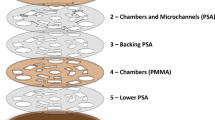
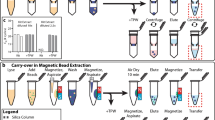
Abstract
We present a disc-based module for rotationally controlled solid-phase purification of RNA from cell lysate. To this end, multi-stage routing of a sequence of aqueous and organic liquids into designated waste and elution reservoirs is implemented by a network of strategically placed, solvent-selective composite valves . Using a bead-based stationary phase at the entrance of the router, we show that total RNA is purified with high integrity from cultured MCF7 and T47D cell lines, human leucocytes and Haemophilus influenzae cell lysates. Furthermore, we demonstrate the broad applicability of the device through the in vitro amplification of RNA purified on-disc using RT-PCR and NASBA. Our novel router will be at the pivot of a forthcoming, fully integrated and automated sample preparation system for RNA-based analysis .








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamo A, Heider PL, Weeranoppanant N, Jensen KF (2013) Membrane-based, liquid–liquid separator with integrated pressure control. Ind Eng Chem Res 31:10802–10808
Balladur V, Theretz A, Mandrand B (1997) Determination of the main forces driving DNA oligonucleotide adsorption onto aminated silica wafers. J Colloid Interface Sci 2:408–418
Boom R, Sol CJ, Salimanas MM, Jansen CL, Wertheim van Dillen PM, van der Noordaa J (1990) Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microb 28:495–503
Brenner T, Glatzel T, Zengerle R, Ducrée J (2005) Frequency-dependent transversal flow control in centrifugal microfluidics. Lab Chip 5:146–150
Bustin SA, Nolan T (2004) Pitfalls of quantitative real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction. J Biomol Tech 3:155–166
Cho YK, Lee JG, Park JM, Lee BS, Lee Y, Ko C (2007) One-step pathogen specific DNA extraction from whole blood on a centrifugal microfluidic device. Lab Chip 7:565–573
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Acid three phase phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem 1:156–159
Clancy E, Glynn B, Reddington K, Smith TJ, Barry T (2012) Culture confirmation of Listeria monocytogenes using tmRNA as a diagnostics target. J Microbiol Methods 3:427–435
Copois V, Bibeau F, Bascoul-Mollevi C, Salvetat N, Chalbos P, Bareil C, Candeil L, Fraslon C, Conseiller E, Granci V, Maziére P, Kramar A, Ychou M, Pau B, Martineau P, Molina F, Del Rio M (2007) Impact of RNA degradation on gene expression profiles: assessment of different methods to reliably determine RNA quality. J Biotech 127:549–559
Duarte GRM, Price CW, Littlewood JL, Haverstick DM, Ferrance JP, Carrilho E, Landers JP (2010) Characterization of dynamic solid phase DNA extraction from blood with magnetically controlled silica beads. Analyst 135:531–537
Duarte GRM, Price CW, Augustine BH, Carrilho E, Landers JP (2011) Dynamic solid phase DNA extraction and PCR amplification in polyester-toner based microchip. Anal Chem 83:5182–5189
Ducrée J, Haeberle S, Lutz S, Pausch S, Stetten FV, Zengerle R (2007) The centrifugal microfluidic. Bio-Disk platform J Micromech Microeng 17:103–115
Foudeh AM, Fatanat TD, Veres T, Tabrizian M (2012) Microfluidic designs and techniques using lab-on-a-chip devices for pathogen detection for point-of-care diagnostics. Lab Chip 12:3249–3266
Garcia-Cordero JL, Basabe-Desmonts L, Ducrée J, Ricco AJ (2010) Liquid recirculation in microfluidic channels by the interplay of capillary and centrifugal forces. Microfluidics Nanofluidics 9:695–703
Gorkin R III, Nwankire CE, Gaughran J, Zhang J, Donohoe GG, Rock M, O’Kennedy R, Ducrée J (2012) Centrifugo-pneumatic valving utilizing dissolvable films. Lab Chip 12:2894–2902
