Abstract
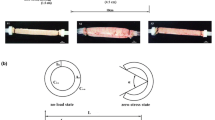
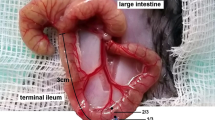
Intestinal obstruction prompts luminal dilation and wall remodeling proximal to the site of obstruction. Studies on temporal and spatial morphomechanical remodeling are needed for comprehending the pathophysiology of acute intestinal obstruction. The aim was to estimate the no-load and zero-stress morphomechanical properties in circumferential and longitudinal direction at 0, 6, 12, 24, 36, and 48 h after complete intestinal obstruction. Obstruction of the distal ileum was created surgically by placement of a polyethylene ring for up to 48 h in 30 rats. Sham and normal groups were also studied (n = 12). Five 6 cm-long intestinal segments proximal to the obstruction site were used for histological, morphometric and mechanical analysis at the designated times. Morphomechanical changes were huge but only subtle changes were observed between the 5 segments during the obstruction period. Due to dilation, the serosal length and mucosal length increased continuously from 6 to 48 h (p < 0.001). The wall area increased at 24 h and beyond (p < 0.001), demonstrating tissue growth. The opening and bending angle decreased to minimum values at 24 h where after the opening angle increased and the bending angle returned to pre-obstruction levels. For the residual stretch ratios and the position of the neutral axis the turning point was found after 24 h. Histologically, the thickness and area of most wall layers were quite stable for the first 12 h but with an increase at the 24 h time point that continued to the 48 h time point. The most pronounced change was found for the circumferential muscle layer (p < 0.05). Analysis of picrosirius red stained slides showed that submucosal type 3 collagen fraction increased significantly (p < 0.001), whereas the fraction of type 1 collagen decreased (p < 0.001). In conclusion, pronounced time-dependent morphomechanical remodeling was found. The obstructed intestine went from dilation remodeling to growth remodeling during the interval 12–24 h after creating the obstruction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bertoni, S., and G. Gabella. Hypertrophy of mucosa and serosa in the obstructed intestine of rats. J. Anat. 199:725–734, 2001.
Bertoni, S., G. Gabella, P. Ghizzardi, V. Ballabeni, M. Impicciatore, C. Lagrasta, M. L. Arcari, and E. Barocelli. Motor responses of rat hypertrophic intestine following chronic obstruction. Neurogastr. Motil. 16:365–374, 2004.
Chang, I. Y., N. J. Glasgow, I. Takayama, K. Horiguchi, K. M. Sanders, and S. M. Ward. Loss of interstitial cells of Cajal and development of electrical dysfunction in murine small bowel obstruction. J. Physiol. 536:555–568, 2001.
De Giorgio, R., R. F. Cogliandro, G. Barbara, R. Corinaldesi, and V. Stanghellini. Chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction: clinical features, diagnosis, and therapy. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 40:787–807, 2011.
DiBaise, J. K., and E. M. Quigley. Tumor-related dysmotility: gastrointestinal dysmotility syndromes associated with tumors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 43:1369–1401, 1998.
Díte, P., J. Lata, and I. Novotný. Intestinal obstruction and perforation—the role of the gastroenterologist. Dig. Dis. 21:63–67, 2003.
Ekblad, E., R. Sjuve, A. Arner, and F. Sundler. Enteric neuronal plasticity and a reduced number of interstitial cells of Cajal in hypertrophic rat ileum. Gut 42:836–844, 1998.
Fung, Y. C. Biomechaincs. Properties of Living Tissues. Berlin: Springer, 1993.
Gabella, G. Development and ageing of intestinal musculature and nerves: the guinea-pig taenia coli. J. Neurocytol. 30:733–766, 2001.
Geuna, S., S. Cardillo, and M. G. Giacobini-Robecchi. Smooth muscle cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia in the partially obstructed gut of the rat: a quantitative evaluation. Cells Tissues Organs 163:69–74, 1998.
Gregersen, H. Biomechanics of the Gastrointestinal Tract. London: Springer, 2002.
Gregersen, H., J. L. Emery, and A. D. McCulloch. History-dependent mechanical behavior of guinea-pig small intestine. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 26:850–858, 1998.
Holzapfel, G. A., T. C. Gasser, and R. W. Ogden. A new constitutive framework for arterial wall mechanics and a comparative study of material models. J. Elast. 61:1–48, 2000.
Katis, P. G., and S. M. Dias. Volvulus: a rare twist on small-bowel obstruction. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 171:728, 2004.
Lattouf, R., R. Younes, D. Lutomski, N. Naaman, G. Godeau, K. Senni, and S. Changotade. Picrosirius red staining: a useful tool to appraise collagen networks in normal and pathological tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 62:751–758, 2014.
Lawrance, I. C., G. Rogler, G. Bamias, C. Breynaert, J. Florholmen, G. Pellino, S. Reif, S. Speca, and G. Latella. Cellular and molecular mediators of intestinal fibrosis. J. Crohns Colitis 11(12):1491–1503, 2015.
