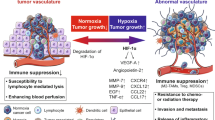
Abstract
TH17 cells play important yet complex roles in cancer development and progression. We previously reported that TH17 cells and IL-17 mediate resistance to anti-VEGF therapy by inducing recruitment of immunosuppressive and proangiogenic myeloid cells to the tumor microenvironment. Here, we demonstrate that IL-22, a key effector cytokine expressed by TH17 cells, directly acts on endothelial cells to promote tumor angiogenesis. IL-22 induces endothelial cell proliferation, survival, and chemotaxis in vitro and neovascularization in an ex vivo mouse choroid explant model. Blockade of IL-22, with a neutralizing antibody, significantly inhibits tumor growth associated with reduced microvascular density. No synergistic effect of IL-22 with VEGF was observed. These results identify IL-22 as a potential therapeutic target for blocking tumor angiogenesis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferrara N, Adamis AP (2016) Ten years of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15(6):385–403
Brauer MJ, Zhuang G, Schmidt M, Yao J, Wu X, Kaminker JS, Jurinka SS, Kolumam G, Chung AS, Jubb A, Modrusan Z, Ozawa T, James CD, Phillips H, Haley B, Tam RN, Clermont AC, Cheng JH, Yang SX, Swain SM, Chen D, Scherer SJ, Koeppen H, Yeh RF, Yue P, Stephan JP, Hegde P, Ferrara N, Singh M, Bais C (2013) Identification and analysis of in vivo VEGF downstream markers link VEGF pathway activity with efficacy of anti-VEGF therapies. Clin Cancer Res 19(13):3681–3692
Landskron G, De la Fuente M, Thuwajit P, Thuwajit C, Hermoso MA (2014) Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/149185
Motz GT, Santoro SP, Wang LP, Garrabrant T, Lastra RR, Hagemann IS, Lal P, Feldman MD, Benencia F, Coukos G (2014) Tumor endothelium FasL establishes a selective immune barrier promoting tolerance in tumors. Nat Med 20(6):607–615
Quail DF, Bowman RL, Akkari L, Quick ML, Schuhmacher AJ, Huse JT, Holland EC, Sutton JC, Joyce JA (2016) The tumor microenvironment underlies acquired resistance to CSF-1R inhibition in gliomas. Science 352(6288):aad3018. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad3018
Negri L, Ferrara N (2018) The prokineticins: neuromodulators and mediators of inflammation and myeloid cell-dependent angiogenesis. Physiol Rev 98(2):1055–1082
Pietras K, Pahler J, Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Functions of paracrine PDGF signaling in the proangiogenic tumor stroma revealed by pharmacological targeting. PLoS Med 5(1):e19
Crawford Y, Kasman I, Yu L, Zhong C, Wu X, Modrusan Z, Kaminker J, Ferrara N (2009) PDGF-C mediates the angiogenic and tumorigenic properties of fibroblasts associated with tumors refractory to anti-VEGF treatment. Cancer Cell 15:21–34
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8(3):235–253
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ (2008) VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat Rev Cancer 8(8):579–591
Chung AS, Wu X, Zhuang G, Ngu H, Kasman I, Zhang J, Vernes JM, Jiang Z, Meng YG, Peale FV, Ouyang W, Ferrara N (2013) An interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Med 19:1114–1123
Coffelt SB, Kersten K, Doornebal CW, Weiden J, Vrijland K, Hau CS, Verstegen NJ, Ciampricotti M, Hawinkels LJ, Jonkers J, de Visser KE (2015) IL-17-producing gammadelta T cells and neutrophils conspire to promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 522(7556):345–348
Saharinen P, Eklund L, Alitalo K (2017) Therapeutic targeting of the angiopoietin-TIE pathway. Nat Rev Drug Discov 16(9):635–661
Liang W, Ferrara N (2016) The complex role of neutrophils in tumor angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Immunol Res 4(2):83–91. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066
Fridman WH, Pages F, Sautes-Fridman C, Galon J (2012) The immune contexture in human tumours: impact on clinical outcome. Nat Rev Cancer 12(4):298–306
Basu R, Hatton RD, Weaver CT (2013) The Th17 family: flexibility follows function. Immunol Rev 252(1):89–103
