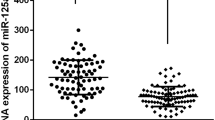
Abstract
Circulating microRNAs (miRNAs) in patient body fluids have recently been considered to hold the potential of being novel disease biomarkers and drug targets. We aimed to investigate the correlation between the levels of circulating miR-214 and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the pathogenesis of coronary heart disease patients to further explore the mechanism involved in the vasculogenesis. Three different cohorts, including 13 acute myocardial infarction patients, 176 angina pectoris patients, and 127 control subjects, were enrolled to investigate the expression levels of circulating miR-214 in patients with myocardial ischemia and also the relationship between plasma miR-214 and severity of coronary stenosis. Plasma miR-214 levels of participants were examined by real-time quantitative PCR. Simultaneously, plasma cardiac troponin I concentrations were measured by ELISA assays. We further detected the correlation of miR-214 and VEGF by molecular and animal assays. MiR-214 was enriched in not only diseased endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) but also the plasma of coronary artery disease (CAD) patients. Besides, we found out miR-214 was able to suppress VEGF expression and EPC activities. Reporter assays confirmed the direct binding and repression of miR-214 to the 39-UTR of VEGF mRNA. Knockdown of miR-214 not only restored VEGF levels and angiogenic activities of diseased EPCs in vitro, but also further promoted blood flow recovery in ischemic limbs of mice. Circulating miR-214 may be a new biomarker for CAD and as a potential diagnostic tool. And increased miR-214 level may be used to predict the presence and severity of coronary lesions in CAD patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang HW, Huang TS, Lo HH, Huang PH, Lin CC, Chang SJ, Liao KH, Tsai CH, Chan CH, Tsai CF, Cheng YC, Chiu YL, Tsai TN, Cheng CC, Cheng SM (2014) Deficiency of the microRNA-31-microRNA-720 pathway in the plasma and endothelial progenitor cells from patients with coronary artery disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 34(4):857–869
Bollati V, Angelici L, Rizzo G, Pergoli L, Rota F, Hoxha M, Nordio F, Bonzini M, Tarantini L, Cantone L, Pesatori AC, Apostoli P, Baccarelli AA, Bertazzi PA (2014) Microvesicle-associated microRNA expression is altered upon particulate matter exposure in healthy workers and in A549 cells. J Appl Toxicol. doi:10.1002/jat.2987. [Epub ahead of print]
Xiong XD, Cho M, Cai XP, Cheng J, Jing X, Cen JM, Liu X, Yang XL, Suh Y (2014) A common variant in pre-miR-146 is associated with coronary artery disease risk and its mature miRNA expression. Mutat Res, Fundam Mol Mech Mutagen 761:15–20
Slagsvold KH, Rognmo O, Høydal M, Wisløff U, Wahba A (2014) Remote ischemic preconditioning preserves mitochondrial function and influences myocardial microRNA expression in atrial myocardium during coronary bypass surgery. Circ Res 114(5):851–859. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.302751. Epub 2013 Dec 26
Stratz C, Nührenberg T, Fiebich BL, Amann M, Kumar A, Binder H, Hoffmann I, Valina C, Hochholzer W, Trenk D, Neumann FJ (2014) Controlled type II diabetes mellitus has no major influence on platelet micro-RNA expression. Results from micro-array profiling in a cohort of 60 patients. Thromb Haemost 111(5):902–911. doi:10.1160/TH13-06-0476. Epub 2013 Dec 19
D’Alessandra Y, Carena MC, Spazzafumo L, Martinelli F, Bassetti B, Devanna P, Rubino M, Marenzi G, Colombo GI, Achilli F, Maggiolini S, Capogrossi MC, Pompilio G (2013) Diagnostic potential of plasmatic microRNA signatures in stable and unstable angina. PLoS ONE 8(11):e80345. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0080345 eCollection 2013
Kula D, Jadczyk T, Krajewska M, Kowalówka A, Dworowy S, Hrycek E, Włudarczyk W, Parma Z, Tendera M, Wojakowski W (2013) Circulating microRNAs (miR-423-5p, miR-208a and miR-1) in acute myocardial infarction and stable coronary heart disease. Minerva Cardioangiol 61(6):627–637
Vickers KC, Moore KJ (2013) Small RNA overcomes the challenges of therapeutic targeting of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein. Circ Res 113(11):1189–1191
