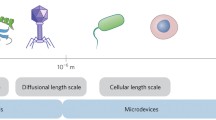
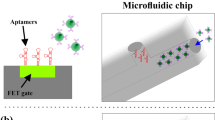
Abstract
Rapid screening of biomarkers, with high specificity and accuracy, is critical for many point-of-care diagnostics. Microfluidics, the use of microscale channels to manipulate small liquid samples and carry reactions in parallel, offers tremendous opportunities to address fundamental questions in biology and provide a fast growing set of clinical tools for medicine. Emerging multi-dimensional nanostructures, when coupled with microfluidics, enable effective and efficient screening with high specificity and sensitivity, both of which are important aspects of biological detection systems. In this review, we provide an overview of current research and technologies that utilize nanostructures to facilitate biological separation in microfluidic channels. Various important physical parameters and theoretical equations that characterize and govern flow in nanostructure-integrated microfluidic channels will be introduced and discussed. The application of multi-dimensional nanostructures, including nanoparticles, nanopillars, and nanoporous layers, integrated with microfluidic channels in molecular and cellular separation will also be reviewed. Finally, we will close with insights on the future of nanostructure-integrated microfluidic platforms and their role in biological and biomedical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor clusters, nanocrystals, and quantum dots. Science (80-) 271:933–937, 1996.
Arosio, P., T. Müller, L. Mahadevan, and T. P. J. Knowles. Density-gradient-free microfluidic centrifugation for analytical and preparative separation of nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 14:2365–2371, 2014.
Bhushan, B. Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology. Springer, 2010. https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=me1grr_pobMC&pgis=1.
Blinka, E., K. Loeffler, Y. Hu, A. Gopal, K. Hoshino, K. Lin, X. Liu, M. Ferrari, and J. X. J. Zhang. Enhanced microcontact printing of proteins on nanoporous silica surface. Nanotechnology 21:415302, 2010.
Bohunicky, B., and S. A. Mousa. Biosensors: the new wave in cancer diagnosis. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 4:1–10, 2010.
Burger, R., P. Reith, G. Kijanka, V. Akujobi, P. Abgrall, and J. Ducrée. Array-based capture, distribution, counting and multiplexed assaying of beads on a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 12:1289–1295, 2012.
Cao, Y. C., R. Jin, and C. A. Mirkin. Nanoparticles with Raman spectroscopic fingerprints for DNA and RNA detection. Science 297:1536–1540, 2002.
Chen, G. D., C. J. Alberts, W. Rodriguez, and M. Toner. Concentration and purification of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions by microfluidic separation of superparamagnetic nanoparticles. Anal. Chem. 82:723–728, 2010.
Chen, P., Y.-Y. Huang, K. Hoshino, and X. Zhang. On-chip magnetic field modulation for distributed immunomagnetic detection of circulating tumor cells. Solid-State Sens. 2013. doi:10.1109/Transducers.2013.6626989.
Chen, P., Y.-Y. Huang, K. Hoshino, and J. X. J. Zhang. Microscale magnetic field modulation for enhanced capture and distribution of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 5:8745, 2015.
Chen, W., S. Weng, F. Zhang, S. Allen, X. Li, L. Bao, R. H. W. Lam, J. A. Macoska, S. D. Merajver, and J. Fu. Nanoroughened surfaces for efficient capture of circulating tumor cells without using capture antibodies. ACS Nano 7:566–575, 2013.
Chikkaveeraiah, B. V., V. Mani, V. Patel, J. S. Gutkind, and J. F. Rusling. Microfluidic electrochemical immunoarray for ultrasensitive detection of two cancer biomarker proteins in serum. Biosens. Bioelectron. 26:4477–4483, 2011.
Cho, B. S., T. G. Schuster, X. Zhu, D. Chang, G. D. Smith, and S. Takayama. Passively driven integrated microfluidic system for separation of motile sperm. Anal. Chem. 75:1671–1675, 2003.
Day, E. S., L. R. Bickford, J. H. Slater, N. S. Riggall, R. A. Drezek, and J. L. West. Antibody-conjugated gold-gold sulfide nanoparticles as multifunctional agents for imaging and therapy of breast cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 5:445–454, 2010.
Delamarche, E., D. Juncker, and H. Schmid. Microfluidics for processing surfaces and miniaturizing biological assays. Adv. Mater. 17:2911–2933, 2005.
