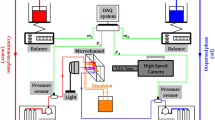
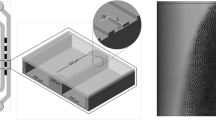
Abstract
The capacity of microfluidic technology to fabricate monodisperse emulsion droplets is well established. Parallelisation of droplet production is a prerequisite for using such an approach for making high-quality materials for either fundamental or industrial applications where product quantity matters. Here, we investigate the emulsification efficiency of parallelised drop generators based on a flow-focusing geometry when incorporating the role of partial wetting in order to make emulsion droplets with a diameter below 10 μm. Confinement intrinsically encountered in microsystems intensifies the role played by interfaces between liquids and solids. We thus take advantage of partial wetting to enhance the maximum confinement accessible due to liquid flow focusing. We compare the performances brought by partial wetting to more established routes such as step emulsification. We show that the step configuration and the partial wetting regime are both well suited for being parallelised and thus open the way to the production of fine and calibrated emulsions for further applications. Finally, this new route of emulsification that exploits partial wetting between the fluids and the channel walls opens possibilities to the formation of substantially smaller droplets, as required in many fields of application.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate AR, Poitzsch A, Hwang Y, Lee J, Czerwinska J, Weitz DA (2009) Impact of inlet channel geometry on microfluidic drop formation. Phys Rev E 80(2):026310
Anna SL, Mayer HC (2006) Microscale tipstreaming in a microfluidic flow focusing device. Phys Fluids 18(12):121512
Anna SL, Bontoux N, Stone HA (2003) Formation of dispersions using “flow focusing” in microchannels. Appl Phys Lett 82(3):364–366
Barbier V, Willaime H, Tabeling P, Jousse F (2006) Producing droplets in parallel microfluidic systems. Phys Rev E 74(4):046306
Bartolo D, Degre G, Nghe P, Studer V (2008) Microfluidic stickers. Lab Chip 8(2):274–279
Bonfillon A, Langevin D (1993) Viscoelasticity of monolayers at oil-water interfaces. Langmuir 9(8):2172–2177
Bremond N, Bibette J (2012) Exploring emulsion science with microfluidics. Soft Matter 8(41):10549–10559
Castro-Hernandez E, van Hoeve W, Lohse D, Gordillo JM (2011) Microbubble generation in a co-flow device operated in a new regime. Lab Chip 11(12):2023–2029
Christopher GF, Anna SL (2007) Microfluidic methods for generating continuous droplet streams. J Phys D 40(19):R319–R336
Cygan ZT, Cabral JT, Beers KL, Amis EJ (2005) Microfluidic platform for the generation of organic-phase microreactors. Langmuir 21(8):3629–3634
Dangla R, Fradet E, Lopez Y, Baroud CN (2013) The physical mechanisms of step emulsification. J Phys D Appl Phys 46(11):114003
Dendukuri D, Doyle PS (2009) The synthesis and assembly of polymeric microparticles using microfluidics. Adv Mater 21(41):4071–4086
Dollet B, van Hoeve W, Raven JP, Marmottant P, Versluis M (2008) Role of the channel geometry on the bubble pinch-off in flow-focusing devices. Phys Rev Lett 100(3):034504
Dreyfus R, Tabeling P, Willaime H (2003) Ordered and disordered patterns in two-phase flows in microchannels. Phys Rev Lett 90(14):144505
Fitch R (1997) Polymer colloids: a comprehensive introduction. Academic Press, San Diego
Ganan-Calvo AM, Gordillo JM (2001) Perfectly monodisperse microbubbling by capillary flow focusing. Phys Rev Lett 87(27):274501
Ganan-Calvo AM, Gonzalez-Prieto R, Riesco-Chueca P, Herrada MA, Flores-Mosquera M (2007) Focusing capillary jets close to the continuum limit. Nature Phys 3(10):737–742
Glotzer SC, Solomon MJ (2007) Anisotropy of building blocks and their assembly into complex structures. Nat Mater 6(8):557–562