Sun X, He S, Wara AK, Icli B, Shvartz E, Tesmenitsky Y, Belkin N, Li D, Blackwell TS, Sukhova GK, Croce K, Feinberg MW (2014) Systemic delivery of microRNA-181b inhibits nuclear factor-κB activation, vascular inflammation, and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circ Res 114(1):32–40
Wang F, Long G, Zhao C, Li H, Chaugai S, Wang Y, Chen C, Wang DW (2013) Plasma microRNA-133a is a new marker for both acute myocardial infarction and underlying coronary artery stenosis. J Transl Med 23(11):222
Lu HQ, Liang C, He ZQ, Fan M, Wu ZG (2013) Circulating miR-214 is associated with the severity of coronary artery disease. J Geriatr Cardiol 10(1):34–38. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-5411.2013.01.007
Jansen F, Yang X, Hoelscher M, Cattelan A, Schmitz T, Proebsting S, Wenzel D, Vosen S, Franklin BS, Fleischmann BK, Nickenig G, Werner N (2013) Endothelial microparticle-mediated transfer of MicroRNA-126 promotes vascular endothelial cell repair via SPRED1 and is abrogated in glucose-damaged endothelial microparticles. Circulation 128(18):2026–2038
Tousoulis D, Papageorgiou N, Androulakis E, Siasos G, Latsios G, Tentolouris K, Stefanadis C (2013) Diabetes mellitus-associated vascular impairment: novel circulating biomarkers and therapeutic approaches. J Am Coll Cardiol 62(8):667–676. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2013.03.089
Liao XB, Zhang ZY, Yuan K, Liu Y, Feng X, Cui RR, Hu YR, Yuan ZS, Gu L, Li SJ, Mao DA, Lu Q, Zhou XM, de Jesus Perez VA, Yuan LQ (2013) MiR-214 modulates osteogenic differentiation of vascular smooth muscle cells. Endocrinology 154(9):3344–3352. doi:10.1210/en.2012-2236. Epub 2013 Jun 24
Danowski N, Manthey I, Jakob HG, Siffert W, Peters J, Frey UH (2013) Decreased expression of miR-214 but not of miR-1 is associated with signs of heart failure in patients undergoing coronary bypass surgery. Cardiology 125(2):125–130. doi:10.1159/000348563. Epub 2013 May 24
Coleman CB, Lightell DJ Jr, Moss SC, Bates M, Parrino PE, Woods TC (2013) Elevation of miR-221 and -222 in the internal mammary arteries of diabetic subjects and normalization with metformin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 374(1-2):125–129. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2013.04.019. Epub 2013 May 3
Huang F, Li ML, Fang ZF, Hu XQ, Liu QM, Liu ZJ, Tang L, Zhao YS, Zhou SH (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-1 improves the efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after myocardial infarction. Cardiology 125(1):18–30. doi:10.1159/000347081. Epub 2013 Apr 20
Wagner J, Riwanto M, Besler C, Knau A, Fichtlscherer S, Röxe T, Zeiher AM, Landmesser U, Dimmeler S (2013) Characterization of levels and cellular transfer of circulating lipoprotein-bound microRNAs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(6):1392–1400
Tomé-Carneiro J, Larrosa M, Yáñez-Gascón MJ, Dávalos A, Gil-Zamorano J, Gonzálvez M, García-Almagro FJ, Ruiz Ros JA, Tomás-Barberán FA, Espín JC, García-Conesa MT (2013) One-year supplementation with a grape extract containing resveratrol modulates inflammatory-related microRNAs and cytokines expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 2 diabetes and hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. Pharmacol Res 72:69–82. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2013.03.011. Epub 2013 Apr 1
Wang J, Yan CH, Li Y, Xu K, Tian XX, Peng CF, Tao J, Sun MY, Han YL (2013) MicroRNA-31 controls phenotypic modulation of human vascular smooth muscle cells by regulating its target gene cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes. Exp Cell Res 319(8):1165–1175. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.03.010. Epub 2013 Mar 19
Hutcheson R, Terry R, Chaplin J, Smith E, Musiyenko A, Russell JC, Lincoln T, Rocic P (2013) MicroRNA-145 restores contractile vascular smooth muscle phenotype and coronary collateral growth in the metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33(4):727–736
Zhang X, Mao H, Chen JY, Wen S, Li D, Ye M, Lv Z (2013) Increased expression of microRNA-221 inhibits PAK1 in endothelial progenitor cells and impairs its function via c-Raf/MEK/ERK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 431(3):404–408. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.157. Epub 2013 Jan 16
