Abstract
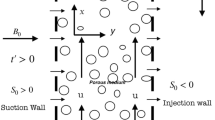
In this research, the three-dimensional (3D) steady and incompressible laminar Homann stagnation point nanofluid flow over a porous moving surface is addressed. The disturbance in the porous medium has been characterized by the Darcy-Forchheimer relation. The slip for viscous fluid is considered. The energy equation is organized in view of radiative heat flux which plays an important role in the heat transfer rate. The governing flow expressions are first altered into first-order ordinary ones and then solved numerically by the shooting method. Dual solutions are obtained for the velocity, skin friction coefficient, temperature, and Nusselt number subject to sundry flow parameters, magnetic parameter, Darcy-Forchheimer number, thermal radiation parameter, suction parameter, and dimensionless slip parameter. In this research, the main consideration is given to the engineering interest like skin friction coefficient (velocity gradient or surface drag force) and Nusselt number (temperature gradient or heat transfer rate) and discussed numerically through tables. In conclusion, it is noticed from the stability results that the upper branch solution (UBS) is more reliable and physically stable than the lower branch solution (LBS).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ξU, ξV :
-
velocities in x- and y-directions, respectively
- α :
-
momentum accommodation coefficient
- K*:
-
permeability of porous space
- Kn :
-
Knudsen number
- Λ:
-
mean free path
- M 1, M 2 :
-
slip coefficients in x- and y-directions
- x, y, z :
-
Cartesian coordinates
- u, v, w :
-
velocity vectors
- T ∞ :
-
ambient temperature
- k*:
-
mean absorption coefficient
- Q*:
-
heat generation/absorption coefficient
- β*:
-
porosity parameter
- Re :
-
Reynold number
- C f1, C f2 :
-
skin frictions
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- ν nf :
-
kinematic viscosity
- \(F\left(\frac{C_b}{xK^{* \frac{1}{2}}}\right)\) :
-
coefficient of non-uniform inertia
- T :
-
temperatures
- c p :
-
specific heat
- k nf :
-
thermal conductivity
- σ*:
-
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
- u w(x):
-
stretching velocity
- C b :
-
drag coefficient
- μ f :
-
dynamic viscosity
- w 0 :
-
suction/injection
- Tw:
-
wall temperature
- s :
-
suction/injection variable
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- R :
-
radiation number
- A, B :
-
slip parameters in x- and y-directions
- λ, λ 1 :
-
dimensionless constant parameters
- Q*:
-
heat generation parameter
- F x, F y :
-
coefficients of inertia in x- and y-directions
References
FANG, T., ZHANG, J., and YAO, S. A new family of unsteady boundary layers over a stretching surface. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 217, 3747–3755 (2010)
KHAN, M. I., WAQAS, M., HAYAT, T., and ALSAEDI, A. A comparative study of Casson fluid with homogeneous-heterogeneous reactions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 498, 85–90 (2017)
SAHOO, B. and SHEVCHUK, I. V. Heat transfer due to revolving flow of Reiner-Rivlin fluid over a stretchable surface. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 10, 327–336 (2019)
KHAN, M., AHMAD, J., and AHMAD, L. Chemically reactive and radiative von Kármán swirling flow due to a rotating disk. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 39(9), 1295–1310 (2018) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-018-2368-9
MUHAMMAD, R., KHAN, M. I., KHAN, N. B., and JAMEEL, M. Magnetohydrodynamics (MHD) radiated nanomaterial viscous material flow by a curved surface with second order slip and entropy generation. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 189, 105294 (2020)
SAKIADIS, B. C. Boundary layer behavior on continuous solid surfaces: I. boundary layer equations for two dimensional and axisymmetric flow. AIChE Journal, 7, 26–28 (1961)
CRANE, L. J. Flow past a stretching plate. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Physics (ZAMP), 21, 645–647 (1970)
RASHIDI, M. M., ALI, M., ROSTAMI, B., ROSTAMI, P., and XIE, G. N. Heat and mass transfer for MHD viscoelastic fluid flow over a vertical stretching sheet with considering soret and Dufour effects. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 861065 (2015)
WAQAS, H., IMRAN, M., KHAN, S. U., SHEHZAD, S. A., and MERAJ, M. A. Slip flow of Maxwell viscoelasticity-based micropolar nanoparticles with porous medium: a numerical study. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(9), 1255–1268 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2518-9
MUHAMMAD, R., KHAN, M. I., JAMEEL, M., and KHAN, N. B. Fully developed Darcy-Forchheimer mixed convective flow over a curved surface with activation energy and entropy generation.Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 188, 105298 (2020)
SUN, X., WANG, S., and ZHAO, M. Numerical solution of oscillatory flow of Maxwell fluid in a rectangular straight duct. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(11), 1647–1656 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2535-6
SCHLICHTING, H. Boundary Layer Theory, 7th Edition, McGraw-Hill, New York (1960)
CHARI, K. and RAJAGOPALAN, R. Deposition of colloidal particles in stagnation-point flow. Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions, 81, 1345–1366 (1985)
HAFIDZUDDIN, E. H., NAZAR, R., ARIFIN, N. M., and POP, I. Effects of anisotropic slip on three-dimensional stagnation-point flow past a permeable moving surface. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 65, 515–521 (2017)
BÉG, O. A., BAKIER, A. Y., PRASAD, V. R., ZUECO, J., and GHOSH, S. K. Nonsimilar, laminar, steady, electrically-conducting forced convection liquid metal boundary layer flow with induced magnetic field effects. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 48, 1596–1606 (2019)
SHAH, F., KHAN, M. I., HAYAT, T., MOMANI, S., and KHAN, M. I. Cattaneo-Christov heat flux (CC model) in mixed convective stagnation point flow towards a Riga plate. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 196, 105564 (2020)
AL-BALUSHI, L. M., RAHMAN, M. M., and POP, I. Three-dimensional axisymmetric stagnation-point flow and heat transfer in a nanofluid with anisotropic slip over a striated surface in the presence of various thermal conditions and nanoparticle volume fractions. Thermal Science and Engineering Progress, 2, 26–42 (2017)
KHAN, M. I., ALZAHRANI, F., HOBINY, A., and ALI, Z. Modeling of Cattaneo-Christov double diffusions (CCDD) in Williamson nanomaterial slip flow subject to porous medium. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 9, 6172–6177 (2020)
MAHAPATRA, T. R. and SIDUI, S. Non-axisymmetric Homann stagnation-point flow of a viscoelastic fluid towards a fixed plate. European Journal of Mechanics-B/Fluids, 79, 38–43 (2020)
KHAN, M., EL SHAFEY, A. M., SALAHUDDIN, T., and KHAN, F. Chemically Homann stagnation point flow of Carreau fluid. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 551, 124066 (2020)
WANG, C. Stagnation slip flow and heat transfer on a moving plate. Chemical Engineering Science, 61, 7668–7672 (2006)
WEIDMAN, P., KUBITSCHEK, D., and DAVIS, A. The effect of transpiration on self-similar boundary layer flow over moving surfaces. International Journal of Engineering Sciences, 44, 730–737 (2006)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11971142, 11871202, 61673169, 11701176, 11626101, and 11601485)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, Y., Khan, M.I., Rehman, M.I.U. et al. Stability analysis and modeling for the three-dimensional Darcy-Forchheimer stagnation point nanofluid flow towards a moving surface. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 42, 357–370 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2700-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-021-2700-7
Key words
- viscous slip
- Darcy-Forchheimer relation
- thermal radiation
- stagnation point flow
- dual solution
- heat generation/absorption
- stability result