects the expression of vitellogenin and fecundity of a biological control agent, Neoseiulus cucumeris. Exp Appl Acarol 63:333–347
Zhu L, Wilken J, Phillips NB, Narendra U, Chan G, Stratton SM, Kent SB, Weiss MA (2000) Sexual dimorphism in diverse metazoans is regulated by a novel class of intertwined zinc fingers. Gen Dev 14:1750–1764
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Davies Fisher and Eckes Endowment in Biological Control to M.A. Hoy. We thank Dr. Ke Wu for his constructive suggestions and useful discussions and Godfey Maina for assistance in rearing the colonies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pomerantz, A.F., Hoy, M.A. Expression analysis of Drosophila doublesex, transformer-2, intersex, fruitless-like, and vitellogenin homologs in the parahaploid predator Metaseiulus occidentalis (Chelicerata: Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol 65, 1–16 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-014-9855-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-014-9855-2