Abstract
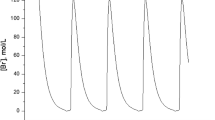
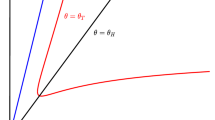
This paper investigates the difference between price and quantity competition in a mixed duopoly game. We describe the behavior of a duopolistic Bertrand competition market with environmental taxes. There are two cases. In the first, the public firm is privatized and in the second, it is not privatized. In case I, private duopoly (postprivatization) where players use different production methods and choose their prices with (bounded rationality and naive). In case II, mixed duopoly (preprivatization) in this case there are two levels for the market including standard objective of the private firm is to maximize profits and including another objective function of the public firm namely “private welfare maximization”. We study numerically the dynamical behaviors of the models. The Nash equilibrium loses stability through a period-doubling bifurcation and the market in the end gets to be disordered. The disordered behavior of the market has been controlled by using feedback control method.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
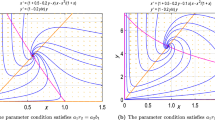
We mention here, the second order condition for the optimal environmental tax in the stage of p–p game \(\frac{\partial \tau ^{ pp }}{\partial d}=\frac{ 8(1+d)^{2}\left( A-1\right) (9d^{2}+29d+23)}{\left( 18d^{2}+47d+31\right) ^{2}}\ge 0\), since \(d^{2}\ge \frac{29d+23}{-\,9}.\)
We mention here, the second order condition for the optimal environmental tax in the stage of q–q game \(\frac{\partial \tau ^{ qq }}{\partial d}=\frac{ 3\left( A-1\right) (d^{2}-14d-11)}{\left( d^{2}+6d-31\right) ^{2}}\ge 0,\) since \(d^{2}\ge 14d+11.\)
References
Ahmed, E., Elsadany, A. A., & Puu, T. (2015). On Bertrand duopoly game with differentiated goods. Applied Mathematics and Computations, 251, 169–179.
Ahmed, E., Hegazi, A. S., & Abd El-Hafez, A. T. (2003). On multiobjective oligopoly. Nonlinear Dynamics, Psychology, and Life Sciences, 7(2), 205–219.
Beladi, H., & Chao, C. C. (2006). Does privatization improve the environment? Economics Letters, 93, 343–347.
Bertrand, J. (1883). Thorie mathmatique de la richesse sociale. Journal des Savants, 48, 499–508.
Bhattacharjee, T., & Pal, R. (2013). Price vs. quantity in duopoly with strategic delegation: Role of network externalitie. Mumbai: Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research. http://www.igidr.ac.in/pdf/publication/WP-2013-010.pdf.
Brcena-Ruiz, J. C., & Sedano, M. (2011). Endogenous timing in a mixed duopoly: Weighted welfare and price competition. The Japanese Economic Review, 62, 485–503.
Carraro, C., & Soubeyaran, A. (1996). Environmental taxation, market share, and profits in oligopoly. In C. Carraro, Y. Katsoulacos, A. Xepapadeas (Eds.), Environmental policy and market structure (pp. 23–44).
Chen, F., Ma, J. H., & Chen, X. Q. (2009). The study of dynamic process of the triopoly games in chinese 3G telecommunication market. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 42, 1542–1551.
Cournot, A. (1838). Rcherches sur les principes mathmatiques de la thorie des richesses. Paris: Dunod.
Dixit, A. K. (1979). A model of duopoly suggesting a theory of entry barriers. Bell Journal Economics, 10, 20–32.
D-Teleszynski, T. (2010). Complex dynamics in a Bertrand duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Central European Journal of Economic Modelling and Econometrics, 2, 95–116.
Elabbasy, E. M., Agiza, H. N., EL-Metwally, H., & Elsadany, A. A. (2007). Bifurcation analysis, chaos and control in the Burgers mapping. International Journal of Nonlinear Science, 4, 171–185.
Elabbasy, E. M., Agiza, H. N., Elsadany, A. A., & EL-Metwally, H. (2007). The dynamics of triopoly game with heterogeneous players. International Journal of Nonlinear Science, 3, 83–90.
Elsadany, A. A. (2012). Competition analysis of a triopoly game with bounded rationality. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 45, 1343–1348.
Elsadany, A. A. (2015). A dynamic Cournot duopoly model with different strategies. Journal of the Egyptian Mathematical Society, 23, 56–61.