Liao, D., J. Zhao, and H. Gregersen. 3d Mechanical properties of the partially obstructed guinea pig small intestine. J. Biomech. 43:2079–2086, 2010.
Liu, D. H., X. Huang, X. Guo, X. M. Meng, Y. S. Wu, H. L. Lu, C. M. Zhang, Y. C. Kim, and W. X. Xu. Voltage dependent potassium channel remodeling in murine intestinal smooth muscle hypertrophy induced by partial obstruction. PLoS ONE 9:e86109, 2014.
Markogiannakis, H., E. Messaris, D. Dardamanis, N. Pararas, D. Tzertzemelis, P. Giannopoulos, A. Larentzakis, E. Lagoudianakis, A. Manouras, and I. Bramis. Acute mechanical bowel obstruction: clinical presentation, etiology, management and outcome. World J. Gastroenterol. 13:432–437, 2007.
Miyamoto, M., K. Egami, S. Maeda, K. Ohkawa, N. Tanaka, E. Uchida, and T. Tajiri. Hirschsprung’s disease in adults: report of a case and review of the literature. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 72:113–120, 2005.
Nguyen, V. H. Intestinal obstruction due to tuberculosis. Asian J. Surg. 25:145–148, 2002.
Prihoda, M., A. Flatt, and R. W. Summers. Mechanisms of motility changes during acute intestinal obstruction in the dog. Am. J. Physiol. 247:G37–G42, 1984.
Silva, A. C., M. Pimenta, and L. S. Guimaraes. Small bowel obstruction: what to look for. Radiographics 29:423–439, 2009.
Storkholm, J. H., J. Zhao, G. E. Villadsen, and H. Gregersen. Spontaneous and bolus-induced motility in the chronically obstructed guinea-pig small intestine in vitro. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53:413–420, 2008.
Storkholm, J. H., J. Zhao, G. E. Villadsen, H. Hager, S. L. Jensen, and H. Gregersen. Biomechanical remodeling of the chronically obstructed Guinea pig small intestine. Dig. Dis. Sci. 52:336–346, 2007.
Sun, D., J. Zhao, D. Liao, P. Chen, and H. Gregersen. Shear modulus of the partially obstructed rat small intestine. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 45:1069–1082, 2017.
Tuca, A., E. Guell, E. Martinez-Losada, and N. Codorniu. Malignant bowel obstruction in advanced cancer patients: epidemiology, management, and factors influencing spontaneous resolution. Cancer Manag. Res. 4:159–169, 2012.
Vilz, T. O., B. Stoffels, C. Strassburg, H. H. Schild, and J. C. Kalff. Ileus in Adults. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 114:508–518, 2017.
Wilkins, B. M., and L. Spitz. Incidence of postoperative adhesion obstruction following neonatal laparotomy. Br. J. Surg. 73:762–764, 1986.
Wu, C. C., Y. M. Lin, J. Gao, J. H. Winston, L. K. Cheng, and X. Z. Shi. Are interstitial cells of Cajal involved in mechanical stress-induced gene expression and impairment of smooth muscle contractility in bowel obstruction? PLoS ONE 8:e76222, 2013.
Yamada, H., and F. G. Evans. Strength of Biological Materials. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins, 1970.
Yang, J., J. Zhao, P. Chen, T. Nakaguchi, D. Grundy, and H. Gregersen. Interdependency between mechanical parameters and afferent nerve discharge in hypertrophic intestine of rats. Am. J. Physiol-Gastr. Liver Physiol. 310:G376–G386, 2016.
Zhao, J., D. Liao, J. Yang, and H. Gregersen. Biomechanical remodelling of obstructed guinea pig jejunum. J. Biomech. 43:1322–1329, 2010.
Zhao, J., D. Liao, J. Yang, and H. Gregersen. Phasic and tonic smooth muscle function of the partially obstructed guinea pig intestine. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011:489720, 2011.
Zhao, J., D. Liao, J. Yang, and H. Gregersen. Stress and strain analysis of contractions during ramp distension in partially obstructed guinea pig jejunal segments. J. Biomech. 44:2077–2082, 2011.
Zissin, R., M. Hertz, H. Paran, J. Bernheim, M. Shapiro-Feinberg, and G. Gayer. Small bowel obstruction secondary to Crohn disease: CT findings. Abdom. Imaging 29:320–325, 2004.
Acknowledgments
This study was partially supported by a grant from Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (cstc2013kjrc-ljrccj10003) and National “111 Plan” Base (B06023) and Karen Elise Jensen foundation. These contributions did not constitute any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Sean S. Kohles oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, D., Zhao, J., Liao, D. et al. The Turning Point for Morphomechanical Remodeling During Complete Intestinal Obstruction in Rats Occurs After 12–24 h. Ann Biomed Eng 46, 705–716 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-1992-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-018-1992-z