Su X, Ye J, Hsueh EC, Zhang Y, Hoft DF, Peng G (2010) Tumor microenvironments direct the recruitment and expansion of human Th17 cells. J Immunol 184(3):1630–1641
Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J, Ouyang W (2007) Interleukin-22, a T(H)17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature 445(7128):648–651
Rutz S, Eidenschenk C, Ouyang W (2013) IL-22, not simply a Th17 cytokine. Immunol Rev 252(1):116–132
Wu T, Cui L, Liang Z, Liu C, Liu Y, Li J (2013) Elevated serum IL-22 levels correlate with chemoresistant condition of colorectal cancer. Clin Immunol 147(1):38–39
Kirchberger S, Royston DJ, Boulard O, Thornton E, Franchini F, Szabady RL, Harrison O, Powrie F (2013) Innate lymphoid cells sustain colon cancer through production of interleukin-22 in a mouse model. J Exp Med 210(5):917–931
Sabat R, Ouyang W, Wolk K (2014) Therapeutic opportunities of the IL-22-IL-22R1 system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 13(1):21–38
Nowak-Sliwinska P, Alitalo K, Allen E, Anisimov A, Aplin AC, Auerbach R, Augustin HG, Bates DO, van Beijnum JR, Bender RHF, Bergers G, Bikfalvi A, Bischoff J, Bock BC, Brooks PC, Bussolino F, Cakir B, Carmeliet P, Castranova D, Cimpean AM, Cleaver O, Coukos G, Davis GE, De Palma M, Dimberg A, Dings RPM, Djonov V, Dudley AC, Dufton NP, Fendt SM, Ferrara N, Fruttiger M, Fukumura D, Ghesquiere B, Gong Y, Griffin RJ, Harris AL, Hughes CCW, Hultgren NW, Iruela-Arispe ML, Irving M, Jain RK, Kalluri R, Kalucka J, Kerbel RS, Kitajewski J, Klaassen I, Kleinmann HK, Koolwijk P, Kuczynski E, Kwak BR, Marien K, Melero-Martin JM, Munn LL, Nicosia RF, Noel A, Nurro J, Olsson AK, Petrova TV, Pietras K, Pili R, Pollard JW, Post MJ, Quax PHA, Rabinovich GA, Raica M, Randi AM, Ribatti D, Ruegg C, Schlingemann RO, Schulte-Merker S, Smith LEH, Song JW, Stacker SA, Stalin J, Stratman AN, Van de Velde VM, van Hinsbergh VWM, Vermeulen PB, Waltenberger J, Weinstein BM, Xin H, Yetkin-Arik B, Yla-Herttuala S, Yoder MC, Griffioen AW (2018) Consensus guidelines for the use and interpretation of angiogenesis assays. Angiogenesis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9613-x
Xin H, Zhong C, Nudleman E, Ferrara N (2016) Evidence for pro-angiogenic functions of VEGF-Ax. Cell 167(1):275–284 e276
Shao Z, Friedlander M, Hurst CG, Cui Z, Pei DT, Evans LP, Juan AM, Tahiri H, Duhamel F, Chen J, Sapieha P, Chemtob S, Joyal JS, Smith LE (2013) Choroid sprouting assay: an ex vivo model of microvascular angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69552
Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C, Baldwin ME, Schanz S, Fuh G, Gerber HP, Ferrara N (2007) Tumor refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b + Gr1 + myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol 25(8):911–920
Tan AH, Lam KP (2010) Pharmacologic inhibition of MEK-ERK signaling enhances Th17 differentiation. J Immunol 184(4):1849–1857
Dumoutier L, Van Roost E, Colau D, Renauld JC (2000) Human interleukin-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor: molecular cloning and functional characterization as an hepatocyte-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(18):10144–10149
He X, Li H, Chen Y, Chen A, Shan K, Chen J, Zhao H, Zhang X, Cai T (2016) The Effects of IL-22 on the Inflammatory Mediator Production, Proliferation, and Barrier Function of HUVECs. Inflammation 39(3):1099–1107
Wu Z, Hu Z, Cai X, Ren W, Dai F, Liu H, Chang J, Li B (2017) Interleukin 22 attenuated angiotensin II induced acute lung injury through inhibiting the apoptosis of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep 7(1):2210
Shang WQ, Yu JJ, Zhu L, Zhou WJ, Chang KK, Wang Q, Li MQ (2015) Blocking IL-22, a potential treatment strategy for adenomyosis by inhibiting crosstalk between vascular endothelial and endometrial stromal cells. Am J Transl Res 7(10):1782–1797
Lejeune D, Dumoutier L, Constantinescu S, Kruijer W, Schuringa JJ, Renauld JC (2002) Interleukin-22 (IL-22) activates the JAK/STAT, ERK, JNK, and p38 MAP kinase pathways in a rat hepatoma cell line. Pathways that are shared with and distinct from IL-10. J Biol Chem 277(37):33676–33682
