Abstract
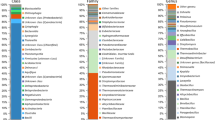
Molecular and culture-based methods were used to investigate the microbial diversity in produced water obtained from the high-temperature Troll oil formation in the North Sea. 16S rRNA gene libraries were generated from total community DNA, using universal archaeal or bacterial oligonucleotide primer sets. Sequence analysis of 88 clones in the bacterial library indicated that they originated from members of Firmicutes (48 sequences), Bacteroidetes (17 sequences), δ-Proteobacteria (15 sequences), Spirochaetes (5 sequences), Thermotogales (2 sequences) and γ-Proteobacteria (1 sequence). Twenty-two sequences in the archaeal library were close relatives to members of the genera Methanococcus (18 sequences), Methanolobus (3 sequences) and Thermococcus (1 sequence). Most of the bacterial sequences shared less than 95% identity with their closest match in GenBank, indicating that the produced water harbours a unique community of novel bacterial species or genera. Members of the thermophilic genera Thermosipho, Thermotoga, Anaerophaga and Thermovirga were isolated. The Troll formations are not injected with sea water. Thus, dramatic changes of the in situ conditions have been avoided, and a common source of continuous contamination from injection water can be excluded. However, the majority of the organisms detected in the gene libraries were most closely related to cultivated organisms with optimum temperatures for growth well below the in situ reservoir temperature (70°C), indicating that produced water from the Troll platform harbours a substantial amount of non-indigenous organisms. This was confirmed by the isolation of a number of mesophilic and moderately thermophilic organisms that were unable to grow at reservoir temperature.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucl Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Ashelford KE, Chuzhanova NA, Fry JC, Jones AJ, Weightman AJ (2005) At least 1 in 20 16s rRNA sequence records currently held in public repositories is estimated to contain substantial anomalies. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:7724–7736
Balch WE, Fox GE, Magrum LJ, Woese CR, Wolfe RS (1979) Methanogens: re-evaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev 43:260–296
Basso O, Lascourreges JF, Jarry M, Magot M (2005) The effect of cleaning and disinfecting the sampling well on the microbial communities of deep subsurface water samples. Environ Microbiol 7:13–21
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL (2005) GenBank. Nucl Acids Res 33:D34–D38
Birkeland NK (2004) The microbial diversity of deep subsurface oil reservoirs. In: Vazquez-Duhalt R, Quintero-Ramirez R (eds) Petroleum biotechnology: developments and perspectives. Elsevier B.V., Amsterdam, pp 385–403
Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA, Miroshnichenko ML, Lebedinsky AV, Chernyh NA, Nazina TN, Ivoilov VS, Belyaev SS, Boulygina ES, Lysov YP, Perov AN, Mirzabekov AD, Hippe H, Stackebrandt E, L’Haridon S, Jeanthon C (2003) Radioisotopic, culture-based, and oligonucleotide microchip analyses of thermophilic microbial communities in a continental high-temperature petroleum reservoir. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:6143–6151
Cashion P, Holderfranklin MA, McCully J, Franklin M (1977) Rapid method for base ratio determination of bacterial DNA. Anal Biochem 81:461–466
Deley J, Cattoir H, Reynaert A (1970) Quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Denger K, Warthmann R, Ludwig W, Schink B (2002) Anaerophaga thermohalophila gen. nov., sp nov., a moderately thermohalophilic, strictly anaerobic fermentative bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:173–178
Donachie SP, Bowman JP, On SLW, Alam M (2005) Arcobacter halophilus sp nov., the first obligate halophile in the genus Arcobacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1271–1277
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Garnova ES, Zhilina TN, Tourova TP, Kostrikina NA, Zavarzin GA (2004) Anaerobic, alkaliphilic, saccharolytic bacterium Alkalibacter saccharofermentans gen. nov., sp nov from a soda lake in the Transbaikal region of Russia. Extremophiles 8:309–316
Grabowski A, Nercessian O, Fayolle F, Blanchet D, Jeanthon C (2005) Microbial diversity in production waters of a low-temperature biodegraded oil reservoir. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 54:427–443
Head IM, Jones DM, Larter SR (2003) Biological activity in the deep subsurface and the origin of heavy oil. Nature 426:344–352
Huber R, Woese CR, Langworthy TA, Fricke H, Stetter KO (1989) Thermosipho-africanus Gen-Nov, represents a new genus of thermophilic eubacteria within the Thermotogales. Syst Appl Microbiol 12:32–37
Huss VAR, Festl H, Schleifer KH (1983) Studies on the Spectrophotometric determination of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Syst Appl Microbiol 4:184–192
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 211–232
Lane DJ (1991) 16 s/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucelic acid techniques in bacterial systematics. Wiley & Sons Ltd., Chichester, UK, pp 115–148
