Abstract
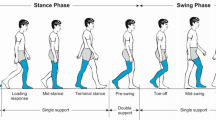
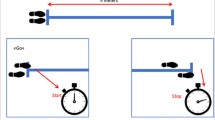
Accelerometer-based assessments can identify elderly with an increased fall risk and monitor interventions. Smart devices, like the iPod Touch, with built-in accelerometers are promising for clinical gait and posture assessments due to easy use and cost-effectiveness. The aim of the present study was to establish the validity and reliability of the iPod Touch for gait and posture assessment. Sixty healthy participants (aged 18–75 years) were measured with an iPod Touch and stand-alone accelerometer while they walked under single- and dual-task conditions, and while standing in parallel and semi-tandem stance with eyes open, eyes closed and when performing a dual task. Cross-correlation values (CCV) showed high correspondence of anterior–posterior and medio-lateral signal patterns (CCV’s ≥ 0.88). Validity of gait parameters (foot contacts, index of harmonicity, and amplitude variability) and standing posture parameters [root mean square of accelerations, median power frequency (MPF) and sway area] as indicated by intra-class correlation (ICC) was high (ICC = 0.85–0.99) and test–retest reliability was good (ICC = 0.81–0.97), except for MPF (ICC = 0.59–0.87). Overall, the iPod Touch obtained valid and reliable measures of gait and postural control in healthy adults of all ages under different conditions. Additionally, smart devices have the potential to be used for clinical gait and posture assessments.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boulgarides, L., and S. McGinty. Use of clinical and impairment-based tests to predict falls by community-dwelling older adults. Phys. Ther. 83:328–339, 2003.
De Groot, M. H., J. P. C. M. van Campen, M. A. Moek, L. R. Tulner, J. H. Beijnen, and C. J. C. Lamoth. The effects of fall-risk-increasing drugs on postural control: a literature review. Drugs Aging 30:901–920, 2013.
De Groot, M. H., H. C. van der Jagt-Willems, J. P. C. M. van Campen, W. F. Lems, J. H. Beijnen, and C. J. C. Lamoth. A flexed posture in elderly patients is associated with impairments in postural control during walking. Gait Posture 39:767–772, 2014.
Hartmann, A., K. Murer, R. A. de Bie, and E. D. de Bruin. Reproducibility of spatio-temporal gait parameters under different conditions in older adults using a trunk tri-axial accelerometer system. Gait Posture 30:351–355, 2009.
Howcroft, J., J. Kofman, and E. D. Lemaire. Review of fall risk assessment in geriatric populations using inertial sensors. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 10:91, 2013.
Hufschmidt, A., J. Dichgans, K. H. Mauritz, and M. Hufschmidt. Some methods and parameters of body sway quantification and their neurological applications. Arch. Psychiatr. Nervenkr. 228:135–150, 1980.
Ijmker, T., and C. J. C. Lamoth. Gait and cognition: the relationship between gait stability and variability with executive function in persons with and without dementia. Gait Posture 35:126–130, 2012.
Karlsson, M. K., T. Vonschewelov, C. Karlsson, M. Cöster, and B. E. Rosengen. Prevention of falls in the elderly: a review. Scand. J. Public Health 41:442–454, 2013.
Kwok, T. M. K., and C. Y. Tong. Effects on centre-based training and home-based training on physical function, quality of life and fall incidence in community dwelling older adults. Physiother. Theory Pract. 30:243–248, 2014.
Lamoth, C. J. C., E. Ainsworth, W. Polomski, and H. Houdijk. Variability and stability analysis of walking of transfemoral amputees. Med. Eng. Phys. 32:1009–1014, 2010.
Lamoth, C. J. C., P. J. Beek, and O. G. Meijer. Pelvis-thorax coordination in the transverse plane during gait. Gait Posture 16:101–114, 2002.
Lamoth, C. J., F. J. van Deudekom, J. P. van Campen, B. A. Appels, O. J. de Vries, and M. Pijnappels. Gait stability and variability measures show effects of impaired cognition and dual tasking in frail people. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 8:2, 2011.
Lamoth, C. J. C., and M. J. G. van Heuvelen. Sports activities are reflected in the local stability and regularity of body sway: older ice-skaters have better postural control than inactive elderly. Gait Posture 35:489–493, 2012.
Lee, J., A. I. Geller, and D. C. Strasser. Analytical review: focus on fall screening assessments. PM R 5:609–621, 2013.
