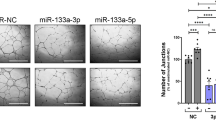
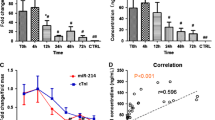
Abstract
Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by arteriovenous malformations and hemorrhages. This vascular disease results mainly from mutations in 2 genes involved in the TGF-β pathway (ENG and ALK1) that are exclusively expressed by endothelial cells. The present study identified miR-27a and miR-205 as two circulating miRNAs differentially expressed in HHT patients. The plasma levels of miR-27a are elevated while those of miR-205 are reduced in both HHT1 and HHT2 patients compared to healthy controls. The role of miR-205 in endothelial cells was further investigated. Our data indicates that miR-205 expression displaces the TGF-β balance towards the anti-angiogenic side by targeting Smad1 and Smad4. In line, overexpression of miR-205 in endothelial cells reduces proliferation, migration and tube formation while its inhibition shows opposite effects. This study not only suggests that detection of circulating miRNA (miR-27a and miR-205) could help for the screening of HHT patients but also provides a functional link between the deregulated expression of miR-205 and the HHT phenotype.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonald J, Bayrak-Toydemir P, Pyeritz RE (2011) Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: an overview of diagnosis, management, and pathogenesis. Genet Med 13(7):607–616. doi:10.1097/GIM.0b013e3182136d32
Mahmoud M, Upton PD, Arthur HM (2011) Angiogenesis regulation by TGFbeta signalling: clues from an inherited vascular disease. Biochem Soc Trans 39(6):1659–1666. doi:10.1042/BST20110664
Wu MY, Hill CS (2009) Tgf-beta superfamily signaling in embryonic development and homeostasis. Dev Cell 16(3):329–343. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2009.02.012
Pardali E, Goumans MJ, ten Dijke P (2010) Signaling by members of the TGF-beta family in vascular morphogenesis and disease. Trends Cell Biol 20(9):556–567. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2010.06.006
Goumans MJ, Valdimarsdottir G, Itoh S, Rosendahl A, Sideras P, ten Dijke P (2002) Balancing the activation state of the endothelium via two distinct TGF-beta type I receptors. EMBO J 21(7):1743–1753. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.7.1743
Bartel DP (2009) MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 136(2):215–233. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.002
Yang WJ, Yang DD, Na S, Sandusky GE, Zhang Q, Zhao G (2005) Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J Biol Chem 280(10):9330–9335
Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C, Pober JS, Sessa WC (2007) Dicer dependent microRNAs regulate gene expression and functions in human endothelial cells. Circ Res 100(8):1164–1173
Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2007) Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res 101(1):59–68
Wang S, Olson EN (2009) AngiomiRs-key regulators of angiogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 19(3):205–211. doi:10.1016/j.gde.2009.04.002
Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Dimmeler S (2008) Targeting microRNA expression to regulate angiogenesis. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29(1):12–15
Zhou Q, Gallagher R, Ufret-Vincenty R, Li X, Olson EN, Wang S (2011) Regulation of angiogenesis and choroidal neovascularization by members of microRNA-23 ~ 27 ~ 24 clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(20):8287–8292. doi:10.1073/pnas.1105254108
Lebrin F, Goumans MJ, Jonker L, Carvalho RL, Valdimarsdottir G, Thorikay M, Mummery C, Arthur HM, ten Dijke P (2004) Endoglin promotes endothelial cell proliferation and TGF-beta/ALK1 signal transduction. EMBO J 23(20):4018–4028. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600386
Blanco FJ, Santibanez JF, Guerrero-Esteo M, Langa C, Vary CP, Bernabeu C (2005) Interaction and functional interplay between endoglin and ALK-1, two components of the endothelial transforming growth factor-beta receptor complex. J Cell Physiol 204(2):574–584. doi:10.1002/jcp.20311
Korchynskyi O, ten Dijke P (2002) Identification and functional characterization of distinct critically important bone morphogenetic protein-specific response elements in the Id1 promoter. J Biol Chem 277(7):4883–4891. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111023200
Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H, Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm C, Röxe T, Müller-Ardogan M, Bonauer A, Zeiher A, Dimmeler S (2010) Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ Res 107(5):677–684. doi:10.1161/circresaha.109.215566
Mitchell P, Parkin R, Kroh E, Fritz B, Wyman S, Pogosova-Agadjanyan E, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant K, Allen A, Lin D, Urban N, Drescher C, Knudsen B, Stirewalt D, Gentleman R, Vessella R, Nelson P, Martin D, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(30):10513–10518. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804549105
Rong H, Liu T, Yang K, Yang H, Wu D, Liao C, Hong F, Yang H, Wan F, Ye X, Xu D, Zhang X, Chao C, Shen Q (2011) MicroRNA-134 plasma levels before and after treatment for bipolar mania. J Psychiatr Res 45(1):92–95. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.04.028
Wang K, Zhang S, Marzolf B, Troisch P, Brightman A, Hu Z, Hood L, Galas D (2009) Circulating microRNAs, potential biomarkers for drug-induced liver injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(11):4402–4407. doi:10.1073/pnas.0813371106
Sadick H, Naim R, Gossler U, Hormann K, Riedel F (2005) Angiogenesis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia: vEGF165 plasma concentration in correlation to the VEGF expression and microvessel density. Int J Mol Med 15(1):15–19
