Abstract
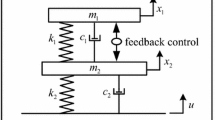
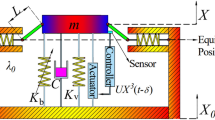
Traditional passive vibration absorbers are effective only when their natural frequencies are close to those of the excitations. To solve this problem, a vibration absorber with time-delayed feedback control is proposed to suppress vibration of the primary system under excitation with changing frequency. Firstly, the mechanical model of the delay coupled system is established. Then, the displacement transfer ratio of the system is obtained. The stability of the system is analyzed since delay may result in destabilization. Next, in order to design the control parameters, the vibration absorption performances of the proposed time-delayed vibration absorber are studied. The vibration absorption region is shown. The results show that time-delayed feedback control is able to change the response of the system. The effective vibration absorption frequency band is adjustable by tuning the control gain and time delay. The effective frequency band can be widened when choosing appropriate control parameters. The vibration absorption performances can be greatly improved by the time-delayed absorber. In addition, the optimum control parameters are obtained. Finally, the experimental prototype is constructed. Several tests with different control parameters are taken. The experimental and analytical results match quite well.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hermann, F.: Device for damping vibrations of bodies. U.S. Patent Application No. 989,958 (1909)
Benacchio, S., Malher, A., Boisson, J., et al.: Design of a magnetic vibration absorber with tunable stiffnesses. Nonlinear Dyn. 85, 893–911 (2016)
Acar, M.A., Yilmaz, C.: Design of an adaptive-passive dynamic vibration absorber composed of a string-mass system equipped with negative stiffness tension adjusting mechanism. J. Sound Vib. 332, 231–245 (2013)
Shui, X., Wang, S., Shui, X., et al.: Investigation on a mechanical vibration absorber with tunable piecewise-linear stiffness. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 330–343 (2018)
Sun, S., Yang, J., Li, W., et al.: Development of an MRE adaptive tuned vibration absorber with self-sensing capability. Smart Mater. Struct. 24, 095012 (2015)
Kumbhar, S.B., Chavan, S.P., Gawade, S.S.: Adaptive tuned vibration absorber based on magnetorheological elastomer-shape memory alloy composite. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 100, 208–223 (2018)
Lin, J., Huang, C.J., Chang, J., et al.: Active-passive vibration absorber of beam-cart-seesaw system with piezoelectric transducers. J. Sound Vib. 329, 4109–4123 (2010)
Shan, J., Liu, H.T., Sun, D.: Slewing and vibration control of a single-link flexible manipulator by positive position feedback (PPF). Mechatronics 15, 487–503 (2005)
El-Ganaini, W.A., Saeed, N.A., Eissa, M.: Positive position feedback (PPF) controller for absorption of nonlinear system vibration. Nonlinear Dyn. 72, 517–537 (2013)
El-Ganaini, W.A., Kandil, A., Eissa, M., et al.: Effects of delayed time active controller on the vibration of a nonlinear magnetic levitation system to multi excitations. J. Vib. Control 4, 1074–1090 (2014)
Mcdaid, A.J., Mace, B.R.: A robust adaptive tuned vibration absorber using semi-passive shunt electronics. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 63, 5069–5077 (2016)
Kim, S.M., Wang, S., Brennan, M.J.: Optimal and robust modal control of a flexible structure using an active dynamic vibration absorber. Smart Mater. Struct. 20, 45003–45013 (2011)
Lin, J.: An active vibration absorber of smart panel by using a decomposed parallel fuzzy control structure. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 18, 985–998 (2005)
Huang, S.J., Man, R.J.: Active vibration control of a dynamic absorber using fuzzy algorithms. Mechatronics 6, 317–336 (1996)
Lin, J., Liu, W.Z.: Experimental evaluation of a piezoelectric vibration absorber using a simplified fuzzy controller in a cantilever beam. J. Sound Vib. 296, 567–582 (2006)
Chang, C.S., Liu, T.S.: LQG controller for active vibration absorber in optical disk drive. IEEE Trans. Magn. 43, 799–801 (2007)
Thenozhi, S., Yu, W.: Sliding mode control of wind-induced vibrations using fuzzy sliding surface and gain adaptation. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 47, 1258–1267 (2016)
Ma, R.P., Sinha, A.: Neural network based active vibration absorber with state feedback control. J. Sound Vib. 190, 121–128 (1996)
Liu, Y., Zhao, S.: Controllability for a class of linear time-varying impulsive systems with time delay in control input. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56, 395–399 (2011)
Du, H.P., Zhang, N.: H-infinity, control for buildings with time delay in control via linear matrix inequalities and genetic algorithms. Eng. Struct. 30, 81–92 (2008)
