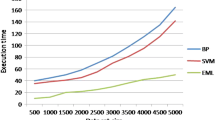
Abstract
In this paper, an efficient projection wavelet weighted twin support vector regression (PWWTSVR) algorithm is proposed. PWWTSVR determines the regression function by solving a pair of smaller unconstrained minimization problems in primal space, which can reduce computational costs. Classical SVR algorithms give the same emphasis to all training samples, which degrades performance. PWWTSVR gives samples penalty weights determined by wavelet transforms. These are applied to both the quadratic empirical risks term and the first-degree empirical risks term to reduce the influence of outliers. A projection axis in each objective function is sought to minimize the variance of the projected points due to the utilization of a priori information of training data. Therefore, data structure terms are added to the penalty functions. The final regressor can avoid the overfitting problem to a certain extent, and yields great generalization ability. Numerical experiments on artificial and benchmark datasets demonstrate the feasibility and validity of the proposed algorithm.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vapnik VN (1995) The natural of statistical learning theroy. Springer, New York
Vapnik VN (1998) Statistical learning theroy. Wiley, New York
Khemchandani JR, Chandra S (2007) Twin support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 29(5):905–910
Peng X (2010) TSVR: an efficient twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Netw 23(3):356–372
Suykens JAK, Lukas L, Dooren V (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers: a large scale algorithm. In: Proceedings of ECCTD. Italy, pp 839–842
Suykens JAK, Vandewalle J (1999) Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Process Lett 9(3):293–300
Scholkopf B, Smola AJ, Williamson RC, Bartlett PL (2000) New support vector algorithms. Neurocomputing 12(5):1207–1245
Huang XL, Shi L, Pelckmans K, Suykens JAK (2014) Asymmetric ν-tube support vector regression. Comput Stat Data Anal 77:371–382
Huang XL, Shi L, Suykens JAK (2014) Support vector machine classifier with pinball loss. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal 36:984– 997
Xu Y, Yang Z, Pan X (2016) A novel twin support vector machine with pinball loss. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 28(2):359–370
Xu Y, Yang Z, Zhang Y, Pan X, Wang L (2016) A maximum margin and minimum volume hyper-spheres machine with pinball loss for imbalanced data classification. Knowl-Based Syst 95:75–85
Xu Y, Li X, Pan X, Yang Z (2017) Asymmetric ν-twin support vector regression. Neural Comput Appl 2:1–16
Shao Y, Zhang C, Yang Z, Jing L, Deng N (2013) An ν-twin support vector machine for regression. Neural Comput Appl 23:175–185
Rastogi R, Anand P, Chandra S (2017) A v-twin support vector machine based regression with automatic accuracy control. Appl Intell 46:670–683
Peng X, Xu D, Shen J (2014) A twin projection support vector machine for data regression. Neuro Comput 138:131–141
Melki G, Cano A, Kecman V, Ventura S (2017) Multi-target support vector regression via correlation regressor chains. Info Sci s415–416:53–69
Ding S, Wu F, Shi Z (2014) Wavelet twin support vector machine. Neural Comput Appl 25(6):1241–1247
Melki G, Cano A, Ventura S (2018) MIRSVM: multi-instance support vector machine with bag representatives. Pattern Recogn 79:228–241
Melki G, Kecman V, Ventura S, Cano A (2018) OLLAWV: OnLine learning algorithm using worst-violators. Appl Soft Comput 66:384–393
Xu Y, Wang L (2014) K-nearest neighbor-based weighted twin support vector regression. Appl Intell 41:299–309
Gupta D (2017) Training primal K-nearest neighbor based weighted twin support vector regression via unconstrained convex minimization. Appl Intell 47:962–991
Chapelle O (2007) Training a support vector machine in the primal. Neurocomputing 19(5):1155–1178
Ye Y, Bai L, Hua X, Shao Y, Wang Z, Deng N (2016) Weighted Lagrange ν-twin support vector regression. Neurocomputing 197:53–68
Shevade S, Keerthi S, Bhattacharyya C (2000) Improvements to the SMO algorithm for SVM regression. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 11(5):1188–1193
Lee Y, Hsieh W, Huang C (2005) SSVR: a smooth support vector machine for insensitive regression. IEEE Trans Knowl Data En 17(5):678–685
Peng X, Chen D (2018) PTSVRs: regression models via projection twin support vector machine. Info Sci 435:1–14
Horn RA, Johnson CR (2013) Matrix analysis, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, New York
Zhang F (2005) The Schur complement and its applications. Springer, New York
Blake C, Merz C (1998) UCI repository for machine learning databases. http://www.ics.uci.edu/mlearn/MLRepository.html
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 71571091 and 71771112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Gao, C., Zhao, N. et al. A projection wavelet weighted twin support vector regression and its primal solution. Appl Intell 49, 3061–3081 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01422-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-019-01422-7