Liston, R. A., and B. J. Brouwer. Reliability and validity of measures obtained from stroke patients using the Balance Master. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 77:425–430, 1996.
Mancini, M., A. Salarian, P. Carlson-Kuhta, C. Zampieri, L. King, L. Chiari, and F. B. Horak. ISway: a sensitive, valid and reliable measure of postural control. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 9:59, 2012.
Martinez-Mendez, R., M. Sekine, and T. Tamura. Postural sway parameters using a triaxial accelerometer: comparing elderly and young healthy adults. Comput. Methods Biomech. Biomed. Engin. 15:899–910, 2012.
Moe-Nilssen, R. A new method for evaluating motor control in gait under real-life environmental conditions. Part 2: gait analysis. Clin. Biomech. 13:328–335, 1998.
Moe-Nilssen, R. Test-retest reliability of trunk accelerometry during standing and walking. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 79:1377–1385, 1998.
Nguyen, U. S. D. T., D. P. Kiel, W. Li, A. M. Galica, H. G. Kang, V. A. Casey, and M. T. Hannan. Correlations of clinical and laboratory measures of balance in older men and women. Arthritis Care Res. (Hoboken) 64:1895–1902, 2012.
Nishiguchi, S., M. Yamada, K. Nagai, S. Mori, Y. Kajiwara, T. Sonoda, K. Yoshimura, H. Yoshitomi, H. Ito, K. Okamoto, T. Ito, S. Muto, T. Ishihara, and T. Aoyama. Reliability and validity of gait analysis by android-based smartphone. Telemed. J. E. Health. 18:292–296, 2012.
Patterson, J. A., R. Z. Amick, T. Thummar, and M. E. Rogers. Validation of measures from the smartphone sway balance application: a pilot study. Int. J. Sports Phys. Ther. 9:135–139, 2014.
Pluijm, S. M. F., J. H. Smit, E. A. M. Tromp, V. S. Stel, D. J. H. Deeg, L. M. Bouter, and P. Lips. A risk profile for identifying community-dwelling elderly with a high risk of recurrent falling: results of a 3-year prospective study. Osteoporos. Int. 17:417–425, 2006.
Schmand, B., S. C. Groenink, and M. den Dungen. Letterfluency: psychometrische eigenschappen en Nederlandse normen. Tijdschr. Gerontol. Geriatr. 39:64–74, 2008.
Sherafat, S., M. Salavati, I. Ebrahimi Takamjani, B. Akhbari, S. Mohammadirad, M. Mazaheri, and H. Negahban. Intrasession and intersession reliability of postural control in participants with and without nonspecific low back pain using the Biodex Balance System. J. Manipulative Physiol. Ther. 36:111–118, 2013.
Shrout, P. E., and J. L. Fleiss. Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 86:420–428, 1979.
Spain, R. I., R. J. St George, A. Salarian, M. Mancini, J. M. Wagner, F. B. Horak, and D. Bourdette. Body-worn motion sensors detect balance and gait deficits in people with multiple sclerosis who have normal walking speed. Gait Posture 35:573–578, 2012.
Tromp, A. M., S. M. F. Pluijm, J. H. Smit, D. J. H. Deeg, L. M. Bouter, and P. Lips. Fall-risk screening test : a prospective study on predictors for falls in community-dwelling elderly. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 54:837–844, 2001.
Van Hees, V. T., S. M. Slootmaker, G. De Groot, W. Van Mechelen, and R. C. Van Lummel. Reproducibility of a triaxial seismic accelerometer (DynaPort). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 41:810–817, 2009.
Zijlstra, W., and A. L. Hof. Assessment of spatio-temporal gait parameters from trunk accelerations during human walking. Gait Posture 18:1–10, 2003.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kees Hoogendijk for developing the data collection and storage app on the iPod, and Esther du Pre and Yvonne Dikkema for their help in collecting the data. The project was financed by the Institut Universitair de France and Investments for the Future IRT NanoElec. We certify that the studies sponsors had no involvement in the study design, in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no proprietary, financial, professional, or other personal competing interests of any nature or kind.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Tingrui Pan oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosse, N.M., Caljouw, S., Vervoort, D. et al. Validity and Reliability of Gait and Postural Control Analysis Using the Tri-axial Accelerometer of the iPod Touch. Ann Biomed Eng 43, 1935–1946 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1232-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1232-0