Abstract
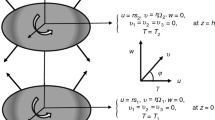
The unsteady, laminar, incompressible, and two-dimensional flow of a micropolar fluid between two orthogonally moving porous coaxial disks is considered. The extension of von Karman’s similarity transformations is used to reduce the governing partial differential equations (PDEs) to a set of non-linear coupled ordinary differential equations (ODEs) in the dimensionless form. The analytical solutions are obtained by employing the homotopy analysis method (HAM). The effects of various physical parameters such as the expansion ratio and the permeability Reynolds number on the velocity fields are discussed in detail.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Connor, J. J., Boyd, J., and Avallone, E. A. Standard Handbook of Lubrication Engineering, McGraw-Hill, New York (1968)
Elcrat, A. R. On the radial flow of a viscous fluid between porous disks. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis, 61, 91–96 (1976)
Rasmussen, H. Steady viscous flow between two porous disks. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Physik, 21, 187–195 (1970)
Berman, A. S. Laminar flow in channels with porous walls. Journal of Applied Physics, 24, 1232–1235 (1953)
Eringen, A. C. Theory of thermomicrofluids. Journal of Mathematical Analysis and Applications, 38, 480–496 (1972)
Aero, E. L., Bulygin, A. N., and Kuvshinskii, E. V. Asymmetric hydromechanics. Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 29(2), 297–308 (1965)
Anwar, K.M., Ashraf, M., and Syed, K. S. Numerical solution of steady viscous flow of a micropolar fluid driven by injection between two porous disks. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 179, 1–10 (2006)
Ashraf, M., Anwar, K. M., and Syed, K. S. Numerical simulation of flow of a micropolar fluid between a porous disk and a non-porous disk. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 33, 1933–1943 (2009)
Ariman, T., Turk, M. A., and Sylvester, N. D. Microcontinuum fluid mechanics-a review. International Journal of Engineering Science, 11, 905–930 (1973)
Ariman, T., Turk, M. A., and Sylvester, N. D. Application of microcontinuum fluid mechanics-a review. International Journal of Engineering Science, 12, 273–293 (1974)
Eringen, A. C. Microcontinuum Field Theories II: Fluent Media, Springer, New York (2001)
Guram, G. S. and Anwar, M. Steady flow of a micropolar fluid due to a rotating disk. Journal of Engineering Mathematics, 13, 223–234 (1979)
Guram, G. S. and Anwar, M. Micropolar flow due to a rotating disc with suction and injection. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 61, 589–605 (1981)
Atif, N. and Tahir, M. Analysis of flow and heat transfer of viscous fluid between contracting rotating disks. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 35, 3154–3165 (2011)
Uchida, S. and Aoki, H. Unsteady flows in a semi-infinite contracting or expanding pipe. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 82, 371–387 (1977)
Ohki, M. Unsteady flows in a porous, elastic, circular tube-I: the wall contracting or expanding in an axial direction. Bulletin of the JSME, 23, 679–686 (1980)
Barron, J., Majdalani, J., and van Moorhem, W. K. A novel investigation of the oscillatory field over a transpiring surface. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 235, 281–297 (2000)
Majdalani, J., Zhou, C., and Dawson, C. A. Two-dimensional viscous flows between slowly expanding or contracting walls with weak permeability. Journal of Biomechanics, 35, 1399–1403 (2002)
Majdalani, J. and Zhou, C. Moderate-to-large injection and suction driven channel flows with expanding or contracting walls. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 83(3), 181–196 (2003)
Dauenhauer, C. E. and Majdalani, J. Exact self-similarity solution of the Navier-Stokes equations for a porous channel with orthogonally moving walls. Physics of Fluids, 15, 1485–1495 (2003)
Asghar, S., Mushtaq, M., and Hayat, T. Flow in a slowly deforming channel with weak permeability: an analytical approach. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 11, 555–561 (2010)
Dinarvand, S. and Rashidi, M. M. A reliable treatment of a homotopy analysis method for twodimensional viscous flow in a rectangular domain bounded by two moving porous walls. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 11, 1502–1512 (2010)
Si, X. H., Zheng, L. C., Zhang, X. X., and Chao, Y. The flow of a micropolar fluid through a porous channel with expanding or contracting walls. Central European Journal of Physics, 9, 825–834 (2011)
Si, X. H., Zheng, L. C., Zhang, X. X., Si, X. Y., and Yang, J. H. Flow of a viscoelastic through a porous channel with expanding or contracting walls. Chinese Physics Letters, 28(4), 044702 (2011)
Xu, H., Lin, Z. L., Liao, S. J., Wu, J. Z., and Majdalani, J. Homotopy based solutions of the Navier-Stokes equations for a porous channel with orthogonlly moving walls. Physics of Fluids, 22, 053601 (2010)
Liao, S. J. Beyond Perturbation: Introduction to Homotopy Analysis Method, Chapman Hall/CRC Press, Rocal Raton (2003)
Liao, S. J. On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 147, 499–513 (2004)
Hayat, T. and Khan, M. Homotopy solution for a generalized second grade fluid past a porous plate. Non-Linear Dynamics, 42, 395–405 (2005)
Hayat, T., Khan, M., and Asghar, S. Magnetohydrodynamic flow of an Oldroyd 6-constant fluid. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 155, 417–425 (2004)
Abbas, Z., Sajid, M., and Hayat, T. MHD boundary-layer flow of an upper-convected Maxwell fluid in a porous channel. Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics, 20, 229–238 (2006)
Sajid, M., Hayat, T., and Asghar, S. On the analytic solution of the steady flow of a fourth grade fluid. Physics Letters A, 355, 18–26 (2006)
Abbasbandy, S., Shivanian, E., and Vajravelu, K. Mathematical properties of h-curve in the frame work of the homotopy analysis method. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 16, 4268–4275 (2011)
Abbasbandy, S. Approximate analytical solutions to thermo-poroelastic equations by means of the iterated homotopy analysis method. International Journal of Computer Mathematics, 88, 1763–1775 (2011)
Abbasbandy, S., Magyari, E., and Shivanian, E. The homotopy analysis method for multiple solutions of nonlinear boundary value problems. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 14, 3530–3536 (2009)
Rees, D. A. S. and Pop, I. Free convection boundary-layer flow of a micropolar fluid from a vertical flat plate. Journal of Applied Mathematics, 61, 179–197 (1998)
Guram, G. S. and Smith, A. C. Stagnation flows of micropolar fluids with strong and weak interactions. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 6, 213–233 (1980)
Von Karman, T. Über laminare und turbulente Reibung. Zeitschrift für Angewandte Mathematik und Mechanik, 1, 233–252 (1921)
Liao, S. J. An optimal homotopy-analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 15, 2003–2016 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51004013, 50936003, 51174028, and 50905013), the Research Foundation of Engineering Research Institute of University of Science and Technology Beijing (No.Yj2011-015), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No.T-RF-TP-12-108A)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Si, Xh., Zheng, Lc., Zhang, Xx. et al. Flow of micropolar fluid between two orthogonally moving porous disks. Appl. Math. Mech.-Engl. Ed. 33, 963–974 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-012-1598-8
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-012-1598-8