Desai, T. A., D. J. Hansford, L. Leoni, M. Essenpreis, and M. Ferrari. Nanoporous anti-fouling silicon membranes for biosensor applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 15:453–462, 2000.
Di Carlo, D. Inertial microfluidics. Lab Chip 9:3038–3046, 2009.
Duncombe, T. A., and A. E. Herr. Photopatterned free-standing polyacrylamide gels for microfluidic protein electrophoresis. Lab Chip 13:2115–2123, 2013.
Eck, W., G. Craig, A. Sigdel, G. Ritter, L. J. Old, L. Tang, M. F. Brennan, P. J. Allen, and M. D. Mason. PEGylated gold nanoparticles conjugated to monoclonal F19 antibodies as targeted labeling agents for human pancreatic carcinoma tissue. ACS Nano 2:2263–2272, 2008.
Feng, P., X. Bu, and D. J. Pine. Control of pore sizes in mesoporous silica templated by liquid crystals in block copolymer–cosurfactant–water systems. Langmuir 16:5304–5310, 2000.
Fu, J., R. B. Schoch, A. L. Stevens, S. R. Tannenbaum, and J. Han. A patterned anisotropic nanofluidic sieving structure for continuous-flow separation of DNA and proteins. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2:121–128, 2007.
Gupta, A. K., and M. Gupta. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 26:3995–4021, 2005.
Haas, F. Quantum Plasmas. New York: Springer, 2011.
Hornbeck, P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. Chapter 2: Unit 2.1, 2001.
Horsman, K. M., S. L. R. Barker, J. P. Ferrance, K. A. Forrest, K. A. Koen, and J. P. Landers. Separation of sperm and epithelial cells in a microfabricated device: potential application to forensic analysis of sexual assault evidence. Anal. Chem. 77:742–749, 2005.
Hosta-Rigau, L., I. Olmedo, J. Arbiol, L. J. Cruz, M. J. Kogan, and F. Albericio. Multifunctionalized gold nanoparticles with peptides targeted to gastrin-releasing peptide receptor of a tumor cell line. Bioconjug. Chem. 21:1070–1078, 2010.
Hou, H. W., M. E. Warkiani, B. L. Khoo, Z. R. Li, R. A. Soo, D. S.-W. Tan, W.-T. Lim, J. Han, A. A. S. Bhagat, and C. T. Lim. Isolation and retrieval of circulating tumor cells using centrifugal forces. Sci. Rep. 3:1259, 2013.
Hu, Y., A. Bouamrani, E. Tasciotti, L. Li, X. Liu, and M. Ferrari. Tailoring of the nanotexture of mesoporous silica films and their functionalized derivatives for selectively harvesting low molecular weight protein. ACS Nano 4:439–451, 2010.
Huang, N.-T., W. Chen, B.-R. Oh, T. T. Cornell, T. P. Shanley, J. Fu, and K. Kurabayashi. An integrated microfluidic platform for in situ cellular cytokine secretion immunophenotyping. Lab Chip 12:4093–4101, 2012.
Huang, L. R., E. C. Cox, R. H. Austin, and J. C. Sturm. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304:987–990, 2004.
Huang, Y., K. Hoshino, P. Chen, C. Wu, N. Lane, M. Huebschman, H. Liu, K. Sokolov, J. W. Uhr, E. P. Frenkel, and J. X. J. Zhang. Immunomagnetic nanoscreening of circulating tumor cells with a motion controlled microfluidic system. Biomed. Microdevices 15:673–681, 2013.
Huang, Y. Y., P. Chen, K. Hoshino, C. H. Wu, N. Lane, M. Huebschman, J. Uhr, K. Sokolov, E. Frenkel, and X. Zhang. Patterned nanomagnets on-chip for screening circulating tumor cells in blood. MicroTAS, 2012.
Innocenzi, P., and L. Malfatti. Mesoporous thin films: properties and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42:4198–4216, 2013.
Innocenzi, P., L. Malfatti, and G. J. A. A. Soler-Illia. Hierarchical mesoporous films: from self-assembly to porosity with different length scales. Chem. Mater. 23:2501–2509, 2011.
Innocenzi, P., Y. L. Zub, and V. G. Kessler. Sol-Gel Methods for Materials Processing. Dordrecht: Springer, 2008. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-8514-7.
