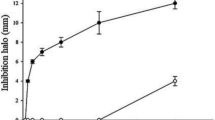
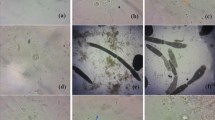
Abstract
The activity of lysozyme, the enzyme that hydrolyzes peptidoglycan in G+ bacterial cell walls, was detected in whole mite extracts (WME) and in spent growth medium extracts (SGME) of 14 species of synanthropic mites (Acari: Acaridida). The adaptation of lysozyme for digestive activity and bacteriophagy was based on: (i) high lysozyme activity in SGME, and (ii) the correlation of maximum lysozyme activity at acidic pH values, corresponding to pH in the ventriculus and caeca. We show that the digestion of fluorescein-labeled Micrococcus lysodeikticus cells began in ventriculus and continued during the passage of a food bolus through the gut. The fluorescein was absorbed by midgut cells and penetrated to parenchymal tissues. Eight species showed a higher rate of population growth on a M. lysodeikticus diet than on a control diet. The lysozyme activity in SGME was positively correlated to the standardized rate (r s) of population growth, although no correlation was found between r s and lysozyme activity in WME. The lysozyme activity in WME was negatively correlated to that in SGME. The highest activity of digestive lysozyme was found in Lepidoglyphus destructor, Chortoglyphus arcuatus and Dermatophagoides farinae. All of these findings indicate that lysozyme in acaridid mites possesses both defensive and digestive functions. The enzymatic properties of mite lysozyme are similar to those of the lysozymes present in the ruminant stomach and in the insect midgut.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akimov IA (1985) The biological aspects of digestion of acaroid mites. Akademija Nauk Ukrainskoj SSR, Kiev (in Ukrainan)
Akimov IA, Barabanova VV (1976) The digestive enzymes of acaroid mites. Dopov Akad Nauk Ukr 6:547–549 (in Ukrainan)
Akimov IA, Barabanova VV (1978) The influence of the feeding to the activity of the digestive enzymes of acaroid mites. Ekologia (Russian) 2:27–31 (in Russian)
Aspaly G, Stejskal V, Pekar S, Hubert J (2007) Temperature-dependent population growth of three species of stored product mites (Acari: Acaridida). Exp Appl Acarol 42:37–46
Bachali S, Jager M, Hassanin A, Schoentgen F, Jolles P, Fiala-Medioni A, Deutsch JS (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of invertebrate lysozymes and the evolution of lysozyme function. J Mol Evol 54:652–664
Bowman CE (1984) Comparative enzymology of economically important astigmatid mites. In: Griffiths DA, Bowman CE (eds) Acarology 6. Ellis Horwood Publishing, Chichester, pp 993–1001
Camara VM, Prieur DJ (1980) Lysozyme activity in gastrointestinal and lymphoreticular tissues of rabbits genetically deficient in lysozyme. Lab Invest 43:352–357
Camara VM, Prieur DJ (1984) Secretion of colonic isozyme of lysozyme in association with cecotrophy of rabbits. Am J Physiol 247:G19–G23
Carsky J (1981) The preparation of buffers and isotonic solutions. In: Ferencik M, Skarka B et al (eds) Biochemical and laboratory methods. ALFA, Bratislava, pp 39–86 (in Czech)
Childs M, Bowman CE (1981) Lysozyme activity in 6 species of economically important astigmatid mites. Comp Biochem Physiol 70B:615–617
Chipman DM, Sharon N (1969) Mechanism of lysozyme action. Science 165:454–465
Dobson DE, Prager EM, Wilson AC (1984) Stomach lysozymes of ruminants. I. Distribution and catalytic properties. J Biol Chem 259:11607–11616
Dominguez-Bello MG, Pacheco MA, Ruiz MC, Michelangeli F, Leippe M, de Pedro MA (2004) Resistance of rumen bacteria murein to bovine gastric lysozyme. BMC Ecol 4:7
Espinoza-Fuentes FP, Ribeiro AF, Terra WR (1987) Microvillar and secreted digestive enzymes from Musca domestica larvae. Subcellular fractionation of midgut cells with electron microscopy monitoring. Insect Biochem 17:819–827
Grunclova L, Fouquier H, Hypsa V, Kopacek P (2003) Lysozyme from the gut of the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata: the sequence, phylogeny and post-feeding regulation. Dev Comp Immunol 27:651–660
Hakkaart GA, Aalberse RC, Van RR (1997) Lack of lysozyme activity of natural and yeast-derived recombinant Der p2. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 114:202–204
Hamilton KA, Nisbet AJ, Lehane MJ, Taylor MA, Billingsley PF (2003) A physiological and biochemical model for digestion in the ectoparasitic mite, Psoroptes ovis (Acari: Psoroptidae). Int J Parasitol 33:773–785
