Abstract
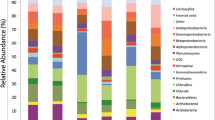
Bacterial and archaeal diversity in surface soils of three coal-fire vents was investigated by T-RFLP analysis and clone libraries of 16S rRNA genes. Soil analysis showed that underground coal fires significantly influenced soil pH, moisture and NO3 − content but had little effect on other elements, organic matter and available nutrients. Hierarchical cluster analysis showed that bacterial community patterns in the soils were very similar, but abundance varied with geographic distance. A clone library from one soil showed that the bacterial community was mainly composed of Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Planctomycetes, Actinobacteria, and unidentified groups. Of these, Firmicutes was the most abundant, accounting for 71.4 % of the clones, and was mainly represented by the genera Bacillus and Paenibacillus. Archaeal phylotypes were closely related to uncultivated species of the phyla Crenarchaeota (97.9 % of clones) and Thaumarchaeota (2.1 %). About 28 % of archaeal phylotypes were associated with ammonia oxidization, especially phylotypes that were highly related to a novel, ammonia-oxidizing isolate from the phylum Thaumarchaeota. These results suggested that microbial communities in the soils were diverse and might contain a large number of novel cultivable species with the potential to assimilate materials by heterotrophic metabolism at high temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bano N, Ruffin S, Ranson B, Hollibaugh JT (2004) Phylogenetic composition of Arctic Ocean archaeal assemblages and comparison with Antarctic assemblages. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:781–789
Brochier-Armanet C, Boussau B, Gribaldo S, Forterre P (2008) Mesophilic crenarchaeota: proposal for a third archaeal phylum, the Thaumarchaeota. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:245–252
Bruins ME, Janssen Ae M, Boom RM (2001) Thermozymes and their applications: a review of recent literature and patents. Appl Biochem Biotech 90:155–186
Cavicchioli R (2002) Extremophiles and the search for extraterrestrial life. Astrobiology 2:281–292
Dang H, Luan XW, Chen R, Zhang X, Guo L, Klotz MG (2010) Diversity, abundance and distribution of amoA-encoding archaea in deep-sea methane seep sediments of the Okhotsk Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 72:370–385
Franklin RB, Blum LK, McComb AC, Mills AL (2002) A geostatistical analysis of small-scale spatial variability in bacterial abundance and community structure in salt marsh creek bank sediments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 42:71–80
Good IJ (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Gubry-Rangin C, Nicol GW, Prosser JI (2010) Archaea rather than bacteria control nitrification in two agricultural acidic soils. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 74:566–574
Herrmann M, Saunders AM, Schramm A (2009) Effect of lake trophic status and rooted macrophytes on community composition and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing prokaryotes in freshwater sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:3127–3136
Hewson I, Fuhrman JA (2004) Richness and diversity of bacterioplankton species along an estuarine gradient in Moreton Bay, Australia. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:3425–3433
Horikoshi K (1999) Some applications of their products for biotechnology. Microbiol Mol Biol R 63:735–750
Horner-Devine MC, Lage M, Hughes JB, Bohannan BJM (2004) A taxa-area relationship for bacteria. Nature 432:750–753
Hugenholtz P, Pitulle C, Hershberger KL, Pace NR (1998) Novel division level bacterial diversity in a Yellowstone hot spring. J Bacteriol 180:366–376
Itay M, Hill CR, Glasser D (1989) A study of the low temperature oxidation of coal. Fuel Process Technol 21:81–97
Jiang H, Huang Q, Dong H, Wang P, Wang F, Li W, Zhang C (2010) RNA-based investigation of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in hot springs of Yunnan Province, China. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:4538–4541
Kuske CR, Ticknor LO, Miller ME, Dunbar JM, Davis JA, Barns SM, Belnap J (2002) Comparison of soil bacterial communities in rhizospheres of three plant species and the interspaces in an arid grassland. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1854–1863
Lesaulnier C, Papamichail D, McCorkle S, Ollivier B, Skiena S, Taghavi S, Zak D, Lelie DVD (2008) Elevated atmospheric CO2 affects soil microbial diversity associated with trembling aspen. Environ Microbiol 10:926–941
