Abstract
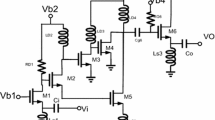
This paper presents a detailed design of a broadband power amplifier (PA) utilizing 0.18-μm CMOS technology, operating in the frequency range of 2–5 GHz. This ultra-wideband (UWB) power amplifier uses a cascode topology with current reuse to enhance gain over the desired frequency band, utilizing an inductive source degenerate design to achieve the best linearity and output power and gain while maintaining a wide bandwidth. The inductive source degenerate adopts bondwire and microstrip line design. The paper includes extensive analysis, simulation results, and measurements to verify the performance of the amplifier and demonstrate its suitability for broadband power amplifier applications. The measured results for the proposed UWB power amplifier show excellent performance, with an impressive third-order input intercept point (IIP3) ranging from 15 to 18.7 dBm over the frequency range of 2–5 GHz. The output third-order intercept point (OIP3) ranges from 33 to 35 dBm. Additionally, the gain flatness is specified as 12.5 ± 1.5 dB. The reverse isolation is greater than or equal to − 40 dBm. The PA has a P1dB output power (OP1dB) of 10.2 dBm at 3 GHz, 9.2 dBm at 4 GHz, and 9.2 dBm at 5 GHz, respectively. The PA has a P1dB power-added efficiency of 30.5% at 3 GHz, 23% at 4 GHz, and 22% at 5 GHz with a 50 Ω load termination. The power dissipation is 33.3 mW at a supply voltage of 1.8 V. In addition, the PA has an excellent small group delay variation of ± 65 ps. The chip area is 1.01 × 1.08 mm2, including the pads. The proposed UWB PA demonstrates exceptional linearity, efficiency, and group delay in the 2–5 GHz frequency band.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Bucolo, A. Buscarino, C. Famoso, L. Fortuna, S. Gagliano, Imperfections in integrated devices allow the emergence of unexpected strange attractors in electronic circuits. IEEE Access. 9, 29573–29583 (2021)
C. Cao, J. Liu, Y. Li, T. Tan, Z. Huang, P. Zhang, X. Li, A power amplifier with bandwidth expansion and linearity enhancement in 130 nm complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor process. Int. J. RF Microwave Comput. Aided Eng. 31(6), e22626 (2021)
M. Cen, S. Song, A high gain, low-power low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband wireless systems. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(10), 3251–3262 (2014)
J.D. Chen, A low-voltage high-linearity ultra-wideband down-conversion mixer in 0.18-μm CMOS technology. Microelectron. J. 42(1), 113–126 (2011)
J.D. Chen, S.H. Wang, A low-power and high-gain ultra-wideband down-conversion active mixer in 0.18-μm SiGe Bi-CMOS technology. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 36(7), 2635–2653 (2017)
J.D. Chen, W.J. Wang, A 1.5∼5 GHz CMOS broadband low-power high-efficiency power amplifier for wireless communications. Integr. VLSI J. 63, 167–173 (2018)
J.D. Chen, M.K. Jian, A 1.5–7 GHz wideband low-voltage low-power switched transconductor up-conversion mixer. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 134, 153681 (2021)
J.D. Chen, Z.X. Chen, A 2.8–10-GHz CMOS current reuse cascaded linearity improving ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 42, 5091–5107 (2023)
S.C. Cripps, RF Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communications, 2nd edn. (Artech Inc., 2004)
J.L. Dawson, T.H. Lee, Feedback Linearization of RF Power Amplifiers (Springer, 2007)
S. Du, X. Zhu, H. Yin, W. Huang, Low-power CMOS power amplifier for 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wideband transmitter. IETE J. Res. 62(1), 113–119 (2016)
W.S. Feng, C.I. Yeh, M.Z. Zhou, 3.1–10.6 GHz UWB low-power CMOS power amplifier. Int. J. Electron. Lett. 1(2), 87–95 (2013)
P.R. Gray, P.J. Hurst, S.H. Lewis, R.G. Meyer, Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits (Wiley, 2024)
W. Hallberg, Analytical Approaches to Load Modulation Power Amplifier Design (Chalmers Tekniska Hogskola (Sweden) Inc., 2019)
S. Kang, B. Choi, B. Kim, Linearity analysis of CMOS for RF application. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 51(3), 972–977 (2003)
T.W. Kim, B. Kim, K. Lee, Highly linear receiver front-end adopting MOSFET transconductance linearization by multiple gated transistors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 39(1), 223–229 (2004)
W.J. Kim, S.P. Stapleton, J.H. Kim, C. Edelman, Digital predistortion linearizes wireless power amplifiers. IEEE Microw. Mag. 6(3), 54–61 (2005)
Y.M. Kim, H. Han, T.W. Kim, A 0.6-V+ 4 dBm IIP3 LC folded cascode CMOS LNA with gm linearization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 60(3), 122–126 (2013)