Hogg JC, Lehane MJ (1999) Identification of bacterial species associated with the sheep scab mite (Psoroptes ovis) by using amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4227–4229
Hoogenraad NJ, Hird FJ (1970) The chemical composition of rumen bacteria and cell walls from rumen bacteria. Br J Nutr 24:119–127
Hubert J, Stejskal V, Kubatova A, Munzbergova Z, Vanova M, Zdarkova E (2003) Mites as selective fungal carriers in stored grain habitats. Exp Appl Acarol 29:69–87
Hubert J, Krizkova-Kudlikova I, Stejskal V (2004) Review of digestive enzymes of stored product and house dust mites. Phytophaga 14:695–710
Hubert J, Doleckova-Maresova L, Hyblova J, Kudlikova I, Stejskal V, Mares M (2005) In vitro and in vivo inhibition of alpha-amylases of stored-product mite Acarus siro. Exp Appl Acarol 35:281–291
Hughes AM (1976) The mites of stored food and houses. MAFF Technical Bulletin 9, 2nd edn. London, UK, p 400
Hughes TE (1950) The physiology of the alimentary canal of Tyrophagus farinae. Quart J Microsc Sci 91:54–60
Ito Y, Hirashima M, Yamada H, Imoto T (1994) Colonic lysozymes of rabbit (Japanese white): recent divergence and functional conversion. J Biochem (Tokyo) 116:1346–1353
Ito Y, Nakamura M, Hotani T, Imoto T (1995) Insect lysozyme from house fly (Musca domestica) larvae: possible digestive function based on sequence and enzymatic properties. J Biochem (Tokyo) 118:546–551
Jolles P, Jolles J (1984) What’s new in lysozyme research? Always a model system, today as yesterday. Mol Cell Biochem 63:165–189
Jolles J, Schoentgen F, Croizier G, Croizier L, Jolles P (1979) Insect lysozymes from three species of Lepidoptera: their structural relatedness to the C (chicken) type lysozyme. J Mol Evol 14:267–271
Kaneko N (1988) Feeding habits and cheliceral size of oribatid mites in cool temperate forest soils in Japan. Rev Ecol Biol Sol 25:353–363
Kylsten P, Kimbrell DA, Daffre S, Samakovlis C, Hultmark D (1992) The lysozyme locus in Drosophila melanogaster: different genes are expressed in midgut and salivary glands. Mol Gen Genet 232:335–343
Labischinski H, Maidhof H (1994) Bacterial peptidoglycan. Overview and evolving concepts. In: Ghuysen JM, Hakenbeck R (eds) Bacterial cell wall. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 23–38
Lemos FJ, Terra WR (1991a) Properties and intracellular distribution of a cathepsin D-like proteinase active at the acid region of Musca domestica. Insect Biochem 21:457–465
Lemos FJ, Terra WR (1991b) Digestion of bacteria and the role of midgut lysozyme in some insect larvae. Comp Biochem Physiol 100B:265–268
Lemos FJ, Ribeiro AF, Terra WR (1993) A bacteria-digesting midgut lysozyme from Musca domestica (Diptera) larvae. Purification, properties and secretory mechanism. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 24:533–541
Luxton M (1972) Studies on the oribatid mites of Danish beech wood soil. Pedobiologia 12:434–463
Maraun M, Martens H, Migge M, Theenshaus H, Scheu S (2003) Adding to ‘the enigma of soil animal diversity: fungal feeders and saprophagous soil invertebrates prefer similar food substrates. Eur J Soil Biol 39:85–95
Mathaba LT, Pope CH, Lenzo J, Hartofillis M, Peake H, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Bubert A, Thompson PJ, Stewart GA (2002) Isolation and characterisation of a 13.8-kDa bacteriolytic enzyme from house dust mite extracts: homology with prokaryotic proteins suggests that the enzyme could be bacterially derived. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 33:77–88
Matsumoto K (1965) Studies on environmental factors for breeding of grain mites VII. Relationship between reproduction of mites and kind of carbohydrates in the diet. Jpn J Sanit Zool 16:118–122 (in Japanese)
Morgan MS, Arlian LG (2006) Enzymatic activity in extracts of allergy-causing astigmatid mites. J Med Entomol 43:1200–1207
OConnor BM (1979) Evolutionary origins of astigmatid mites inhabiting stored products. Rec Adv Acarol 1:273–278
Oh H, Ishii A, Tongu Y, Itano K (1986) Microorganisms associated with the house dust mite, Dermatophagoides. Jpn J Sanit Zool 37:229–235 (in Japanese)
Orskov ER, MacLeod NA (1982) The determination of the minimal nitrogen excretion in steers and dairy cows and its physiological and practical implications. Br J Nutr 47:625–626
