Abstract
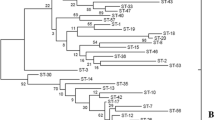
It is hard to accurately identify specific species of the Lactobacillus casei group using phenotypic techniques alone. Some strains of this species group are considered to be probiotic and are widely applied in the food industry. In this study, we compared the use of two phylogenetic markers, the 16S rRNA and dnaK genes, for species discrimination of the members of the L. casei group using sequencing and RFLP. The results showed that L. casei, Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus zeae and Lactobacillus rhamnosus could be clearly distinguished based on the dnaK gene. The average sequence similarity for the dnaK gene (87.8%) among type strains was significantly less than that of the 16S rRNA sequence (99.1%). Therefore, the dnaK gene can be proposed as an additional molecular phylogenetic marker for L. casei that provides higher resolution than 16S rRNA. Species-specific RFLP profiles of the Lactobacillus strains were obtained with the enzyme ApoI. Our data indicate that the phylogenetic relationships between these strains are easily resolved using sequencing of the dnaK gene or RFLP assays.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrne S, Molin G, Stahl S (1989) Plasmids in Lactobacillus strains isolated from meat and meat products. Syst Appl Microbiol 11:320–325
Baken KA, Ezendam J, Gremmer ER, de Klerk A, Pennings JL, Matthee B, Peijnenburg AA, van Loveren H (2006) Evaluation of immunomodulation by Lactobacillus casei Shirota: immune function, autoimmunity and gene expression. Int J Food Microbiol 112:8–18
Blaiotta G, Fusco V, Ercolini D, Aponte M, Pepe O, Villani F (2008) Lactobacillus strain diversity based on partial hsp60 gene sequences and design of PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism assays for species identification and differentiation. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:208–215
Boyd MA, Antonio MAD, Hillier SL (2005) Comparison of API 50 CH strips to whole-chromosomal DNA probes for identification of Lactobacillus species. J Clin Microbiol 43:5309–5311
Bringel F, Castioni A, Olukoya DK, Felis GE, Torriani S, Dellaglio F (2005) Lactobacillus plantarum subsp. argentoratensis subsp. nov., isolated from vegetable matrices. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1629–1634
Charteris WP, Kelly PM, Morelli L, Collins JK (2001) Quality control Lactobacillus strains for use with the API 50CH and API ZYM systems at 37 degrees C. J Basic Microbiol 41:541–551
Chavagnat F, Haueter M, Jimeno J, Casey MG (2002) Comparison of partial tuf gene sequences for the identification of lactobacilli. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217:177–183
Collins MD, Phillips BA, Zanoni P (1989) Deoxyribonucleic acid homology studies of Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus paracasei sp. nov., subsp. paracasei and subsp. tolerans, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus sp. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:105–108
Desai AR, Shah NP, Powell IB (2006) Discrimination of dairy industry isolates of the Lactobacillus casei group. J Dairy Sci 89:3345–3351
Felis GE, Dellaglio F (2007) Taxonomy of Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria. Curr Issues Intest Microbiol 8:44–61
Felis GE, Dellaglio F, Mizzi L, Torriani S (2001) Comparative sequence analysis of a recA gene fragment brings new evidence for a change in the taxonomy of the Lactobacillus casei group. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2113–2117
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (phylogeny inference package), version 3.5c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Gancheva A, Pot B, Vanhonacker K, Hoste B, Kersters K (1999) A polyphasic approach towards the identification of strains belonging to Lactobacillus acidophilus and related species. Syst Appl Microbiol 22:573–585
Gevers D, Huys G, Swings J (2001) Applicability of rep-PCR fingerprinting for identification of Lactobacillus species. FEMS Microbiol Lett 205:31–36
Gogarten JP (1994) Which is the most conserved group of proteins? Homology-orthology, paralogy, xenology, and the fusion of independent. J Mol Evol 39:541–543
Holzapfel WH, Haberer P, Geisen R, Bjorkroth J, Schillinger U (2001) Taxonomy and important features of probiotic microorganisms in food and nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr 73:365S–373S