Wolk K, Kunz S, Witte E, Friedrich M, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2004) IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immunity 21(2):241–254
Kohler T, Reizis B, Johnson RS, Weighardt H, Forster I (2012) Influence of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha on dendritic cell differentiation and migration. Eur J Immunol 42(5):1226–1236
Brembilla NC, Dufour AM, Alvarez M, Hugues S, Montanari E, Truchetet ME, Lonati P, Fontao L, Gabrielli A, Vettori S, Valentini G, Boehncke WH, Meroni P, Chizzolini C (2016) IL-22 capacitates dermal fibroblast responses to TNF in scleroderma. Ann Rheum Dis 75(9):1697–1705
Bendell JC, Hochster H, Hart LL, Firdaus I, Mace JR, McFarlane JJ, Kozloff M, Catenacci D, Hsu JJ, Hack SP, Shames DS, Phan SC, Koeppen H, Cohn AL (2017) A phase II randomized trial (GO27827) of first-line FOLFOX plus bevacizumab with or without the met inhibitor onartuzumab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncologist 22(3):264–271
Spigel DR, Edelman MJ, O’Byrne K, Paz-Ares L, Mocci S, Phan S, Shames DS, Smith D, Yu W, Paton VE, Mok T (2016) Results from the phase III randomized trial of onartuzumab plus erlotinib versus erlotinib in previously treated stage IIIB or IV non-small-cell lung cancer: METLung. J Clin Oncol 31(32):4105–4114
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(4):273–286
Hlatky L, Hahnfeldt P, Folkman J (2002) Clinical application of antiangiogenic therapy: microvessel density, what it does and doesn’t tell us. J Natl Cancer Inst 94(12):883–893
Teicher BA, Dupuis N, Kusomoto T (1994) Antiangiogenic agents can increase tumor oxygenation and response to radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol Investig 2(6):269–276
Teicher BA, Holden SA, Ara G, Dupuis NP, Liu F, Yuan J, Ikebe M, Kakeji Y (1995) Influence of an anti-angiogenic treatment on 9L gliosarcoma: oxygenation and response to cytotoxic therapy. Int J Cancer 61(5):732–737
Jain RK (2001) Normalizing tumor vasculature with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination therapy. Nat Med 7(9):987–989
Jacobs VL, Valdes PA, Hickey WF, De Leo JA (2011) Current review of in vivo GBM rodent models: emphasis on the CNS-1 tumour model. ASN Neuro 3(3):e00063. https://doi.org/10.1042/AN20110014
Acknowledgements
We thank Genentech. Inc. for generously providing us with the anti-VEGF and anti-IL-22 antibodies for neutralization experiments. We thank Dr. Wenjun Ouyang (Amgen, Inc.) for helpful discussion and advice. We also thank Dr. Karen Messer and Yuqi Qin from the department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics at Moores UCSD Cancer Center for help and advice with statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10456_2018_9658_MOESM1_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Fig. 1 Expression of IL-22 by EL4 cells. EL4 cells were treated with 1 ng/mL of TGFβ and 20 ng/mL IL-6 under normoxia and hypoxia (1% O2). IL-22 protein levels in the EL4 cell conditioned medium were determined by ELISA. Error bars indicate standard deviation, n = 3–7 replicates from 3 independent experiments. n.s. not significant, *p < 0.05. Supplementary material 1 (PPTX 587 KB)
10456_2018_9658_MOESM2_ESM.pptx
Supplementary Fig. 2 Anti-IL-22 does not Inhibit EL4 (a) or GL261 (b) cell growth in vitro. Cell viability was assessed by the Alamar blue assay and fluorescence readings at 590 nm (excited at 530 nm) were used as readouts. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Data from three experiments were pooled for a total number of 5–8 replicates per experimental condition. n.s. not significant. Supplementary material 2 (PPTX 1274 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Protopsaltis, N.J., Liang, W., Nudleman, E. et al. Interleukin-22 promotes tumor angiogenesis. Angiogenesis 22, 311–323 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9658-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-018-9658-x