Abstract
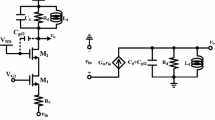
This paper presents a noise figure optimization technique for source-degenerated cascode CMOS LNAs with lossy gate inductors. The optimization technique, based on two-port theory, takes into account second order parasitic components. The effect of inductive source degeneration on LNA noise parameters is discussed. Measured noise figures agree well with the simulations confirming the accuracy of the noise model and allowing us to investigate the contributions of various components to the overall noise figure. A 0.18-μm CMOS LNA with an integrated inductor (Q = 7.5) achieves a noise figure of 1.16 dB and a return loss of 20 dB at 1.4 GHz, drawing 39 mA from a 1.8-V voltage supply, having gain (S 21) of 14.5 dB, input P1dB of −17.5 dBm, and input IP3 of −13 dBm. LNAs with external inductors having quality factor of Q = 170 and Q = 40 achieve noise figures of 0.65 dB and 0.68 dB and a return loss of 20 dB at 1.4 GHz, drawing 37 mA from a 1.8-V voltage supply, having gain (S 21) of 17 dB, input P1dB of −22 dBm, and input IP3 of −14 dBm. The large power consumption of the presented designs was intentionally selected in order to reduce the noise figure, an acceptable trade-off for LNA’s targeted for radio telescope applications, and to assess the impact of the large currents flowing through interconnect metals on the noise figure
















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
In (15), (20), and (21) “l.ch.” denotes “long channel”.
Since (29) and (30) are approximate, in the case when C ex ≈0, the two expressions may not be exactly consistent. In this case (29) should be used.
References
Hall, P. J. (2004). The square kilometre array: An international engineering perspective. Experimental Astronomy, 17, 5–16.
Belostotski, L., & Haslett, J. (2006). Noise figure optimization of inductively degenerated CMOS LNAs with integrated gate inductors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-Part I: Regular Papers, 53, 1409–1422.
Shaeffer, D. K., & Lee, T. H. (1997). A 1.5-V, 1.5-GHz CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 32, 745–759.
Goo, J.-S., Ahn, H.-T., Ladwig, D. J., Yu, Z., Lee, T. H., & Dutton, R. W. (2002). A noise optimization technique for integrated low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 37, 994–1002.
Rothe, H. (1954). The theory of noisy four-poles. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 1, 258–259.
Haus, H. A., Atkinson, W. R., Fonger, W. H., Mcleod, W. W., Branch, G. M., Harris, W. A., Stodola, E. K., Davenport, W. B., Jr., Harrison, S. W., & Talpey, T. E. (1960). Representation of noise in linear twoports, Proceedings of the Institution of Radio Engineers, 48, 66–74.
Hillbrand, H., & Russer, P. H. (1976). An efficient method for computer aided noise analysis of linear amplifier networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, 23, 235–238.
Lee, T. H. (2004). The design of CMOS radio-frequency integrated circuits. New York: Cambridge University Press.
van der Ziel, A. (1986). Noise in solid state devices and circuits. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Boglione, L., Pollard, R. D., & Postoyalko, V. (1997). Analytical behavior of the noise resistance and the noise conductance for a network with parallel and series feedback. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 45, 301–304.
Girlando, G., & Palmisano, G. (1999). Noise figure and impedance matching in RF cascode amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II, 46, 1388–1396.
Ko, P. K. (1989). Advanced MOS Device Physics, vol. 18 of VLSI electronics: Microstructure science (ch. 1, pp. 1–37). Academic Press, Inc.
Zine-El-Abidine, I., & Okoniewski, M. (2007). High quality factor micromachined toroid and solenoid inductors. In M. Okoniewski (Ed.) IEEE Proceedings of European Microwave Conference (pp 1149–1152). Munich (9–12 October 20007).
Scholten, A., Tiemeijer, L., van Langevelde, R., Havens, R., Van Duijnhoven, A., de Kort R., & Klaassen, D. (2004). Compact modelling of noise for RF CMOS circuit design. In IEE Proceedings-Circuits, Devices and Systems (vol. 151, pp. 167–174) (12 April 2004).
Belostotski, L., & Haslett, J. W. (2007). Noise figure optimization of wide-band inductively-degenerated CMOS LNAs. In IEEE Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (pp. 1002–1005). Canada: Montreal (5–8 August 2007).
Yamamoto, K., Heima, T., Furukawa, A., Ono, M., Hashizume, Y., Komurasaki, H., Maeda, S., Sato, H., & Kato, N. (2001). A 2.4-GHz-band 1.8-V operation single-chip Si-CMOS T/R-MMIC front-end with a low insertion loss switch. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 36, 1186–1197.
Krug, F., Russer, P., Beffa, F., Bachtold, W., & Lott, U. (April 2003). A switched-LNA in 0.18 μm CMOS for Bluetooth applications. In Silicon Monolithic Integrated Circuits in RF Systems, (pp. 80–83).
Shouxian, M., Jian-Guo, M., Seng, Y. K., & Anh, D. M. (2005). A modified architecture used for input matching in CMOS low-noise amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 52, 784–788.
Belostotski, L., & Haslett, J. W. (2007). Wide band room temperature 0.35-dB noise figure LNA in 90-nm bulk CMOS. In IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (pp. 221–224). 7–11 January 2007 (Long Beach).
Belostotski, L., & Haslett, J. W. (2007). Sub-0.2 dB noise figure wide-band room-temperature CMOS LNA with non-50 \(\Upomega\) signal-source impedance. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 42, 2492–2502.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by The Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, The Alberta Provincial Government’s iCORE program, The National Research Council’s Dominion Radio Astrophysical Observatory, CMC Microsystems, and TRLabs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belostotski, L., Haslett, J.W. Two-port noise figure optimization of source-degenerated cascode CMOS LNAs. Analog Integr Circ Sig Process 55, 125–137 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-008-9142-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10470-008-9142-4