Abstract
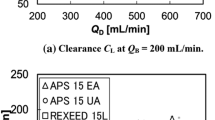
The mathematical theory that underlies a novel non-regenerated recirculating dialysate system (RDS) for improving diffusive clearance in hemodialyzers is presented. The theory states the conditions that hemodialyzers must meet to be suitable in RDS optimization. We have verified the applicability of the RDS for several Cuprophan and polysulfone (PS) commercial dialyzers, showing that PS (synthetic) membranes achieve the highest increments of diffusive clearance. A numerical simulation analysis over more general conditions defined by the dimensionless groups of the system demonstrated that the highest diffusive clearance improvements are achieved in dialyzers operating with a low value of the diffusive mass-transfer area/blood flow rate ratio. This study has provided the base for the assessment of the performance of the RDS as compared to several high-efficiency systems, presented in Part II of this work [M. Prado, L. M. Roa, A. Palma, and J. A. Milán, Ann. Biomed. Eng. (2004) submitted].
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen, R., T. H. Frost, and N. A. Hoenich. The influence of the dialysate flow rate on hollow fiber hemodialyzer performance. Artif. Organs 19(11):1176–1180, 1995.
Brendolan, A., C. Ronco, C. Crepaldi, L. Bragantini, M. Milan, F. Gastaldon, and G. La Greca. Double pass dialysis: A new method of renal replacement in patients with malfunctioning vascular access. Int. J. Artif. Organs 17(7):379–84, 1994.
Britton, N. F. A new method for mass transport problems with an application to haemofilters. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 52(3):630–650, 1992.
Buckingham, E. On physically similar systems: Illustration of the use of dimensional equations. Phys. Rev. 4(4):345–376, 1914.
Clark, W. R., R. J. Hamburger, and M. J. Lysaght. Effect of membrane composition and structure on solute removal and biocompatibility in hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 56(6):2005–215, 1999.
Clark, W. R., and J. H. Shinaberger. Clinical evaluation of a new high efficiency hemodialyzer: Polysynthane. Asaio J. 46(3):288–292, 2000.
Daugirdas, J. T., P. G. Blake, and T. S. Ing. Handbook of Dialysis. Lippincot Williams & Wilkins, 2001.
Elangovan, L., C. S. Shinaberger, J. A. Kraut, and J. H. Shinaberger. Hemo equilibrated Kt/V goals are difficult to achieve in large male patients. Asaio J. 47(3):235–239, 2001.
Frank, A., G. G. Lipscomb, and M. Dennis. Visualization of concentration fields in hemodialyzers by computed tomography. J. Membr. Sci. 175(2):239–251, 2000.
Gastaldon, F., A. Brendolan, C. Crepaldi, P. Frisone, S. Zamboni, V. d’Intini, S. Poulin, R. Hector, A. Granziero, K. Martins, R. Gellert, P. Inguaggiato, and C. Ronco. Effects of novel manufacturing technology on blood and dialysate flow distribution in a new low flux ‘‘alpha polysulfone’’ hemodialyzer. Int. J. Artif Organs 26(2):105–112, 2003.
Gotch, F. A., J. A. Sargent, and M. L. Keen. Whither goest Kt/V? Kidney Int. 58(Suppl 76):S3–S18, 2000.
Hauk, M., M. K. Kuhlmann, W. Riegel, and H. Kohler. In vivo effects of dialysate flow rate on Kt/V in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 35(1):105–111, 2000.
Kar, P. M., K. Kellner, T. S. Ing, and D. J. Leehey. Combined high-efficiency hemodialysis and charcoal hemoperfusion in severe n-acetylprocainamide intoxication. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 20(4):403–406, 1992.
Legallais, C., G. Catapano, B. von Harten, and U. Baurmeister. A theoretical model to predict the in vitro performance of hemodiafilters. J. Membr. Sci. 168(1–2):3–15, 2000.
Leon, J. B., and A. R. Sehgal. Identifying patients at risk for hemodialysis underprescription. Am. J. Nephrol. 21(3):200–207, 2001.
Leypoldt, J. K., and A. K. Cheung. Increases in mass transfer-area coefficients and urea Kt/V with increasing dialysate flow rate are greater for high-flux dialyzers. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 38(3):575–579, 2001.
Leypoldt, J. K., A. K. Cheung, L. Y. Agodoa, J. T. Daugirdas, T. Greene, and P. R. Keshaviah. Hemodialyzer mass transfer-area coefficients for urea increase at high dialysate flow rates: The hemodialysis (hemo) study. Kidney Int. 51(6):2013–2017, 1997.
Leypoldt, J. K., A. K. Cheung, and R. B. Deeter. Effect of hemodialyzer reuse: Dissociation between clearances of small and large solutes. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 32(2):295–301, 1998.