Jha, S. K., R. Chand, D. Han, Y.-C. Jang, G.-S. Ra, J. S. Kim, B.-H. Nahm, and Y.-S. Kim. An integrated PCR microfluidic chip incorporating aseptic electrochemical cell lysis and capillary electrophoresis amperometric DNA detection for rapid and quantitative genetic analysis. Lab Chip 12:4455–4464, 2012.
Ji, J., L. Nie, L. Qiao, Y. Li, L. Guo, B. Liu, P. Yang, and H. H. Girault. Proteolysis in microfluidic droplets: an approach to interface protein separation and peptide mass spectrometry. Lab Chip 12:2625–2629, 2012.
Kamholz, A. E., B. H. Weigl, B. A. Finlayson, and P. Yager. Quantitative analysis of molecular interaction in a microfluidic channel: the T-sensor. Anal. Chem. 71:5340–5347, 1999.
Kim, M., and T. Kim. Integration of nanoporous membranes into microfluidic devices: electrokinetic bio-sample pre-concentration. Analyst 138:6007–6015, 2013.
Kim, K. S., and J.-K. Park. Magnetic force-based multiplexed immunoassay using superparamagnetic nanoparticles in microfluidic channel. Lab Chip 5:657–664, 2005.
Lagally, E. T., I. Medintz, and R. A. Mathies. Single-molecule DNA amplification and analysis in an integrated microfluidic device. Anal. Chem. 73:565–570, 2001.
Lagally, E. T., P. C. Simpson, and R. A. Mathies. Monolithic integrated microfluidic DNA amplification and capillary electrophoresis analysis system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 63:138–146, 2000.
Lai, J. J., J. M. Hoffman, M. Ebara, A. S. Hoffman, C. Estournès, A. Wattiaux, and P. S. Stayton. Dual magnetic-/temperature-responsive nanoparticles for microfluidic separations and assays. Langmuir 23:7385–7391, 2007.
Lai, G., J. Wu, H. Ju, and F. Yan. Streptavidin-functionalized silver-nanoparticle-enriched carbon nanotube tag for ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of tumor markers. Adv. Funct. Mater. 21:2938–2943, 2011.
Laurent, S., D. Forge, M. Port, A. Roch, C. Robic, L. Vander Elst, and R. N. Muller. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 108:2064–2110, 2008.
Levine, R. M., C. M. Scott, and E. Kokkoli. Peptide functionalized nanoparticles for nonviral gene delivery. Soft Matter 9:985–1004, 2013.
Li, J. Application of microfluidic devices to proteomics research: identification of trace-level protein digests and affinity capture of target peptides. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1:157–168, 2002.
Liang, P., C.-J. Liu, R.-X. Zhuo, and S.-X. Cheng. Self-assembled inorganic/organic hybrid nanoparticles with multi-functionalized surfaces for active targeting drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 1:4243, 2013.
Lion, N., F. Reymond, H. H. Girault, and J. S. Rossier. Why the move to microfluidics for protein analysis? Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 15:31–37, 2004.
Lu, A., E. Salabas, and F. Schüth. Magnetic nanoparticles: synthesis, protection, functionalization, and application. Chemie Int. Ed., 2007. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/anie.200602866/pdf.
Luo, C., Q. Fu, H. Li, L. Xu, M. Sun, Q. Ouyang, Y. Chen, and H. Ji. PDMS microfludic device for optical detection of protein immunoassay using gold nanoparticles. Lab Chip 5:726–729, 2005.
Malhotra, R., V. Patel, B. V. Chikkaveeraiah, B. S. Munge, S. C. Cheong, R. B. Zain, M. T. Abraham, D. K. Dey, J. S. Gutkind, and J. F. Rusling. Ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers in the clinic by use of a nanostructured microfluidic array. Anal. Chem. 84:6249–6255, 2012.
Mellors, J. S., W. A. Black, A. G. Chambers, J. A. Starkey, N. A. Lacher, and J. M. Ramsey. Hybrid capillary/microfluidic system for comprehensive online liquid chromatography-capillary electrophoresis-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 85:4100–4106, 2013.
Mostert, B., S. Sleijfer, J. A. Foekens, and J. W. Gratama. Circulating tumor cells (CTCs): detection methods and their clinical relevance in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 35:463–474, 2009.
Mucic, R. C., J. J. Storhoff, C. A. Mirkin, and R. L. Letsinger. DNA-directed synthesis of binary nanoparticle network materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120:12674–12675, 1998.