Norris TB, Wraith JM, Castenholz RW, McDermott TR (2002) Soil microbial community structure across a thermal gradient following a geothermal heating event. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:6300–6309
Pone JDN, Hein KAA, Stracher GB, Annegarn H, Finkleman RB, Blake DR, McCormack JK, Schroeder P (2007) The spontaneous combustion of coal and its by products in the Witbank and Sasolburg coalfields of South Africa. Int J Coal Geol 72:124–140
Rothschild LJ, Mancinelli RL (2001) Life in extreme environments. Nature 409:1092–1101
Sakon JJ, Burnap RL (2006) An analysis of potential photosynthetic life on Mars. Int J Astrobiol 5:171–180
Soo RM, Wood SA, Grzymski JJ, McDonald LR, Lary SC (2009) Microbial biodiversity of thermophilic communities in hot mineral soils of Tramway Ridge, Mt. Erebus, Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 11:715–728
Stracher GB, Taylor TP (2004) Coal fires burning out of control around the world: thermodynamic recipe for environmental catastrophe. Int J Coal Geol 59:7–17
Takai K, Moser DP, DeFlaun M, Onstott TC, Fredrickson JK (2001) Archaeal diversity in waters from deep South African gold mines. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:5750–5760
Tammy TJ, Ashley S, Leslie M, Kristina T, Curtina B, Christopher J, Jennie L, Amy M, Daniel R (2005) Nitrogen changes and domain bacteria ribotype diversity in soils overlying the Centralia, Pennsylvania underground coal mine fire. Soil Sci 170:191–201
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weigh matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Torsvik V, Øvreås L (2008) Microbial diversity, life strategies, and adaptation to life in extreme soils. In: Dion P, Nautiyal CS (eds) Microbiology of extreme soils, 2nd edn. Springer, Germany, pp 15–37
Vicente GA, King GM, Nüsslein K (2007) Comparative bacterial diversity in recent Hawaiian volcanic deposits of different ages. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:60–73
Wang S, Xiao X, Jiang L, Peng X, Zhou H, Meng J, Wang F (2009) Diversity and abundance of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in hydrothermal vent chimneys, Juan de Fuca Ridge. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4216–4220
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DA (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Yeager CM, Northup DE, Grow CC, Barns SM, Kuske CR (2005) Changes in nitrogen-fixing and ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in soil of a mixed conifer forest after wildfire. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:2713–2722
Yeates C, Gillings MR, Davison AD, Altavilla N, Veal DA (1999) Methods for extraction of DNA from soil for PCR amplification. Biol Proced Online 1:40–47
Zeikus JG, Vieille C, Savchenko A (1998) Thermozymes: biotechnology and structure-function relationships. Extremophiles 2:179–183
Zhang R, Cao H, Cui Z, Li S, Fan B (2003) Extraction and purification of soil microbial total DNA. Acta Microbiol Sin 43:276–281
Zhang CL, Ye Q, Huang Z, Li W, Chen J, Song Z, Zhao W, Bagwell C, Inskeep WP, Ross C, Gao L, Wiegel J, Romanek CS, Shock EL, Hedlund BP (2008a) Global occurrence of archaeal amoA genes in terrestrial hot springs. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:6417–6426
Zhang R, Thiyagarajan V, Qian PY (2008b) Evaluation of terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis in contrasting marine environments. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:169–178
Zhang LM, Offre PR, He JZ, Verhamme DT, Nicol GM, Prosser JI (2010) Autotrophic ammonia oxidation by soil thaumarchaea. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:17240–17245
Zhao Y, Zhou Z, Li W, Liu B, Pan Y, Zhao LP (2005) DNA extraction from soil for molecular microbial community analysis. J Agron Environ Sci 24:854–860
Zhou J, Bruns MA, Tiedje JM (1996) DNA recovery from soil of diverse composition. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:316–322
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial Supported by the Science & Technology Supporting plan of the science and technology department of Xinjiang (201232121) and the Natural science foundation of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2012211B48) and the Open Project of the Key Lab of Microorganisms in Xinjiang Specific Environment (XJYS0203-2011-02 and XJYS0203-2011-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, T., Xu, J., Zeng, J. et al. Diversity of prokaryotes associated with soils around coal-fire gas vents in MaNasi county of Xinjiang, China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 23–36 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9782-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9782-3