Huang CC, Lee FL (2009) Development of novel species-specific primers for species identification of the Lactobacillus casei group based on the RAPD fingerprints. J Sci Food Agric 89:1831–1837
Huang CC, Lee FL, Liou JS (2010) Rapid discrimination and classification of the Lactobacillus plantarum group based on a partial dnaK sequence and DNA fingerprinting techniques. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:289–296
Huys G, Vancanneyt M, D’Haene K, Vankerckhoven V, Goossens H, Swings J (2006) Accuracy of species identity of commercial bacterial cultures intended for probiotic or nutritional use. Res Microbiol 157:803–810
Janda JM, Abbott SL (2007) 16S rRNA gene sequencing for bacterial identification in the diagnostic laboratory: pluses, perils, and pitfalls. J Clin Microbiol 45:2761–2764
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Massi M, Vitali B, Federici F, Matteuzzi D, Brigidi P (2004) Identification method based on PCR combined with automated ribotyping for tracking probiotic Lactobacillus strains colonizing the human gut and vagina. J Appl Microbiol 96:777–786
McCartney AL (2002) Application of molecular biological methods for studying probiotics and the gut flora. Br J Nutr 88:7–29
Naser SM, Dawyndt P, Hoste B, Gevers D, Vandemeulebroecke K, Cleenwerck I, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2007) Identification of lactobacilli by pheS and rpoA gene sequence analyses. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2777–2789
Netzer WJ, Hartl FU (1998) Protein folding in the cytosol: chaperonin-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Trends Biochem Sci 23:68–73
Olive DM, Bean P (1999) Principles and applications of methods for DNA-based typing of microbial organisms. J Clin Microbiol 37:1661–1669
Petti CA (2007) Detection and identification of microorganisms by gene amplification and sequencing. Clin Infect Dis 44:1108–1114
Pot B, Hertel C, Ludwig W, Descheemaeker P, Kersters K, Schleifer KH (1993) Identification and classification of Lactobacillus acidophilus, L. gasseri and L. johnsonii strains by SDSPAGE and rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probe hybridization. J Gen Microbiol 139:513–517
Roy D, Ward P, Vincent D (1999) Strain identification of probiotic Lactobacillus casei related isolates with randomly amplified polymorphic DNA and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis methods. Biotechnol Tech 13:843–847
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Salminen S (1996) Functional dairy foods with Lactobacillus strain GG. Nutr Rev 54:99–101
Salminen S, Isolauri E, Salminen E (1996) Clinical uses of probiotics for stabilizing the gut mucosal barrier: successful strains for future challenges. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 70:347–358
Stackebrandt E, Frederiksen W, Garrity GM, Grimont PA, Kampfer P, Maiden MC, Nesme X, Rossello-Mora R, Swings J, Truper HG, Vauterin L, Ward AC, Whitman WB (2002) Report of the ad hoc committee for the re-evaluation of the species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1043–1047
Tannock GW (1999) Identification of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria. Curr Issues Mol Biol 1:53–64
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Verdenelli MC, Ghelfi F, Silvi S, Orpianesi C, Cecchini C, Cresci A (2009) Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus paracasei isolated from human faeces. Eur J Nutr 48:355–363
Vincze T, Posfai J, Roberts RJ (2003) NEBcutter: a program to cleave DNA with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3688–3691
Walter J, Tannock GW, Tilsala-Timisjarvi A, Rodtong S, Loach DM, Munro K, Alatossava T (2000) Detection and identification of gastrointestinal Lactobacillus species by using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and species-specific PCR primers. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:297–303
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. S. K. Chen, C. C. Liao and G. F. Yuan (Food Industry Research and Development Institute, Taiwan, ROC) for their encouragement. This research was supported by Ministry of Economic Affairs, ROC (project no. 99-EC-17-A-R7-0525).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CH., Lee, FL. The dnaK gene as a molecular marker for the classification and discrimination of the Lactobacillus casei group. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 99, 319–327 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9493-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-010-9493-6