Chang, P.H., Kim, D.S., Park, K.C.: Robust force/position control of a robot manipulator using time-delay control. Control Eng. Pract. 3, 1255–1264 (1995)
Xu, J., Cao, W.: Synthesized sliding mode and time-delay control for a class of uncertain systems. Automatica 36, 1909–1914 (2000)
Shin, Y.H., Kim, K.J.: Performance enhancement of pneumatic vibration isolation tables in low frequency range by time delay control. J. Sound Vib. 321, 537–553 (2009)
Shin, Y.H., Kim, K.J., Chang, P.H., et al.: Three degrees of freedom active control of pneumatic vibration isolation table by pneumatic and time delay control technique. J. Vib. Acoust. 132, 051013 (2010)
Xu, J., Sun, X.: A multi-directional vibration isolator based on quasi-zero-stiffness structure and time-delayed active control. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 100, 126–135 (2015)
Sun, X., Xu, J., Fu, J.: The effect and design of time delay in feedback control for a nonlinear isolation system. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 87, 206–217 (2017)
Sun, X., Zhang, S., Xu, J.: Parameter design of a multi-delayed isolator with asymmetrical nonlinearity. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 138, 398–408 (2018)
Jiao, G., Sun, X.: A six-direction absolute displacement sensor for time-delayed control based on quasi-zero-stiffness property. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 12, 1550147716673844 (2016)
Sun, X., Wang, F., Xu, J.: Dynamics and realization of a feedback-controlled nonlinear isolator with variable time delay. J. Vib. Acoust. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4041369
Yang, T., Cao, Q.: Delay-controlled primary and stochastic resonances of the SD oscillator with stiffness nonlinearities. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 103, 216–235 (2018)
Cheng, C., Li, S., Wang, Y., et al.: On the analysis of a high-static-low-dynamic stiffness vibration isolator with time-delayed cubic displacement feedback. J. Sound Vib. 378, 76–91 (2016)
Olgac, N., Holm-Hansen, B.T.: A novel active vibration absorption technique-delayed resonator. J. Sound Vib. 176, 93–104 (1994)
Olgac, N., Elmali, H., Vijayan, S.: Introduction to the dual frequency fixed delayed resonator. J. Sound Vib. 189, 355–367 (1996)
Olgac, N., Jalili, N.: Modal analysis of flexible beams with delayed resonator vibration absorber: theory and experiments. Sound Vib. 218, 307–331 (1998)
Jalili, N., Olgac, N.: Multiple delayed resonator vibration absorbers for multi-degree-of-freedom mechanical structures. J. Sound Vib. 223, 567–585 (1999)
Filipović, D., Olgac, N.: Delayed resonator with speed feedback—design and performance analysis. Mechatronics 12, 393–413 (2002)
Dan, P., Vyhlídal, T., Olgac, N.: Delayed resonator with distributed delay in acceleration feedback—design and experimental verification. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatronics 21, 2120–2131 (2015)
Kučera, V., Dan, P., Vyhlídal, T., et al.: Extended delayed resonators—design and experimental verification. Mechatronics 41, 29–44 (2017)
Kammer, A.S., Olgac, N.: Delayed-feedback vibration absorbers to enhance energy harvesting. J. Sound Vib. 363, 54–67 (2016)
Kammer, A.S., Olgac, N.: Delayed feedback control scheme for improved energy harvesting using piezoelectric networks. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 29, 1546–1559 (2018)
Liu, J., Liu, K.: A tunable electromagnetic vibration absorber: characterization and application. J. Sound Vib. 295, 708–724 (2006)
Liu, J., Liu, K.: Application of an active electromagnetic vibration absorber in vibration absorption. Struct. Control Health Monit. 17, 278–300 (2010)
Xu, J., Sun, Y.: Experimental studies on active control of a dynamic system via a time-delayed absorber. Acta Mech. Sin. 31, 229–247 (2015)
Sun, Y., Xu, J.: Experiments and analysis for a controlled mechanical absorber considering delay effect. J. Sound Vib. 339, 25–37 (2015)
Zhao, Y.Y., Xu, J.: Using the delayed feedback control and saturation control to suppress the vibration of the dynamical system. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 735–753 (2011)
Sun, X., Song, Y.: Dynamical performances of a vibration absorber for continuous structure considering time-delay coupling. Shock Vib. 2, 1–15 (2016)
Zhang, X., Xu, J., Ji, J.: Modelling and tuning for a time-delayed vibration absorber with friction. J. Sound Vib. 424, 137–157 (2018)
Zhang, X., Xu, J., Feng, Z.: Nonlinear equivalent model and its identification for a delayed absorber with magnetic action using distorted measurement. Nonlinear Dyn. 88, 937–954 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 11572224 and 11772229).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Xu, J. Parameter design for a vibration absorber with time-delayed feedback control. Acta Mech. Sin. 35, 624–640 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0822-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10409-018-0822-8