Balderman JA, Lee HY, Mahoney CE, DE Handy, White K, Annis S, Lebeche D, Hajjar RJ, Loscalzo J, Leopold JA (2012) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 decreases microRNA-30b and microRNA-30c to promote vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. J Am Heart Assoc 1(6):e003905. doi:10.1161/JAHA.112.003905. Epub 2012 Dec 19
Kin K, Miyagawa S, Fukushima S, Shirakawa Y, Torikai K, Shimamura K, Daimon T, Kawahara Y, Kuratani T, Sawa Y (2012) Tissue- and plasma-specific microRNA signatures for atherosclerotic abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Am Heart Assoc 1(5):e000745
Zhu J, Chen T, Yang L, Li Z, Wong MM, Zheng X, Pan X, Zhang L, Yan H (2012) Regulation of microRNA-155 in atherosclerotic inflammatory responses by targeting MAP3K10. PLoS ONE 7(11):e46551
Barjaktarovic Z, Anastasov N, Azimzadeh O, Sriharshan A, Sarioglu H, Ueffing M, Tammio H, Hakanen A, Leszczynski D, Atkinson MJ, Tapio S (2013) Integrative proteomic and microRNA analysis of primary human coronary artery endothelial cells exposed to low-dose gamma radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 52(1):87–98. doi:10.1007/s00411-012-0439-4. Epub 2012 Nov 9
Greliche N, Zeller T, Wild PS, Rotival M, Schillert A, Ziegler A, Deloukas P, Erdmann J, Hengstenberg C, Ouwehand WH, Samani NJ, Schunkert H, Munzel T, Lackner KJ, Cambien F, Goodall AH, Tiret L, Blankenberg S, Trégouët DA, Cardiogenics Consortium (2012) Comprehensive exploration of the effects of miRNA SNPs on monocyte gene expression. PLoS ONE 7(9):e45863
Sun X, Zhang M, Sanagawa A, Mori C, Ito S, Iwaki S, Satoh H, Fujii S (2012) Circulating microRNA-126 in patients with coronary artery disease: correlation with LDL cholesterol. Thromb J. 10(1):16. doi:10.1186/1477-9560-10-16
Cardin S, Guasch E, Luo X, Naud P, Le Quang K, Shi Y, Tardif JC, Comtois P, Nattel S (2012) Role for microRNA-21 in atrial profibrillatory fibrotic remodeling associated with experimental postinfarction heart failure. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 5(5):1027–1035. doi:10.1161/CIRCEP.112.973214. Epub 2012 Aug 26
Pan Z, Sun X, Shan H, Wang N, Wang J, Ren J, Feng S, Xie L, Lu C, Yuan Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Lu Y, Yang B (2012) MicroRNA-101 inhibited postinfarct cardiac fibrosis and improved left ventricular compliance via the FBJ osteosarcoma oncogene/transforming growth factor-β1 pathway. Circulation 126(7):840–850. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.112.094524. Epub 2012 Jul 18
Gao W, He HW, Wang ZM, Zhao H, Lian XQ, Wang YS, Zhu J, Yan JJ, Zhang DG, Yang ZJ, Wang LS (2012) Plasma levels of lipometabolism-related miR-122 and miR-370 are increased in patients with hyperlipidemia and associated with coronary artery disease. Lipids Health Dis 15(11):55. doi:10.1186/1476-511X-11-55
Hulsmans M, Sinnaeve P, Van der Schueren B, Mathieu C, Janssens S, Holvoet P (2012) Decreased miR-181a expression in monocytes of obese patients is associated with the occurrence of metabolic syndrome and coronary artery disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97(7):E1213–E1218. doi:10.1210/jc.2012-1008. Epub 2012 Apr 24
Tabuchi T, Satoh M, Itoh T, Nakamura M (2012) MicroRNA-34a regulates the longevity-associated protein SIRT1 in coronary artery disease: effect of statins on SIRT1 and microRNA-34a expression. Clin Sci (Lond) 123(3):161–171
Vavuranakis M, Kariori M, Vrachatis D, Aznaouridis K, Siasos G, Kokkou E, Mazaris S, Moldovan C, Kalogeras K, Tousoulis D, Stefanadis C (2013) MicroRNAs in aortic disease. Curr Top Med Chem 13(13):1559–1572
Eskildsen TV, Jeppesen PL, Schneider M, Nossent AY, Sandberg MB, Hansen PB, Jensen CH, Hansen ML, Marcussen N, Rasmussen LM, Bie P, Andersen DC, Sheikh SP (2013) Angiotensin II Regulates microRNA-132/-212 in Hypertensive Rats and Humans. Int J Mol Sci 14(6):11190–11207. doi:10.3390/ijms140611190
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Y., Yang, CJ., Xu, X. et al. MiR-214 regulates the pathogenesis of patients with coronary artery disease by targeting VEGF. Mol Cell Biochem 402, 111–122 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2319-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2319-5