M.G. Kim, T.Y. Yun, Analysis and design of feedforward linearity-improved mixer using inductive source degeneration. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 62(2), 323–331 (2014)
J. Ko, S. Lee, S. Nam, An S/X-band CMOS power amplifier using a transformer-based reconfigurable output matching network, in 2017 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC) (2017), pp. 344–347
Z. Li, B. Liu, Y. Duan et al., Flat-high-gain design and noise optimization in SiGe low-noise amplifier for S–K band applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40, 2720–2740 (2021)
M. Mansour, A. Zekry, M.K. Ali et al., A reconfigurable class-AB/F power amplifier for 0.1–4.2 GHz multistandard applications. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 40, 1111–1126 (2021)
M.M. Milićević, B.S. Milinković, D.N. Grujić, L.V. Saranovac, Power and conjugately matched high band UWB power amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(10), 3138–3149 (2018)
H. Mosalam, A. Allam, H. Jia, A. Abdelrahman, T. Kaho, R. K. Pokharel, 5.0 to 10.6 GHz 0.18 µm CMOS power amplifier with excellent group delay for UWB applications, in 2015 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium (2015), pp.1–4
H. Mosalam, A. Allam, H. Jia, A.B. Abdel-Rahman, R.K. Pokharel, High efficiency and small group delay variations 0.18-μm CMOS UWB power amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 66(4), 592–596 (2019)
S.A.Z. Murad, R.K. Pokharel, A.I.A. Galal, R. Sapawi, H. Kanaya, K. Yoshida, An excellent gain flatness 3.0–7.0 GHz CMOS PA for UWB applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 20(9), 510–512 (2010)
S.A.Z. Murad, R.K. Pokharel, R. Sapawi, H. Kanaya, K. Yoshida, High efficiency, good linearity, and excellent phase linearity of 3.1–4.8 GHz CMOS UWB PA with a current-reused technique. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 56(3), 1241–1246 (2010)
R. Sapawi, R.K. Pokharel, D.A.A. Mat, H. Kanaya, K. Yoshida, A 3.1–6.0 GHz CMOS UWB power amplifier with good linearity and group delay variation, in Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (2011), pp. 9–12
R. Sapawi, R.K. Pokharel, S.A.Z. Murad et al., Low group delay 3.1–10.6 GHz CMOS power amplifier for UWB applications. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Componen. Lett. 22(1), 41–43 (2011)
R. Sapawi, R.K. Pokharel, D.A.A. Mat, H. Kanaya, K. Yoshida, A 0.9–3.5 GHz high linearity, good efficiency CMOS broadband power amplifier using stagger tuning technique. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 54(12), 2881–2884 (2012)
P. Sivonen, S. Kangasmaa, A. Parssinen, Analysis of packaging effects and optimization in inductively degenerated common-emitter low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 51(4), 1220–1226 (2003)
J.H. Tsai, J.W. Wang, An X-band Half-Watt CMOS power amplifier using interweaved parallel combining transformer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 27(5), 491–493 (2017)
N. Vitee, H. Ramiah, P.-I. Mak, J. Yin, R.P. Martins, A 3.15-mW + 16.0-dBm IIP3 22-dB CG inductively source degenerated Balun-LNA mixer with integrated transformer-based gate inductor and IM2 injection technique. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 28(3), 700–713 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TVLSI.2019.2950961
Z. Wang, Envelope Tracking Power Amplifiers for Wireless Communications (Artech House Inc., 2014)
X. Wang, A. Dinh, D. Teng, A 3–10 GHz ultra wideband receiver LNA in 0.13 μm CMOS. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33, 1669–1687 (2014)
M.S. Yang, S.G. Lee, Linearity improvement technique for the common-source transconductance stage, in IEEE Midwest International Conference on Circuit and System (2003).
M. Yousefi, S.N. Hoseini, S.M. Monfaredi, K., Ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier with tunable bandwidth. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 42, 2557–2572 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan, R.O.C., under Grant MOST 111-2221-E-507-003. National Applied Research Laboratories Taiwan semiconductor research institute (TSRI) for its technical support and measurement. Taiwan.
Funding
All authors declare that: (i) they have not received any support, financial or otherwise, from any organization that may be interested in the submitted work; (ii) have no other relationship or activity that might affect the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise.
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JD., Qian, Jb. A Highly Linear, Low Power, Highly Efficient, CMOS Wideband Power Amplifier for 2–5 GHz Wireless Communications. Circuits Syst Signal Process (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02693-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-024-02693-3