Abstract
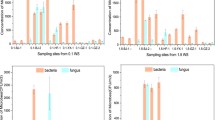
Ambient levels of viable bioaerosol (fungi) were measured at six different sections of a sewage treatment plant in Vasant Kunj, New Delhi. The sampling was carried out for fungal fractions of bioaerosols during the month of June 2012 to May 2013 covering all the four seasons of India, i.e., monsoon, post-monsoon, winter, and pre-monsoon. Sampling was done thrice in a month with the help of a six-stage viable cascade impactor for 10 min each at a flow rate of 28.3 l min−1. Temperature and relative humidity were also recorded during each sampling. It was found that among all the six sites, maximum and minimum fungal concentrations were 1,200 and 829 CFU m−3 in pre-monsoon; 1,198 and 802 CFU m−3 in monsoon; 1,289 and 868 CFU m−3 in post-monsoon; and 516 and 279 CFU m−3 in winter seasons, respectively. A good regression of fine over coarse fungal bioaerosols was observed in all the four seasons. In total, eight genera of fungi were identified, and among the eight genera identified, four, e.g., Mucor, Rhizopus, Aspergillus, and Penicillium, were found in maximum number during all the seasons. This study has revealed interesting results in context to the relationship between concentrations of fungal bioaerosols and environmental factors as well as interparticle size relationship of fungal bioaerosols.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
ACGIH. (1999). Bioaerosols: assessment and control (1st ed.). Cincinnati, OH: American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists.
Baron, E. J., & Finegold, S. M. (1990). Bailey & scott’s diagnostic microbiology. 8th edn. St. Louis: The C.V. Mosby Company, pp. 76, 79, 82, 100–126, 133.
Bausum, H. T., Schaub, S. A., Kenyon, K. F. N., & Small, M. J. (1982). Comparison of coliphage and bacterial aerosols at a waste water spray irrigation site. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 43, 28–38.
Brandi, G., Sisiti, M., & Amagliani, G. (2000). Evaluation of the environmental impact of microbial aerosols generated by waste water plants utilizing different aeration system. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 88, 845–852.
Brenner, K. P., Scarpino, P. V., & Clark, C. S. (1988). Animal viruses, colophages and bacteria in aerosols and waste water at spray irrigation site. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 54, 409–415.
Census of India. (2011). http://www.censusindia.gov.in/.
Clark, C. S. (1987). Potential and actual biological related health risk of wastewater industry employment. Water Pollution Control Federation, 59, 999–1008.
Clark, C. S., Cleary, E. J., Schiff, G. M., Linnemann, C. C, Jr, Phair, J. P., & Briggs, T. M. (1976). Disease risk of occupational exposure to sewage. Journal of Environmental Engineering Division, 102, 375–388.
De Luca, G., Zanetti, F., Fateh-Moghadm, P., & Stampi, S. (1998). Occurrence of Listeria monocytogenes in sewage sludge. Zentralblatt fur Hygiene und Umweltmedizin, 201, 269–277.
Ebner, M. R., Haselwandter, K., & Frank, A. (1989). Seasonal fluctuations of airborne fungal allergens. Mycological Research, 92, 170–176.
Fang, Z., Ouyang, Z., Hu, L., Wang, X., Zheng, H., & Lin, X. (2005). Culturable airborne fungi in outdoor environments in Beijing, China. Science of Total Environment, 350, 47–58.
Fannin, K. F., Vana, S. C., & Jakvbowski, W. (1985). Effect of an activated sludge wastewater treatment plant on ambient air densities of aerosols containing bacteria and viruses. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 49, 1191–1196.
Ferris, L., Mikoczy, Z., Hagmar, L., & Edling, C. (1999). Cancer incidence in a cohort of Swedish sewage workers extended follow up. Occupational Environmental Medicine, 56, 672–673.
Fracchia, L., Pietronave, S., Rinaldi, M., & Martinotti, M. G. (2006). Site related airborne biological hazard and seasonal variations in two wastewater treatment plants. Water Research, 40, 1985–1994.
Ghosh, B., Lal, H., Kushwaha, R., Hazarika, N., Srivastava, A., & Jain, V. K. (2013). Estimation of bioaerosol in indoor environment in the university library of Delhi. Sustainable Environmental Research, 23, 199–207.
Grisoli, P., Rodolfi, M., Villani, S., Grignan, E., Cottica, D., Berri, A., et al. (2009). Assessment of airborne microorganism contamination in an industrial area characterized by an open composting facility and a wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Research, 109, 135–142.
Hansen, E. S., Hilden, J., Klausen, H., & Rusadahl, N. (2003). Waste water exposure and health-a comparative study of occupational groups. Occupational Environmental Medicine, 60, 595–598.