Leypoldt, J. K., and A. K. Cheung. Effect of low dialysate flow rate on hemodialyzer mass transfer area coefficients for urea and creatinine. Home Hemodial. Int. 3:51–54, 1999.
Mac-Kay, M. V., I. P. Fernandez, J. Herrera Carranza, and J. Sancez Burson. An in vitro study of the influence of a drug’s molecular weight on its overall (clt), diffusive (cld) and convective (clc) clearance through dialysers. Biopharmaceutics Drug Disposition 16(1):23–35, 1995.
Mandolfo, S., F. Malberti, E. Imbasciati, P. Cogliati, and A. Gauly. Impact of blood and dialysate flow and surface on performance of new polysulfone hemodialysis dialyzers. Int. J. Artif. Organs 26(2):113–120, 2003.
Michaels, A. S. Operating parameters and performance criteria for hemodialyzers and other membrane—separation devices. Trans. Am. Soc. Artif. Int. Organs 12:387–392, 1966.
Morti, S. M., and A. L. Zydney. Protein-membrane interactions during hemodialysis: Effects on solute transport. Asaio J. 44(4):319–326, 1998.
Ouseph, R., and R. A. Ward. Increasing dialysate flow rate increases dialyzer urea mass transfer-area coefficients during clinical use. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 37(2):316–320, 2001.
Paris, J., P. Guichardon, and F. Charbit. Transport phenomena in ultrafiltration: A new two-dimensional model compared with classical models. J. Membr. Sci. 207(1):43–58, 2002.
Prado, M., L. Roa, J. Reina-Tosina, A. Palma, and J. A. Milán. Virtual center for renal support: Technological approach to patient physiological image. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 49(12):1420–1430, 2002.
Prado, M., L. Roa, J. Reina-Tosina, A. Palma, and J. A. Milán. Renal telehealthcare system based on a patient physiological image: A novel hybrid approach in telemedicine. Telemed. J. e-Health 9(2):149–165, 2003.
Prado, M., Laura M. Roa, A. Palma, and J. A. Milán. Improving hollow fiber dialyzer efficiency with a recirculating dialysate system {II}: Comparision against two chamber dialysis systems. (submitted). Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2004.
Sagiv, A. Theoretical formulation of the diffusion through a slab-theory validation. J. Membr. Sci. 199(1–2):125–134, 2002.
Schepartz, B. Dimensional Analysis in Biomedical Sciences. Thomas, Springfield, IL, 1980.
Scott, M. K., B. A. Mueller, and W. R. Clark. Vancomycin mass transfer characteristics of high-flux cellulosic dialysers. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 12(12):2647–2653, 1997.
Scott, M. K., B. A. Mueller, K. M. Sowinski, and W. R. Clark. Dialyzer-dependent changes in solute and water permeability with bleach reprocessing. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 33(1):87–96, 1999.
Sridhar, N. R., K. Ferrand, D. Reger, P. Hayes, L. Pinnavaia, D. Butts, R. Kohli, and G. Papandenatos. Urea kinetics with dialyzer reuse—a prospective study. Am. J. Nephrol. 19(6):668–673, 1999.
Stiller, S., and H. Mann. A model of solute transport through the dialyzer membrane in hemodiafiltration. Semin. Dial. 12(Suppl 1):S76–S80, 1999.
Teruel, J. L., M. Fernández Lucas, J. R. Rodríguez, J. López Sánchez, R. Marcén, M. Rivera, and F. Liañoy J. Ortuño. [relationship between ionic dialysance and urea clearance] relación entre la dialisancia iónica y el aclaramiento de urea. Nefrología 20(2), 2000.
Ward, R. A., Blood flow rate: An important determinant of urea clearance and delivered Kt/V. Adv. Ren. Replace. Ther. 6(1):75–79, 1999.
Werynski, A., and J. Waniewski. Theoretical description of mass transport in medical membrane devices. Artif. Organs 19(5):420–427, 1995.
Wupper, A., F. Dellanna, C. A. Baldamus, and D. Woermann. Local transport processes in high-flux hollow fiber dialyzers. J. Membr. Sci. 131(1–2):181–193, 1997.
Wupper, A., D. Woermann, F. Dellanna, and C. A. Baldamus. Retrofiltration rates in high-flux hollow fiber hemodialyzers: Analysis of clinical data. J. Membr. Sci. 121(1):109–116, 1996.
Yeh, H. M., T. W. Cheng, and Y. J. Chen. Analysis of dialysis coupled with ultrafiltration in cross-flow membrane modules. J. Membr. Sci. 134(2):151–162, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prado, M., Roa, L.M., Palma, A. et al. Improving Hollow Fiber Dialyzer Efficiency with a Recirculating Dialysate System I: Theory and Applicability. Ann Biomed Eng 33, 642–655 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-4389-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-005-4389-8