Elsadany, A. A., Agiza, H. N., & Elabbasy, E. M. (2013). Complex dynamics and chaos control of heterogeneous quadropoly game. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 219, 11110–11118.
Fanti, L., Gori, L., Mammana, C., & Michetti, E. (2013). The dynamics of a Bertrand duopoly with differentiated products: Synchronization, intermittency and global dynamics. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 52, 73–86.
Ghosh, A., & Mitra, M. (2010). Comparing Bertrand and Cournot in mixed markets. Economic Letters, 109, 72–74.
Hu, R., & Xia, H-s. (2011). Chaotic dynamics in differentiated Bertrand model with heterogeneous players. In Grey systems and intelligent services (GSIS), IEEE international conference (pp. 675–678).
Jury, E. I., & Blanchard, J. (1961). A stability test for linear discrete systems in table form. Proceedings of the Institute of Radio Engineers, 49, 1947–1948.
Kangsik, C. (2012). Cournot and Bertrand competition with asymmetric costs in a mixed duopoly revisited. http://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/37704/. MPRA Paper No. 37704, posted 28. March 2012 12:29 UTC.
Kopel, M. (2014). Price and quantity contracts in a mixed duopoly with a socially concerned firm. Managerial and Decision Economics. https://doi.org/10.1002/mde.2707.
Liu, J., Liu, G., Li, N. & Xu, H. (2014). Dynamics analysis of game and chaotic control in the Chinese fixed broadband telecom market. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, vol. 2014, Article ID 275123, 8 pages.
Ma, J., Zhang, F., & He, Y. (2014). Complexity analysis of a master-slave oligopoly model and chaos control. Abstract and Applied Analysis, vol. 2014, Article ID 970205, 13 pages.
Nakamura, Y. (2014). Social welfare under quantity competition and price competition in a mixed duopoly with network effects: An analysis. Theoretical Economics Letters, 4, 133–138.
Ohori, S. (2013). Price and quantity competition in a mixed duopoly with emission tax. Theoretical Economics Letters, 3, 211–215.
Pu, X., & Ma, J. (2013). Complex dynamics and chaos control in nonlinear four-oligopolist game with different expectations. International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, 23, 1350053. (15 pages) .
Pyrages, K. (1992). Continuous control of chaos by self-controlling feedback. Physics Letters A, 170, 421–4281.
Singh, N., & Vives, X. (1984). Price and quantity competition in a differentiated duopoly. The Rand Journal Economics, 15, 546–554.
Sun, L., & Ma, J. (2015). Study and simulation on discrete dynamics of Bertrand triopoly team-game. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2015, Article ID 960380, 12 pages.
Wang, H., & Ma, J. (2013). Complexity analysis of a Cournot–Bertrand duopoly game model with limited information. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, vol. 2013, Article ID 287371, 6 pages.
Wang, L. F. S., & Wang, J. (2009). Environmental taxes in a differentiated mixed duopoly. Economic Systems, 33, 389–396.
Wang, T., Wang, X., & Wang, M. (2011). Chaotic control of Hénon map with feedback and nonfeedback methods. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 16, 3367–3374.
Wu, F., & Ma, J. (2014). The stability, bifurcation and chaos of a duopoly game in the market of complementary products with mixed bundling pricing. Wseas Transactions on Mathematics, 13, 374–384.
Wu, F., & Ma, J. (2015). The complex dynamics of a multi-product mixed duopoly model with partial privatization and cross-ownerships. Nonlinear Dynamics, 80, 1391–1401.
Xin, B., & Li, Y. (2013). Bifurcation and chaos in a price game of irrigation water in a coastal irrigation district. Discrete Dynamics in Nature and Society, vol. 2013, Article ID 408904, 10 pages.
Yali, L. (2015). Analysis of duopoly output game with different decision-making rules. Management Science and Engineering, 9, 19–24.
Zhang, J., Da, Q., & Wang, Y. (2007). Analysis of nonlinear duopoly game with heterogeneous players. Economic Modelling, 24, 138–148.
Zhang, J., & Wang, Y. (2013). Complex dynamics of Bertrand duopoly games with bounded rationality. International Journal of Social, Education, Economics and Management Engineering, 7, 795–799.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsadany, A.A., Awad, A.M. Dynamics and chaos control of a duopolistic Bertrand competitions under environmental taxes. Ann Oper Res 274, 211–240 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2837-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10479-018-2837-8