Ortego F, Sanchez-Ramos I, Ruiz M, Castanera P (2000) Characterization of proteases from a stored product mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 43:116–124
Regel R, Matioli SR, Terra WR (1998) Molecular adaptation of Drosophila melanogaster lysozymes to a digestive function. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:309–319
Ruiz MC, Dominguez-Bello MG, Michelangeli F (1994) Gastric lysozyme as a digestive enzyme in the hoatzin (Opisthocomus hoazin), a ruminant-like folivorous bird. Cell Mol Life Sci 50:499–501
Sanchez-Ramos I, Hernandez CA, Castanera P, Ortego F (2004) Proteolytic activities in body and faecal extracts of the storage mite, Acarus farris. Med Vet Entomol 18:378–386
Schuster R (1956) Der Anteil der Oribatiden an der Zersetzungsvorgangen im Boden. Z Morph Okol 45:1–33
Siepel H, de Ruiter-Dijkman EM (1993) Feeding guilds of oribatid mites based on their carbohydrase activities. Soil Biol Biochem 25:1491–1497
Sinha RN, Harasymek L (1974) Survival and reproduction of stored-product mites and beetles on fungal and bacterial diets. Environ Entomol 3:243–246
Smrz J, Catska V (1987) Food selection of the field population of Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank) (Acari, Acarida). J Appl Entomol—Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Entomologie 104:329–335
Smrz J, Catska V (1989) The effect of the consumption of some soil fungi on the internal microanatomy of the mite Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank) (Acari, Acaridida). Acta Universitatis Carolinae – Bilogica 33:81–93
Smrz J, Svobodova J, Catska V (1991) Synergetic participation of Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank) (Acari, Acaridida) and its associated bacteria on the destruction of some soil micromycetes. J Appl Entomol—Zeitschrift fur Angewandte Entomologie 111:206–210
Sobotnik J, Alberti G, Weyda F, Hubert J (2008) Ultrastructure of the digestive tract in Acarus siro (Acari: Acaridida). J Morphol 269(1):54–71
Spieksma FT (1997) Domestic mites from an acarologic perspective. Allergy 52:360–368
Stewart CB, Schilling JW, Wilson AC (1987) Adaptive evolution in the stomach lysozymes of foregut fermenters. Nature 330:401–404
Stewart GA, van Hage-Hamsten M, Krska K, Thompson PJ, Olsson S (1998) An enzymatic analysis of the storage mite Lepidoglyphus destructor. Comp Biochem Physiol 119B:341–347
Sustr V, Block W (1998) Temperature dependence and acclimatory response of amylase in the High Arctic springtail Onychiurus arcticus (Tullberg) compared with the temperate species Protaphorura armata (Tullberg). Insect Biochem 44:991–999
Sustr V, Stary J (1998) Digestive enzymes in oribatid mites: Impact of factors. Institute of Soil Biology AS CR, Ceske Budejovice
Terra WR (1990) Evolution of digestive systems of insects. Ann Rev Entomol 35:181–200
Terra WR, Ferreira C, Baker JE (1996) Compartmentalization of digestion. In: Lehane MJ, Billingsley PF (eds) Biology of the insect midgut. Chapman & Hall, London, pp 206–235
Tovey ER, Chapman MD, Platts-Mills TA (1981) Mite faeces are a major source of house dust allergens. Nature 289:592–593
Trivedi BMD, Valerio CBS, Slater JEMD (2003) Endotoxin content of standardized allergen vaccines. J Allergy Clin Immunol 111:777–783
Valerio CR, Murray P, Arlian LG, Slater JE (2005) Bacterial 16S ribosomal DNA in house dust mite cultures. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:1296–1300
Voet D, Voet JG (2004) Sugars and polysaccharides: bacterial cell walls. In: Biochemistry, 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken, pp 372–375
Acknowledgements
Tomas Erban was supported by project COST 1P040C853.003, and Jan Hubert, by the project of the Ministry of Agriculture—MZE-000-2700603. Authors are obliged to Jaroslav Smrz for his kind advice, Martina Zilova-Janouskova, Iva Kudlikova-Krizkova, Vladimir Sustr and Palmiro Poltronieri for their critical comments to the manuscript. We thank to Sarka Tuckova and Marta Nesvorna for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erban, T., Hubert, J. Digestive function of lysozyme in synanthropic acaridid mites enables utilization of bacteria as a food source. Exp Appl Acarol 44, 199–212 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9138-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-008-9138-x