Abstract
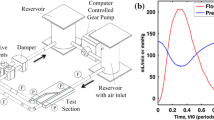
In the present study, a novel carotid covered stent design has been developed. Prototypes of different geometrical design parameters have been fabricated and their performance has been evaluated in vitro under physiological pulsatile flow condition, utilizing flow visualization (dye injection), and particle image velocimetry techniques. These evaluations include the assessment of emboli prevention capability, side-branch flow preservation, and influence on the branch flow pattern and velocity field. The novel covered stents demonstrated significantly higher emboli prevention capability than the corresponding bare metal stent, while preserving more than 83% of the original flow of the external carotid artery (ECA). Flow in the ECA through these covered stents was uniform without evidence of undesirable flow recirculation and reversed flow that might predispose the vessel wall to post-stenting intimal thickening and atherosclerotic plaque formation. This study demonstrated the potential of these novel covered stent designs for the treatment of carotid atherosclerotic stenosis. However, further computational and in vivo investigations of hemodynamics, biological effects, and mechanical performance of this covered stent design is warranted.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bharadvaj, B. K., R. F. Mabon, and D. P. Giddens. Steady flow in a model of the human carotid bifurcation. Part I—Flow visualization. J. Biomech. 15(5):349–362, 1982.
Coggia, M., O. Goëau-Brissonnière, J. L. Duval, J. P. Leschi, M. Letort, and M. D. Nagel. Embolic risk of the different stages of carotid bifurcation balloon angioplasty: an experimental study. J. Vasc. Surg. 31(3):550–557, 2000.
Connors Iii, J. J., D. Seidenwurm, J. C. Wojak, R. W. Hurst, M. E. Jensen, R. Wallace, T. Tomsick, J. Barr, C. Kerber, E. Russell, G. M. Nesbit, A. J. Fox, and F. Y. Tsai. Treatment of atherosclerotic disease at the cervical carotid bifurcation: current status and review of the literature. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 21(3):444–450, 2000.
Cutnell, J., and K. Johnson. Physics. New York: Wiley, 1998.
DeRubertis, B. G., R. A. Chaer, R. Gordon, H. Bell, R. L. Hynecek, F. M. Pieracci, J. Karwowski, K. C. Kent, and P. L. Faries. Determining the quantity and character of carotid artery embolic debris by electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy. J. Vasc. Surg. 45(4):716–725, 2007.
Di Carlo, A. Human and economic burden of stroke. Age Ageing 38(1):4–5, 2009.
Elsner, M., W. Auch-Schwelk, M. Britten, D. H. Walter, V. Schächinger, and A. M. Zeiher. Coronary stent grafts covered by a polytetrafluoroethylene membrane. Am. J. Cardiol. 84(3):335–338, 1999.
Fung, Y. C. Biomechanics, Mechanical Properties of Living Tissues. New York: Springer, 1993.
Greil, O., T. Kleinschmidt, W. Weiss, O. Wolf, P. Heider, S. Schaffner, M. Gianotti, T. Schmid, D. Liepsch, and H. Berger. Flow velocities after carotid artery stenting: impact of stent design. A fluid dynamics study in a carotid artery model with laser doppler anemometry. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 28(1):66–76, 2005.
Ho, P., H. L. Leo, F. Cui, S. H. Ng, and F. Kabinejadian. Membrane for covering a peripheral surface of a stent, (PCT) WO/2013/055293 A1, 2013.
Hoi, Y., B. A. Wasserman, Y. J. Xie, S. S. Najjar, L. Ferruci, E. G. Lakatta, G. Gerstenblith, and D. A. Steinman. Characterization of volumetric flow rate waveforms at the carotid bifurcations of older adults. Physiol. Meas. 31(3):291–302, 2010.
Hughes, P. E., and T. V. How. Flow structures at the proximal side-to-end anastomosis. Influence of geometry and flow division. J. Biomech. Eng. 117(2):224–236, 1995.
Ishibashi, H., M. Sunamura, and T. Karino. Flow patterns and preferred sites of intimal thickening in end-to-end anastomosed vessels. Surgery 117(4):409–420, 1995.
Kwa, A. T., K. K. Yeo, and J. R. Laird. The role of stent-grafts for prevention and treatment of restenosis. J. Cardiovasc. Surg. 51(4):579–589, 2010.