Guillot P, Colin A, Utada AS, Ajdari A (2007) Stability of a jet in confined pressure-driven biphasic flows at low reynolds numbers. Phys Rev Lett 99(10):104502
Hong L, Jiang S, Granick S (2006) Simple method to produce janus colloidal particles in large quantity. Langmuir 22(23):9495–9499
Humphry KJ, Ajdari A, Fernandez-Nieves A, Stone HA, Weitz DA (2009) Suppression of instabilities in multiphase flow by geometric confinement. Phys Rev E 79(5):056310
Jeong WC, Lim JM, Choi JH, Kim JH, Lee YJ, Kim SH, Lee G, Kim JD, Yi GR, Yang SM (2012) Controlled generation of submicron emulsion droplets via highly stable tip-streaming mode in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 12(8):1446–1453
Joscelyne SM, Tragardh G (2000) Membrane emulsification—a literature review. J Membr Sci 169(1):107–117
Kawakatsu T, Kikuchi Y, Nakajima M (1997) Regular-sized cell creation in microchannel emulsification by visual microprocessing method. J Am Oil Chem Soc 74(3):317–321
Kobayashi I, Nakajima M, Chun K, Kikuchi Y, Fukita H (2002) Silicon array of elongated through-holes for monodisperse emulsion droplets. Aiche Journal 48(8):1639–1644
Kobayashi I, Mukataka S, Nakajima M (2005) Novel asymmetric through-hole array microfabricated on a silicon plate for formulating monodisperse emulsions. Langmuir 21(17):7629–7632
Kobayashi I, Wada Y, Uemura K, Nakajima M (2010) Microchannel emulsification for mass production of uniform fine droplets: integration of microchannel arrays on a chip. Microfluid Nanofluid 8(2):255–262
Leal-Calderon F, Schmitt V, Bibette J (2007) Emulsion science—basic principles. Springer, Berlin
Lee JN, Park C, Whitesides GM (2003) Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 75(23):6544–6554
Li W, Nie ZH, Zhang H, Paquet C, Seo M, Garstecki P, Kumacheva E (2007) Screening of the effect of surface energy of microchannels on microfluidic emulsification. Langmuir 23(15):8010–8014
Li W, Greener J, Voicu D, Kumacheva E (2009) Multiple modular microfluidic (m-3) reactors for the synthesis of polymer particles. Lab Chip 9(18):2715–2721
Liabakk NB, Nustad K, Espevik T (1990) A rapid and sensitive immunoassay for tumor necrosis factor using magnetic monodisperse polymer particles. J Immunol Methods 134(2):253–259
Lucassen-Reynders E, Kuijpers K (1992) The role of interfacial properties in emulsification. Colloids Surf 65(23):175–184
Malloggi F, Pannacci N, Attia R, Monti F, Mary P, Willaime H, Tabeling P, Cabane B, Poncet P (2010) Monodisperse colloids synthesized with nanofluidic technology. Langmuir 26(4):2369–2373
Manoharan VN, Elsesser MT, Pine DJ (2003) Dense packing and symmetry in small clusters of microspheres. Science 301(5632):483–487
Margulies M et al (2005) Genome sequencing in microfabricated high-density picolitre reactors. Nature 437(7057):376–380
McDonald JC, Duffy DC, Anderson JR, Chiu DT, Wu HK, Schueller OJA, Whitesides GM (2000) Fabrication of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane). Electrophoresis 21(1):27–40
Nakashima T, Shimizu M, Kukizaki M (2000) Particle control of emulsion by membrane emulsification and its applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 45(1):47–56
Nisisako T, Torii T (2008) Microfluidic large-scale integration on a chip for mass production of monodisperse droplets and particles. Lab Chip 8(2):287–293
Olsvik O, Popovic T, Skjerve E, Cudjoe KS, Hornes E, Ugelstad J, Uhln M (1994) Magnetic separation techniques in diagnostic microbiology. Clin Microbiol Rev 7(1):43–54
Priest C, Herminghaus S, Seemann R (2006) Generation of monodisperse gel emulsions in a microfluidic device. Appl Phys Lett 88(2):024106
Roberts CC, Rao RR, Loewenberg M, Brooks CF, Galambos P, Grillet AM, Nemer MB (2012) Comparison of monodisperse droplet generation in flow-focusing devices with hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Lab Chip 12(8):1540–1547