Fernandez LA, Garrido-Martin EM, Sanz-Rodriguez F, Ramirez JR, Morales-Angulo C, Zarrabeitia R, Perez-Molino A, Bernabeu C, Botella LM (2007) Therapeutic action of tranexamic acid in hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): regulation of ALK-1/endoglin pathway in endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 97(2):254–262
Urbich C, Kaluza D, Fromel T, Knau A, Bennewitz K, Boon RA, Bonauer A, Doebele C, Boeckel JN, Hergenreider E, Zeiher AM, Kroll J, Fleming I, Dimmeler S (2012) MicroRNA-27a/b controls endothelial cell repulsion and angiogenesis by targeting semaphorin 6A. Blood 119(6):1607–1616. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-08-373886
Ojeda-Fernandez L, Barrios L, Rodriguez-Barbero A, Recio-Poveda L, Bernabeu C, Botella LM (2010) Reduced plasma levels of Ang-2 and sEng as novel biomarkers in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT). Clin Chim Acta 411(7–8):494–499. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2009.12.023
Martinez M, Andriantsitohaina R (2011) Microparticles in angiogenesis: therapeutic potential. Circ Res 109(1):110–119. doi:10.1161/circresaha.110.233049
van den Boorn J, Daßler J, Coch C, Schlee M, Hartmann G (2012) Exosomes as nucleic acid nanocarriers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2012.06.011
Halkein J, Tabruyn SP, Ricke-Hoch M, Haghikia A, Nguyen NQ, Scherr M, Castermans K, Malvaux L, Lambert V, Thiry M, Sliwa K, Noel A, Martial JA, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Struman I (2013) MicroRNA-146a is a therapeutic target and biomarker for peripartum cardiomyopathy. J Clin Investig 123(5):2143–2154. doi:10.1172/JCI64365
Abdalla SA, Letarte M (2006) Hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia: current views on genetics and mechanisms of disease. J Med Genet 43(2):97–110. doi:10.1136/jmg.2005.030833
Barbara NP, Wrana JL, Letarte M (1999) Endoglin is an accessory protein that interacts with the signaling receptor complex of multiple members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. J Biol Chem 274(2):584–594
Derynck R, Zhang YE (2003) Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signalling. Nature 425(6958):577–584. doi:10.1038/nature02006
Pece-Barbara N, Vera S, Kathirkamathamby K, Liebner S, Di Guglielmo GM, Dejana E, Wrana JL, Letarte M (2005) Endoglin null endothelial cells proliferate faster and are more responsive to transforming growth factor beta1 with higher affinity receptors and an activated Alk1 pathway. J Biol Chem 280(30):27800–27808. doi:10.1074/jbc.M503471200
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Bert AG, Goodall GJ (2008) MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Cycle 7(20):3112–3118
Wu H, Zhu S, Mo YY (2009) Suppression of cell growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res 19(4):439–448. doi:10.1038/cr.2009.18
Albinana V, Bernabeu-Herrero ME, Zarrabeitia R, Bernabeu C, Botella LM (2010) Estrogen therapy for hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT): effects of raloxifene, on endoglin and ALK1 expression in endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 103(3):525–534. doi:10.1160/TH09-07-0425
Tabruyn SP, Memet S, Ave P, Verhaeghe C, Mayo KH, Struman I, Martial JA, Griffioen AW (2009) NF-kappaB activation in endothelial cells is critical for the activity of angiostatic agents. Mol Cancer Ther 8(9):2645–2654. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-09-0383
Sabatel C, Cornet AM, Tabruyn SP, Malvaux L, Castermans K, Martial JA, Struman I (2010) Sprouty1, a new target of the angiostatic agent 16 K prolactin, negatively regulates angiogenesis. Mol Cancer 9:231. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-9-231
Sabatel C, Malvaux L, Bovy N, Deroanne C, Lambert V, Gonzalez ML, Colige A, Rakic JM, Noel A, Martial JA, Struman I (2011) MicroRNA-21 exhibits antiangiogenic function by targeting RhoB expression in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 6(2):e16979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0016979
Dennler S, Itoh S, Vivien D, ten Dijke P, Huet S, Gauthier JM (1998) Direct binding of Smad3 and Smad4 to critical TGF beta-inducible elements in the promoter of human plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 gene. EMBO J 17(11):3091–3100. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.11.3091
Acknowledgments
We thank Michelle Lion, Jean-Yves Carabin and Olivier Nivelles for technical assistance. This study was supported by the University of Liège (Fonds Speciaux), le centre anti-cancéreux (CAC ULg), the FRIA (Fonds pour la Recherche Industrielle et Agricole, Belgium), the FNRS (Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique, Belgium), the Neoangio program #616476 of the “Service Public de Wallonie”, la “fédération belge contre le cancer”. This work was supported by the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovacion: Grants SAF2008–01218, SAF2011-23475, SAF2007–61827, and SAF2010–19222, and Fundación Ramón Areces of Spain (Rare and Emergent Diseases). CIBERER is an initiative of the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII) of Spain. L Ojeda-Fernandez is recipient of a CIBERER contract.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that thy have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabruyn, S.P., Hansen, S., Ojeda-Fernández, ML. et al. MiR-205 is downregulated in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia and impairs TGF-beta signaling pathways in endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 16, 877–887 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9362-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-013-9362-9