Müller-Hülsbeck, S., A. Gühne, M. Tsokos, E. J. Hüsler, S. R. Schaffner, F. Paulsen, J. Hedderich, M. Heller, and T. Jahnke. Stent-protected carotid angioplasty using a membrane stent: a comparative cadaver study. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 29(4):630–636, 2006.
Müller-Hülsbeck, S., T. Jahnke, P. Stolzmann, F. Paulsen, R. Wenke, and M. Heller. A new concept for covered stent protected carotid angioplasty: an ex vivo study. Rofo 175(12):1634–1638, 2003.
Perktold, K., M. Resch, and R. O. Peter. Three-dimensional numerical analysis of pulsatile flow and wall shear stress in the carotid artery bifurcation. J. Biomech. 24(6):409–420, 1991.
Raffel, M., C. E. Willert, S. T. Wereley, and J. Kompenhans. Particle Image Velocimetry. Berlin: Springer, 2007.
Rittgers, S. E., P. E. Karayannacos, and J. F. Guy. Velocity distribution and intimal proliferation in autologous vein grafts in dogs. Circ. Res. 42(6):792–801, 1978.
Rosamond, W., K. Flegal, G. Friday, K. Furie, A. Go, K. Greenlund, N. Haase, M. Ho, V. Howard, B. Kissela, S. Kittner, D. Lloyd-Jones, M. McDermott, J. Meigs, C. Moy, G. Nichol, C. J. O’Donnell, V. Roger, J. Rumsfeld, P. Sorlie, J. Steinberger, T. Thom, S. Wasserthiel-Smoller, and Y. Hong. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2007 update: a report from the american heart association statistics committee and stroke statistics subcommittee. Circulation 115(5):e69–e171, 2007.
Schillinger, M., P. Dick, G. Wiest, S. Gentzsch, S. Sabeti, M. Haumer, A. Willfort, C. Nasel, C. Wöber, J. Zeitlhofer, and E. Minar. Covered versus bare self-expanding stents for endovascular treatment of carotid artery stenosis: a stopped randomized trial. J. Endovasc. Ther. 13(3):312–319, 2006.
Sunamura, M., H. Ishibashi, and T. Karino. Flow patterns and preferred sites of intimal thickening in diameter-mismatched vein graft interpositions. Surgery 141(6):764–776, 2007.
Szólics, A., L. K. Sztriha, P. Szikra, M. Sźlics, A. Palḱ, and E. Vörös. The use of covered stents for the endovascular treatment of extracranial internal carotid artery stenosis: a prospective study with a 5-year follow-up. Eur. Radiol. 20(7):1772–1776, 2010.
Tann, S. M., and A. Pershad. A novel approach to the treatment of recurrent non-atherosclerotic carotid stenosis in a patient with Takayasu arteritis. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 80(2):337–341, 2012.
Tsai, M. J., Y. H. Tsai, and Y. M. Kuo. Characterization of the pattern of ischemic stroke induced by artificial particle embolization in the rat brain. Biomaterials 32(27):6381–6388, 2011.
White, S. S., C. K. Zarins, D. P. Giddens, H. Bassiouny, F. Loth, S. A. Jones, and S. Glagov. Hemodynamic patterns in two models of end-to-side vascular graft anastomoses: effects of pulsatility, flow division, reynolds number, and hood length. J. Biomech. Eng. 115(1):104–111, 1993.
Whitlow, P. L., P. Lylyk, H. Londero, O. A. Mendiz, K. Mathias, H. Jaeger, J. Parodi, C. Schönholz, and J. Milei. Carotid artery stenting protected with an emboli containment system. Stroke 33(5):1308–1314, 2002.
Yadav, J. S. Carotid stent, (PCT) WO/1998/053759 A2, 1998.
Zhao, S. Z., X. Y. Xu, A. D. Hughes, S. A. Thom, A. V. Stanton, B. Ariff, and Q. Long. Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a physiologically realistic model of a human carotid arterial bifurcation. J. Biomech. 33(8):975–984, 2000.
Acknowledgments
This project is financially supported by Biomedical Engineering Programme (BEP) of the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), under grant BEP-1021480004.
Conflict of interest
The authors affirm that there are no financial and personal relationships or involvement with any commercial organization that could inappropriately influence or bias the present manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Peter E. McHugh oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kabinejadian, F., Cui, F., Zhang, Z. et al. A Novel Carotid Covered Stent Design: In Vitro Evaluation of Performance and Influence on the Blood Flow Regime at the Carotid Artery Bifurcation. Ann Biomed Eng 41, 1990–2002 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0863-x