Haeberle S, Pausch S, Burger R, Lutz S, von Stetten JDF, Zengerle R (2007) Automation of nucleic acid extraction by a Coriolis-force actuated droplet router. In: \(\mu\)TAS Proceedings, pp 1231–1233
Hagan KA, Meier WL, Ferrance JP, Landers JP (2009) Chitosan-coated silica as a solid phase for RNA purification in a microfluidic device. Anal Chem 81:5249–5256
Heneghan HM, Miller N, Kelly R, Newell J, Kerin MJ (2010) Systemic miRNA-195 differentiates breast cancer from other malignancies and is a potential biomarker for detecting noninvasive and early stage disease. Oncologist 7:673–682
Hiorns LR, Bradshaw TD, Skeleton LA, Yu Q, Kelland LR, Leyland-Jones B (2004) Variation in RNA expression and genomic DNA content acquired during cell culture. Brit J Cancer 90:476–482
Huggett JF, Novak T, Garson J, Green C, Morris-Jones SD, Miller RF, Zumla A (2008) Differential susceptibility of PCR reactions to inhibitors: an important and unrecognised phenomenon. BMC Res Notes 1:70
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2012) MicroRNA involvement in human cancer. Carcinogenesis 33:1126–1133
Jung JH, Park BH, Choi YK, Seo TS (2013) A microbead incorporated centrifugal sample pretreatment microdevice. Lab Chip 13:3383–3388
Katcher HL, Schwartz I (1994) A distinctive property of Taq DNA polymerase: enzymatic amplification in the presence of phenol. Bio Tech 1:84–92
Kim J, Hee Jang S (2004) Cell lysis on a microfluidic CD (compact disc). Lab Chip 5:516–522
Kim J, Kido H, Rangel RH, Madou MJ (2008) Passive flow switching valves on a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Sens Actu B Chem 2:613–621
Kim J, Johnson M, Hill P, Gale BK (2009) Microfluidic sample preparation: cell lysis and nucleic acid purification. Integr Biol Quant Biosci From Nano To Macro 1:574–586
Kinahan DJ, Kearney SM, Dimov N, Glynn MT, Ducrée J (2014) Event-triggered logical flow control for comprehensive process integration of multi-step assays on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Lab Chip. doi:10.1039/C4LC00380B
Kloke A, Fiebach AR, Zhang S, Drechsel L, Niekrawietz S, Hoehl MM, Kneusel R, Panthel K, Steigert J, von Stetten F, Zengerle R, Paust N (2014) The LabTube-a novel microfluidic platform for assay automation in laboratory centrifuges. Lab Chip 9:1527–1537
Kosaka N, Iguchi H, Ochiya T (2010) Circulating microRNA in body fluid: a new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci 101:2087–2092
Lee BS, Lee JN, Park JM, Lee JG, Kim S, Cho YK (2009) A fully automated immunoassay from whole blood on a disc. Lab Chip 9:1548–1555
Lee BS, Lee YU, Kim HS, Kim TH, Park J, Lee JG, Kim J, Kim H, Lee WG, Cho YK (2011) Fully integrated lab-on-a-disc for simultaneous analysis of biochemistry and immunoassay from whole blood. Lab Chip 11:70–78
Linares AV, Gorkin R III, Glynn B, Godino N, Miller N, Kerin M, Barry T, Smith TJ, Ducrée J (2011) Purification of miRNA from whole blood by chemical lysis and phase separation in a centrifugo-pneumatic micro-homogenizer. In: \(\mu\)TAS Proceedings, pp 1460–1462
Madou MJ, Zoval J, Jia G, Kido H, Kim J, Kim N (2006) Lab on a CD. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 8:601–628
Mark D, Haeberle S, Metz T, Lutz S, Ducrée J, Zengerle R, Stetten FV (2008) Aliquoting structure for centrifugal microfluidics. In: MEMS Proceedings, pp 11–14
McCalla SE, Tripathi A (2011) Microfluidic reactors for diagnostics applications. Ann Rev Biomed Eng 13:321–343
Mitchell PS, Parkin RK, Kroh EM, Fritz BR, Wyman SK, Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Peterson A, Noteboom J, O’Briant KC, Allen A, Lin DW, Urban N, Drescher CW, Knudsen BS, Stirewalt DL, Gentleman R, Vessella RL, Nelson PS, Martin DB, Tewari M (2008) Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 50:10513–10521