Nagrath, S., L. V. Sequist, S. Maheswaran, D. W. Bell, D. Irimia, L. Ulkus, M. R. Smith, E. L. Kwak, S. Digumarthy, A. Muzikansky, P. Ryan, U. J. Balis, R. G. Tompkins, D. A. Haber, and M. Toner. Isolation of rare circulating tumour cells in cancer patients by microchip technology. Nature 450:1235–1239, 2007.
Ng, E., A. Gopal, K. Hoshino, and X. Zhang. Multicolor microcontact printing of proteins on nanoporous surface for patterned immunoassay. Appl. Nanosci. 1:79–85, 2011.
Ng, E., K. Hoshino, and X. Zhang. Microfluidic immunodetection of cancer cells via site-specific microcontact printing of antibodies on nanoporous surface. Methods 63:266–275, 2013.
Pumera, M., J. Wang, E. Grushka, and R. Polsky. Gold nanoparticle-enhanced microchip capillary electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 73:5625–5628, 2001.
Punnoose, E. A., S. K. Atwal, J. M. Spoerke, H. Savage, A. Pandita, R.-F. Yeh, A. Pirzkall, B. M. Fine, L. C. Amler, D. S. Chen, and M. R. Lackner. Molecular biomarker analyses using circulating tumor cells. PLoS One 5:e12517, 2010.
Rabilloud, T. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in proteomics: old, old fashioned, but it still climbs up the mountains. Proteomics 2:3–10, 2002.
Sackmann, E. K., A. L. Fulton, and D. J. Beebe. The present and future role of microfluidics in biomedical research. Nature 507:181–189, 2014.
Sharma, T., Y. Hu, M. Stoller, M. Feldman, R. S. Ruoff, M. Ferrari, and X. Zhang. Mesoporous silica as a membrane for ultra-thin implantable direct glucose fuel cells. Lab Chip 11:2460–2465, 2011.
Shi, J., A. P. Fang, L. Malaquin, A. Pépin, D. Decanini, J. L. Viovy, and Y. Chen. Highly parallel mix-and-match fabrication of nanopillar arrays integrated in microfluidic channels for long DNA molecule separation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 91:153114, 2007.
Shih, S. C. C., H. Yang, M. J. Jebrail, R. Fobel, N. McIntosh, O. Y. Al-Dirbashi, P. Chakraborty, and A. R. Wheeler. Dried blood spot analysis by digital microfluidics coupled to nanoelectrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 84:3731–3738, 2012.
Shintaku, H., H. Nishikii, L. A. Marshall, H. Kotera, and J. G. Santiago. On-chip separation and analysis of RNA and DNA from single cells. Anal. Chem. 86:1953–1957, 2014.
Somasundaran, P. Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, Volume 1. CRC Press, 2006, https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=9jAHFOqyX5YC&pgis=1.
Squires, T., and S. Quake. Microfluidics: fluid physics at the nanoliter scale. Rev. Mod. Phys. 77:977–1026, 2005.
Stott, S. L., C.-H. Hsu, D. I. Tsukrov, M. Yu, D. T. Miyamoto, B. A. Waltman, S. M. Rothenberg, A. M. Shah, M. E. Smas, G. K. Korir, F. P. Floyd, A. J. Gilman, J. B. Lord, D. Winokur, S. Springer, D. Irimia, S. Nagrath, L. V. Sequist, R. J. Lee, K. J. Isselbacher, S. Maheswaran, D. A. Haber, and M. Toner. Isolation of circulating tumor cells using a microvortex-generating herringbone-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107:18392–18397, 2010.
Striemer, C. C., T. R. Gaborski, J. L. McGrath, and P. M. Fauchet. Charge- and size-based separation of macromolecules using ultrathin silicon membranes. Nature 445:749–753, 2007.
Strohmeier, O., A. Emperle, G. Roth, D. Mark, R. Zengerle, and F. von Stetten. Centrifugal gas-phase transition magnetophoresis (GTM)–a generic method for automation of magnetic bead based assays on the centrifugal microfluidic platform and application to DNA purification. Lab Chip 13:146–155, 2013.
Sun, W., C. Jia, T. Huang, W. Sheng, G. Li, H. Zhang, F. Jing, Q. Jin, J. Zhao, G. Li, and Z. Zhang. High-performance size-based microdevice for the detection of circulating tumor cells from peripheral blood in rectal cancer patients. PLoS One 8:e75865, 2013.
Taton, T. A. Scanometric DNA array detection with nanoparticle probes. Science 289:1757–1760, 2000.
