Abstract
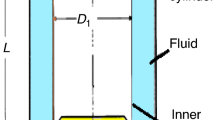
An electronic-nose is developed based on eight quartz-crystal-microbalance (QCM) gas sensors in a sensor box, and is used to detect Chinese liquors at room temperature. Each sensor is a highly-accurate and highly-sensitive oscillator that has experienced airflow disturbances under the condition of varying room temperatures due to unstable flow-induced forces on the sensors surfaces. The three-dimensional (3D) nature of the airflow inside the sensor box and the interactions of the airflow on the sensors surfaces at different temperatures are studied by computational fluid dynamics (CFD) tools. Higher simulation accuracy is achieved by optimizing meshes, meshing the computational domain using a fine unstructural tetrahedron mesh. An optimum temperature, 30 °C, is obtained by analyzing the distributions of velocity streamlines and the static pressure, as well as the flow-induced forces over time, all of which may be used to improve the identification accuracy of the electronic-nose for achieving stable and repeatable signals by removing the influence of temperature.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- t :
-
time, s
- x :
-
x-th component of coordinate vector, m
- y :
-
y-th component of coordinate vector, m
- z :
-
z-th component of coordinate vector, m
- u :
-
x-th component of velocity, m/s
- v :
-
y-th component of velocity, m/s
- w :
-
z-th component of velocity, m/s
- k :
-
heat conductivity constant, W·m−1·K−1
- p :
-
pressure, Pa
- c p :
-
constant pressure specific heat, kJ/(kg-K)
- T :
-
temperature, °C
- D :
-
mass diffusivity, m2/s.
- ρ :
-
density, kg/m3
- λ :
-
thermal conductivity
- Φ:
-
source term
- μ :
-
dynamic viscosity, N·s/m2
- γ :
-
time derivative
- eff:
-
effective
References
WU, J. F. and XU, Y. Comparison of pyrazine compounds in seven Chinese liquors using headspace solid-phase micro-extraction and GC-nitrogen phosphourus detection. Food Science and Biotechnology, 22(5), 1253–1258 (2013)
FAN, W. and QIAN, M. C. Characterization of aroma compounds of Chinese “Wuliangye” and “Jiannanchun” liquors by aroma extract dilution analysis. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 54(2), 2695–2704 (2006)
YAO, F., YI, B., SHEN, C., TAO, F., LIU, Y., LIN, Z., and XU, P. Chemical analysis of the Chinese liquor Luzhoulaojiao by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Scientific Reports, 5, 9553 (2015)
ZHENG, X. W. and HAN, B. Z. Baijiu, Chinese liquor: history, classification and manufacture. Journal of Ethnic Foods, 3(1), 19–25 (2016)
LI, Q., GU, Y., and WANG, N. F. Application of random forest classifier by means of a QCM-based e-nose in the identification of Chinese liquor flavors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(6), 1788–1794 (2017)
LI, Q., GU, Y., and JIA, J. Classification of multiple Chinese liquors by means of a QCM-based e-nose and MDS-SVM classifier. Sensors, 17(2), 272 (2017)
VILLA, F. F., MASTROMATTEO, U., and BARLOCCHI, G. Electronic Detection of Biological Materials, US8586351B2, United States Patent (2013)
JARUWONGRUNGSEE, K., MATUROS, T., SRITONGKUM, P., WISITSORA-AT, A., SANG-WORASIL, M., and TUANTRANONT, A. Analysis of quartz crystal microbalance sensor array with circular flow chamber. International Journal of Applied Biomedical Engineering, 2(2), 50–54 (2009)
HU, Z. and SUN, D. W. Effect of fluctuation in inlet airflow temperature on CFD simulation of air-blast chilling process. Journal of Food Engineering, 48(4), 311–316 (2001)
GIMBUN, J., CHUAH, T. G., FAKHRU’L-RAZI, A., and CHOONG, T. S. Y. The influence of temperature and inlet velocity on cyclone pressure drop: a CFD study. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 44(1), 7–12 (2005)
GU, Y., WANG, Y. F., LI, Q., and LIU, Z. W. A 3D CFD simulation and analysis of flow-induced forces on polymer piezoelectric sensors in a Chinese liquors identification e-nose. Sensors, 16(10), 1738 (2016)
GARDNER, J. W. and BARTLETT, P. N. A brief history of electronic noses. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 18(1–3), 210–211 (1994)
SCHALLER, E., BOSSET, J. O., and ESCHER, F. Electronic noses and their application to food. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 31(4), 305–316 (1998)
COZZOLINO, D., CYNKAR, W., DAMBERGS, R., and SMITH, P. Two-dimensional correlation analysis of the effect of temperature on the fingerprint of wines analysed by mass spectrometry electronic nose. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 145(2), 628–634 (2012)
VICCIONE, G., ZARRA, T., GIULIANI, S., NADDEO, V., and BELGIORNO, V. Performance study of e-nose measurement chamber for environmental odour monitoring. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 30, 109–114 (2012)
VICCIONE, G., SPINIELLO, D., ZARRA, T., and NADDEO, V. Fluid dynamic simulation of odour measurement chamber. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 40, 109–114 (2014)
XIAO, Z., YU, D., NIU, Y., CHEN, F., SONG, S., ZHU, J., and ZHU, G. Characterization of aroma compounds of Chinese famous liquors by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and flash GC electronic-nose. Journal of Chromatography B, 945–946, 92–100 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Citation: LI, Q., GU, Y., and WANG, H. T. The influence of temperature on flow-induced forces on quartz-crystal-microbalance sensors in a Chinese liquor identification electronic-nose: three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics simulation and analysis. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 40(9), 1301–1312 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2512-9
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61876059 and U1501251)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Gu, Y. & Wang, H. The influence of temperature on flow-induced forces on quartz-crystal-microbalance sensors in a Chinese liquor identification electronic-nose: three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics simulation and analysis. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 40, 1301–1312 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2512-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-019-2512-9
Key words
- computational fluid dynamics (CFD)
- temperature
- quartz-crystal-microbalance (QCM) gas sensor
- electronic nose
- identification accuracy