Jeggli, S., Stenier, D., Joller, H., Tschopp, A., & Hotz, P. (2004). Hepatitis E, Helicobactor pylori and gastrointestinal symptoms in workers exposed to waste water. Occupational Environmental Medicine, 61, 627–662.
Korzeniewska, E., Filipkowska, Z., Gotkowska, P. A., Janczukwicz, W., Dixon, B., & Czulowska, M. (2009). Determination of emitted airborne microorganisms from a BIO-PAK wastewater treatment plant. Water Research, 43, 2841–2851.
Lacey, J., & Crook, B. (1988). Review: Fungal and actinomycete spores as pollutants of the workplace and occupational allergens. Annals of Occupational Hygiene, 32, 515–533.
Lacey, J., & Dutkiewicz, J. (1994). Bioaerosols and occupational lung disease. Journal of Aerosol Science, 25, 1371–1404.
Lin, L., Gao, M., & Lin, J. (2011). Distribution characterization of microbial aerosol emitted from wastewater treatment plant using the orbal oxidation ditch process. Process Biochemistry, 46, 910–915.
Orisini, M., Laurenti, P., Boninti, F., Arzani, D., Ianni, A., & Romano-Spica, V. (2002). A molecular typing approach for evaluating bioaerosol exposure in wastewater treatment plant workers. Water Research, 36(5), 1375–1378.
Peat, J. K., Tovey, E., Mellis, C. M., Leeder, S. R., & Woolcock, A. J. (1993). Importance of house dust mite and Alternaria allergens in childhood asthma: an epidemiological study in two climatic regions of Australia. Clinical Experimental Allergy, 23, 812–820.
Pietro, G., Marinella, R., Simona, V., Elena, G., Danilo, C., Anglo, B., et al. (2008). Assessment of airborne microorganism containing in an industrial area characterized by an open composting facility and wastewater treatment plant. Environmental Research, 109, 135–142.
Pillai, S. D., Widmer, K. W., Dowed, S. E., & Ricke, S. C. (1996). Occurence of airborne bacteria and pathogen indicators during land application of sewage sludge. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 62, 296–299.
Ren, P., Ahearn, D. G., & Crow, S. A. (1999). Comparative study of Aspergillus mycotoxin production on enriched media and construction material. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology, 23, 209–213.
Rylander, R. (1999). Health effect among workers in sewage treatment plants. Occupational Environmental Medicine, 56, 354–357.
Rylander, R., Anderson, K., Belin, L., Berglund, G., Bergstron, R., Manson, L. A., et al. (1976). Sewage worker’s syndrome. Lancet, 8, 478.
Sautour, M., Sixt, N., Dalle, F., L’Ollivier, C., Fourquenet, V., Calinon, C., et al. (2009). Profiles and seasonal distribution of airborne fungi in indoor and outdoor environments at a French hospital. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 3766–3771.
Shen, H. D., & Han, S. H. (1998). Characterization of allergens of Penicillium and Aspergillus species. Journal of Microbiology, Immunology, and Infection, 31, 141–145.
Smith, E. G. (1990). Sampling and identifying allergenic pollens and molds (15th ed., pp. 41–49). San Antonio: Blewstone Press.
Sneath, P. H. A., Mair, N., Sharpe, M. E., & Holt, J. G. (1986). Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology (Vol. 2). Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins.
Swan, J. R., Crook, B., & Gilbert, E. J. (2002). Microbial emission from composting sites. Environmental Science and Technology, 18, 23–85.
Taha, M. P. M., Pollard, S. J. T., Sarkar, U., & Longhurust, P. J. (2005). Estimating fugitive bioaerosol releases from static compost windrows: Feasibility of a portable wind tunnel approach. Waste Management, 25, 445–450.
Thorn, J., & Kerekes, E. (2001). Health effect among employees in sewage treatment plants: a literature survey. American Journal of Industrial Medicine, 40, 170–179.
Zofia, P., Ewa, K., Czeslawa, S., Jolanta, S., Grazyna, C., & Jack, D. (2003). Exposure to bioaerosols in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine, 10, 241–248.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the contributions of anonymous reviewers and editor for improving the quality of this manuscript. Authors are also thankful to Himanshu Lal, Bipasha Ghosh, and Anshul Srivastava. AS is thankful to the University Grant Commission (GoI) for financial support in the form of major research project [42-420/2013(SR)]. Authorities at Vasant Kunj sever treatment plant are also duly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maharia, S., Srivastava, A. Influence of seasonal variation on concentration of fungal bioaerosol at a sewage treatment plant (STP) in Delhi. Aerobiologia 31, 249–260 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-014-9361-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10453-014-9361-3