Abstract
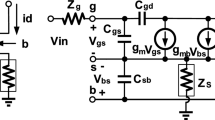
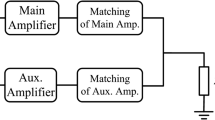
A 24 GHz power amplifier for direct-conversion transceiver using standard 0.18 μm CMOS technology is reported. The three-stage power amplifier comprises two cascaded cascode stages for high power gain, followed by a common-source stage for high power linearity. To increase the saturated output power (Psat) and power-added efficiency (PAE), the output stage adopts a Wilkinson-power-divider- and combiner-based two-way power dividing and combining architecture. The power amplifier consumes 163.8 mW and achieves power gain (S21) of 22.8 dB at 24 GHz. The corresponding 3-dB bandwidth of S21 is 4.2 GHz, from 22.7 to 26.9 GHz. At 24 GHz, the power amplifier achieves Psat of 15.9 dBm and maximum PAE of 14.6 %, an excellent result for a 24 GHz CMOS power amplifier. In addition, the measured output 1-dB compression point (OP1dB) is 7 dBm at 24 GHz. These results demonstrate the proposed power amplifier architecture is very promising for 24 GHz short-range communication system applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gresham, I., Jenkins, A., Egri, R., Eswarappa, C., Kinayman, N., Jain, N., et al. (2004). Ultra-wideband radar sensors for short-range vehicular applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 52(9), 2105–2122.
Jain, V., Sundararaman S., & Heydari, P. (2007). “A CMOS 22–29 GHz receiver front-end for UWB automotive pulse-radars,” IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, pp. 757-760, 2007.
Jain, V., Sundararaman, S., & Heydari, P. (2009). A 22–29-GHz UWB pulse-radar receiver front-end in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 57(8), 1903–1914.
“Technical Requirements for Vehicular Radar Systems,” FCC, Washington, DC, FCC 47 CFR, Sec. 15.515, 2008.
“Commission Decision of 17 Jan. 2005 on the Harmonization of the 24 GHz Range Radio Spectrum Band for the Time-Limited Use by Automotive Short-Range Radar Equipment in the Community,” Official Journal of the European Union, European Radio-communications Office, EC Decision 2005/50/EC, Jan. 2005. (http://www.erodocdb.dk/Docs/doc98/official/pdf/200550EC.PDF).
Kuo, N. C., Kao, J. C., Kuo, C. C., & Wang, H.(2011). “K-band CMOS power amplifier with adaptive bias for enhancement in back-off efficiency,” IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (IMS), 2011, pp. 1–4.
Hung, C. C., Kuo, J. L., Lin, K. Y., & Wang, H.(2010). “A 22.5-dB gain, 20.1-dBm output power K-band power amplifier in 0.18-μm CMOS,” IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 2010, pp. 557–560.
Martineau, B., Knopik, V., Siligaris, A., Gianesello, F., Belot, D. (2010). “A 53-to-68 GHz 18dBm power amplifier with an 8-way combiner in standard 65 nm CMOS,” IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2010, pp. 428–429.
Yu, Y., Baltus, P. G. M., Graauw, Ad., Heijden, Evd., Vaucher, C. S., & Roermund, A. H. Mv. (2010). A 60 GHz phase shifter integrated With LNA and PA in 65 nm CMOS for phased array systems. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 45(9), 1698–1709.
Lin, Y. S., Lee, J. H., Huang, S. L., Wang, C. H., Wang, C. C., & Lu, S. S. (2012). Design and analysis of a 21 ~ 29 GHz ultra-wideband receiver front-end in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques, 60(8), 2590–2604.
Skolnik, M. I. (1980). Introduction to radar systems (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Mahafza, B. R., & Elshebeni, A. Z. (2004). MATLAB simulations for radar system design. New York: CRC Press/Chapman & Hall.
Edwards, M. L., & Sinsky, J. H. (1992). A new criterion for linear 2-port stability using a single geometrically derived parameter. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 40(12), 303–311.
Chiu, H. W., Lu, S. S., & Lin, Y. S. (2005). A 2.17 dB NF, 5 GHz band monolithic CMOS LNA with 10 mW DC power consumption. IEEE Transactions Microwave Theory and Technique, 53(3), 813–824.
Wang, T., Chen, H. C., Chiu, H. W., Lin, Y. S., Huang, G. W., & Lu, S. S. (2006). Micromachined CMOS LNA and VCO by CMOS compatible ICP deep trench technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(2), 580–588.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National Science Council of the R.O.C. under Contracts NSC100- 222-E-260-011-MY3 and NSC100-2221-E-260-006-MY2. The authors are also very grateful for the support from National Chip Implementation Center (CIC), Taiwan, for chip fabrication, and National Nano-Device Laboratory (NDL), Taiwan, for high-frequency measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, YS., Chang, JN. A 24-GHz power amplifier with Psat of 15.9 dBm and PAE of 14.6 % using standard 0.18 μm CMOS technology. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 79, 427–435 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0290-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-014-0290-4