Romanowsky MB, Abate AR, Rotem A, Holtze C, Weitz DA (2012) High throughput production of single core double emulsions in a parallelized microfluidic device. Lab Chip 12(4):802–807
Rotem A, Abate AR, Utada AS, Van Steijn V, Weitz DA (2012) Drop formation in non-planar microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 12(21):4263–4268
Seo M, Nie ZH, Xu SQ, Mok M, Lewis PC, Graham R, Kumacheva E (2005) Continuous microfluidic reactors for polymer particles. Langmuir 21(25):11614–11622
Shah RK, Kim JW, Agresti JJ, Weitz DA, Chu LY (2008) Fabrication of monodisperse thermosensitive microgels and gel capsules in microfluidic devices. Soft Matter 4(12):2303–2309
Shui LL, van den Berg A, Eijkel JCT (2011) Scalable attoliter monodisperse droplet formation using multiphase nano-microfluidics. Microfluid Nanofluid 11(1):87–92
Song H, Chen DL, Ismagilov RF (2006) Reactions in droplets in microflulidic channels. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(44):7336–7356
Stone HA (1990) A simple derivation of the time-dependent convective-diffusion equation for surfactant transport along a deforming interface. Phys Fluids A-Fluid Dyn 2(1):111–112
Sugiura S, Nakajima M, Kumazawa N, Iwamoto S, Seki M (2002) Characterization of spontaneous transformation-based droplet formation during microchannel emulsification. J Phys Chem B 106(36):9405–9409
Tawfik DS, Griffiths AD (1998) Man-made cell-like compartments for molecular evolution. Nat Biotechnol 16(7):652–656
Tetradis-Meris G, Rossetti D, de Torres CP, Cao R, Lian GP, Janes R (2009) Novel parallel integration of microfluidic device network for emulsion formation. Ind Eng Chem Res 48(19):8881–8889
Theberge AB, Courtois F, Schaerli Y, Fischlechner M, Abell C, Hollfelder F, Huck WTS (2010) Microdroplets in microfluidics: an evolving platform for discoveries in chemistry and biology. Angew Chem Int Ed 49(34):5846–5868
van Dijke K, Veldhuis G, Schroen K, Boom R (2009) Parallelized edge-based droplet generation (edge) devices. Lab Chip 9(19):2824–2830
Vladisavljevic GT, Duncanson WJ, Shum HC, Weitz DA (2012a) Emulsion templating of poly(lactic acid) particles: Droplet formation behavior. Langmuir 28(36):12948–12954
Vladisavljevic GT, Kobayashi I, Nakajima M (2012b) Production of uniform droplets using membrane, microchannel and microfluidic emulsification devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 13(1):151–178
Vyawahare S, Griffiths AD, Merten CA (2010) Miniaturization and parallelization of biological and chemical assays in microfluidic devices. Chem Biol 17(10):1052–1065
Wang ZF, Guo HS, Yu YL, He NY (2006) Synthesis and characterization of a novel magnetic carrier with its composition of fe3o4/carbon using hydrothermal reaction. J Magn Magn Mater 302(2):397–404
Ward AFH, Tordai L (1946) Time-dependence of boundary tensions of solutions i. the role of diffusion in time-effects. J Chem Phys 14(7):453–461
Zerrouki D, Baudry J, Pine D, Chaikin P, Bibette J (2008) Chiral colloidal clusters. Nature 455(7211):380–382
Acknowledgments
We thank Mathilde Reyssat, Florent Malloggi and Rémi Dreyfus for fruitful discussions as well as Fabrice Monti for technical help. This work was supported by the EC-Marie Curie actions and BioMaX (Project Number 264637), and Investissement d’Avenir Program DigiDiag.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, C., Giles, R., Sergeyeva, V. et al. Parallelised production of fine and calibrated emulsions by coupling flow-focusing technique and partial wetting phenomenon. Microfluid Nanofluid 17, 959–966 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1363-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-014-1363-5