L’Haridon S, Miroshnichenko ML, Hippe H, Fardeau ML, Bonch-Osmolovskaya E, Stackebrandt E, Jeanthon C (2001) Thermosipho geolei sp nov., a thermophilic bacterium isolated from a continental petroleum reservoir in Western Siberia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:1327–1334
L’Haridon S, Reysenbach AL, Glenat P, Prieur D, Jeanthon C (1995) Hot subterranean biosphere in a continental oil-reservoir. Nature 377:223–224
Li H, Yang SZ, Mu BZ, Rong ZF, Zhang J (2006) Molecular analysis of the bacterial community in a continental high-temperature and water-flooded petroleum reservoir. FEMS Microbiol Lett 257:92–98
Lien T, Beeder J (1997) Desulfobacter vibrioformis sp. nov., a sulfate reducer from a water–oil separation system. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:1124–1128
Magot M (2005) Indigenous microbial communities in oil fields. In: Ollivier B, Magot M (eds) Petroleum microbiology. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 21–33
Magot M, Caumette P, Desperrier JM, Matheron R, Dauga C, Grimont F, Carreau L (1992) Desulfovibrio-Longus Sp-Nov, a sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from an oil-producing well. Int J Syst Bacteriol 42:398–403
Magot M, Fardeau M-L, Arnauld O, Lanau C, Ollivier B, Thomas P, Patel BKC (1997) Spirochaeta smaragdinae sp. nov., a new mesophilic strictly anaerobic spirochete from an oil field. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155:185–191
Magot M, Ollivier B, Patel BKC (2000) Microbiology of petroleum reservoirs. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 77:103–116
McInerney MJ, Sublette KL (eds) (1997) Petroleum microbiology: biofouling, souring, and improved oil recovery. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Miroshnichenko ML, Hippe H, Stackebrandt E, Kostrikina NA, Chernyh NA, Jeanthon C, Nazina TN, Belyaev SS, Bonch-Osmolovskaya EA (2001) Isolation and characterization of Thermococcus sibiricus sp nov from a Western Siberia high-temperature oil reservoir. Extremophiles 5:85–91
Nilsen RK, Torsvik T (1996) Methanococcus thermolithotrophicus isolated from North Sea oil field reservoir water. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:728–731
Orphan VJ, Goffredi SK, Delong EF, Boles JR (2003) Geochemical influence on diversity and microbial processes in high temperature oil reservoirs. Geomicrobiol J 20:295–311
Orphan VJ, Taylor LT, Hafenbradl D, Delong EF (2000) Culture-dependent and culture-independent characterization of microbial assemblages associated with high-temperature petroleum reservoirs. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:700–711
Page RDM (1996) Tree view: an application to display phylogenetic trees on personal computers. Comp Appl Biosci 12:357–358
Rainey FA, Dorsch M, Morgan HW, Stackebrandt E (1992) 16S rDNA analysis of Spirochaeta-thermophila—its phylogenetic position and implications for the systematics of the order Spirochaetales. Syst Appl Microbiol 15:197–202
Reysenbach A-L, Pace NR (1995) Reliable amplification of hyperthermophilic archaeal 16S rRNA genes by the polymerase chain reaction. In: Robb FT, Place AR (eds) Archaea: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory Press, New York, pp 101–107
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The Neighbor-Joining method—a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Slobodkin AI, Jeanthon C, L’Haridon S, Nazina T, Miroshnichenko M, Bonch-Osmolovskaya E (1999) Dissimilatory reduction of Fe(III) by thermophilic bacteria and archaea in deep subsurface petroleum reservoirs of Western Siberia. Curr Microbiol 39:99–102
Stetter KO, Huber R, Blochl E, Kurr M, Eden RD, Fielder M, Cash H, Vance I (1993) Hyperthermophilic archaea are thriving in deep North-Sea and Alaskan oil-reservoirs. Nature 365:743–745
Tardy-Jacquenod C, Magot M, Patel BKC, Matheron R, Caumette P (1998) Desulfotomaculum halophilum sp. nov., a halophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from oil production facilities. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:333–338
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882
von Wintzingerode F, Gobel UB, Stackebrandt E (1997) Determination of microbial diversity in environmental samples: pitfalls of PCR-based rRNA analysis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:213–229
Widdel F, Kohring GW, Mayer F (1983) Studies on dissimilatory sulfate-reducing bacteria that decompose fatty-acids.3. Characterization of the filamentous gliding Desulfonema-limicola Gen-Nov Sp-Nov, and Desulfonema-magnum Sp-Nov. Arch Microbiol 134:286–294
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Norwegian Research Council (grant no. 145854/110) to NKB. We are thankful to Malvin Sperre and Morten Teigland (both at Norsk Hydro) for access to samples and to M. Sperre for information about the chemical composition of produced water.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dahle, H., Garshol, F., Madsen, M. et al. Microbial community structure analysis of produced water from a high-temperature North Sea oil-field. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 93, 37–49 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-007-9177-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-007-9177-z