Nwankire CE, Donohoe GG, Zhang X, Siegrist J, Somers M, Kurzbuch D, Monaghan R, Kitsara M, Burger R, Hearty S, Murrell J, Martin C, Rock M, Barret L, Daniels S, McDonagh C, O’Kennedy R, Ducrée J (2013) At-line bioprocess monitoring by immunoassay with rotationally controlled serial siphoning and integrated supercritical angle fluorescence optics. Anal Chem Acta 781:54–62
O’Grady J, Lacey K, Glynn B, Smith TJ, Barry T, Maher M (2009) tmRNA-a novel high-copy-number RNA diagnostic target-its application for Staphylococcus aureus detection using real-time NASBA. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2:218–223
Park JM, Cho YK, Lee BS, Lee JG, Ko C (2007) Multifunctional microvalves control by optical illumination on nanoheaters and its application in centrifugal microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7:557–564
Park BH, Jung JH, Zhang H, Lee NY, Seo TS (2012) A rotary microsystem for simple, rapid and automatic RNA purification. Lab Chip 12:3875–3881
Park J, Sunkara V, Kim TH, Hwang H, Cho YK (2012) Lab-on-a-disc for fully integrated multiplex immunoassays. Anal Chem 84:2133–2140
Schembri CT, Burd TL, Kopf-Sill AR, Shea LR, Braynin B (1995) Centrifugation and capillarity integrated into a multiple analyte whole blood analyser. J Autom Chem 17:99–104
Schroeder A, Mueller O, Stoccker S, Salowsky R, Leiber M, Gassmann M, Lightfoot S, Menzel W, Granzow M, Regg T (2006) The RIN: an RNA integrity number for assigning integrity values to RNA measurements. BMC Mol Biol 7:3
Steigert J, Brenner T, Grumman M, Riegger L, Lutz S, Zengerle R, Ducrée J (2007) Integrated siphon-based metering and sedimentation of whole blood on a hydrophilic lab-on-a-disk. Biomed Microdev 9:675–679
Summerer D, Marx A (2002) A molecular beacon for quantitative monitoring of the DNA polymerase reaction in real-time. Angew Chem Int Ed 19:3620–3622
Tam MF, Dodd JA, Hill WE (1981) Physical characteristics of 16S rRNA under reconstitution conditions. J Biol Chem 12:6430–6434
Tan SC, Yiap BC (2009) DNA, RNA, and protein extraction: the past and the present. J Biomed Biotechnol 1–10. Article ID 574398. doi:10.1155/2009/574398
Valasek MA, Repa JJ (2005) The power of real-time PCR. Adv Physiol Educ 29:151–159
van Oordt T, Barb Y, Smetana J, Zengerle R, von Stetten F (2013) Miniature stick-packaging—an industrial technology for pre-storage and release of reagents in lab-on-a-chip systems. Lab Chip 15:2888–2892
Wen J, Legendre L, Bienvenue JM, Landers JP (2008) Purification of nucleic acids in microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 80:6472–6479
Zehnle S, Schwemmer F, Roth G, von Stetten F, Zengerle R, Paust N (2012) Centrifugo-dynamic inward pumping of liquids on a centrifugal microfluidic platform. Lab Chip 24:5142–5145
Zhao X, Dong T, Yang Z, Pires N, Høivik N (2012) Compatible immuno-NASBA LOC device for quantitative detection of waterborne pathogens: design and validation. Lab Chip 12:602–612
Zoval J, Madou MJ (2004) Centrifuge-based fluidic platforms. IEEE Proc 92:140–153
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Science Foundation Ireland under Grant 10/CE/B1821. Jennifer Gaughran was funded through BioAnalysis and Therapeutics Structured Ph.D. Programme (Bio-AT) by HEA-PRTLI V. The authors also thank Prof. Richard O’Kennedy’s group in Dublin City University for allowing us to use their cell culture facilities. We would also like to thank Karsten Holona and her team in Harke PackPro for providing dissolvable films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (mpg 23830 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dimov, N., Clancy, E., Gaughran, J. et al. Solvent-selective routing for centrifugally automated solid-phase purification of RNA. Microfluid Nanofluid 18, 859–871 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1477-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1477-9