Taylor, D. D., W. Zacharias, and C. Gercel-Taylor. Exosome isolation for proteomic analyses and RNA profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 728:235–246, 2011.
Théry, C., L. Zitvogel, and S. Amigorena. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2:569–579, 2002.
Tiwari, J. N., R. N. Tiwari, and K. S. Kim. Zero-dimensional, one-dimensional, two-dimensional and three-dimensional nanostructured materials for advanced electrochemical energy devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 57:724–803, 2012.
Tsai, C.-P., C.-Y. Chen, Y. Hung, F.-H. Chang, and C.-Y. Mou. Monoclonal antibody-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSN) for selective targeting breast cancer cells. J. Mater. Chem. 19:5737, 2009.
Wainright, A., U. T. Nguyen, T. Bjornson, and T. D. Boone. Preconcentration and separation of double-stranded DNA fragments by electrophoresis in plastic microfluidic devices. Electrophoresis 24:3784–3792, 2003.
Wang, Z., H. Wu, D. Fine, J. Schmulen, Y. Hu, B. Godin, J. X. J. Zhang, and X. Liu. Ciliated micropillars for the microfluidic-based isolation of nanoscale lipid vesicles. Lab Chip 13:2879–2882, 2013.
Whitesides, G. M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 442:368–373, 2006.
Wilbur, J. L., A. Kumar, H. A. Biebuyck, E. Kim, and G. M. Whitesides. Microcontact printing of self-assembled monolayers: applications in microfabrication. Nanotechnology 7:452–457, 1996.
Wu, C.-H., Y.-Y. Huang, P. Chen, K. Hoshino, H. Liu, E. P. Frenkel, J. X. J. Zhang, and K. V. Sokolov. Versatile immunomagnetic nanocarrier platform for capturing cancer cells. ACS Nano 7:8816–8823, 2013.
Xia, H., X. Gao, G. Gu, Z. Liu, N. Zeng, Q. Hu, Q. Song, L. Yao, Z. Pang, X. Jiang, J. Chen, and H. Chen. Low molecular weight protamine-functionalized nanoparticles for drug delivery to the brain after intranasal administration. Biomaterials 32:9888–9898, 2011.
Xia, N., T. P. Hunt, B. T. Mayers, E. Alsberg, G. M. Whitesides, R. M. Westervelt, and D. E. Ingber. Combined microfluidic-micromagnetic separation of living cells in continuous flow. Biomed. Microdevices 8:299–308, 2006.
Xu, H., Z. P. Aguilar, L. Yang, M. Kuang, H. Duan, Y. Xiong, H. Wei, and A. Wang. Antibody conjugated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for cancer cell separation in fresh whole blood. Biomaterials 32:9758–9765, 2011.
Yamada, M., K. Kano, Y. Tsuda, J. Kobayashi, M. Yamato, M. Seki, and T. Okano. Microfluidic devices for size-dependent separation of liver cells. Biomed. Microdevices 9:637–645, 2007.
Yamada, M., and M. Seki. Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 5:1233–1239, 2005.
Yang, W., Y. Cheng, T. Xu, X. Wang, and L.-P. Wen. Targeting cancer cells with biotin-dendrimer conjugates. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44:862–868, 2009.
Yasui, T., N. Kaji, M. R. Mohamadi, Y. Okamoto, M. Tokeshi, Y. Horiike, and Y. Baba. Electroosmotic flow in microchannels with nanostructures. ACS Nano 5:7775–7780, 2011.
Yasui, T., N. Kaji, R. Ogawa, S. Hashioka, M. Tokeshi, Y. Horiike, and Y. Baba. Arrangement of a nanostructure array to control equilibrium and non-equilibrium transports of macromolecules. Nano Lett. 2015. doi:10.1021/acs.nanolett.5b00783.
Acknowledgments
The research is partially sponsored by National Institute of Health (NIH) National Cancer Institute (NCI) Cancer Diagnosis Program under grant 1R01CA139070. We would like to gratefully thank the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship (Elaine Ng) and the Dartmouth Women in Science Programs scholarship (Kaina Chen, Annie Hang) for the generous support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Associate Editor Jennifer West oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, E., Chen, K., Hang, A. et al. Multi-Dimensional Nanostructures for Microfluidic Screening of Biomarkers: From Molecular Separation to Cancer Cell Detection. Ann Biomed Eng 44, 847–862 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1521-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-015-1521-2