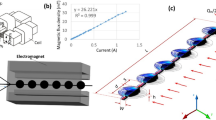
Abstract
We investigate the spreading phenomena caused by the interaction between a uniform magnetic field and a magnetic fluid in microchannels. The flow system consists of two liquids: a ferrofluid and a mineral oil. The ferrofluid consists of superparamagnetic nanoparticles suspended in an oil-based carrier. Under a uniform magnetic field, the superparamagnetic particles are polarized and represent magnetic dipoles. The magnetization of the magnetic nanoparticles leads to a force resulting in the change of diffusion behavior inside the microchannel. Mixing due to secondary flow close to the interface also contributes to the spreading of the ferrofluid. The magnetic force acting on the liquid/liquid interface is caused by the mismatch of magnetization between the nanoparticles and surrounding liquid in a multiphase flow system. This paper examines the roles of magnetic force in the observed spreading phenomena. The effect of particles on the flow field is also considered. These phenomena would allow simple wireless control of a microfluidic system without changing the flow rates. These phenomena can potentially be used for focusing and sorting in cytometry.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knight JB, Vishwanath A, Brody JP, Austin RH (1998) Hydrodynamic focusing on a silicon chip: mixing nanoliters in microseconds. Phys Rev Lett 80(17):3863
Rosensweig RE, Kaiser R, Miskolczy G (1969) Viscosity of magnetic fluid in a magnetic field. J Colloid Interface Sci 29(4):680
Pankhurst Q, Connolly J, Jones S, Dobson J (2003) Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J Phys D Appl Phys 36:R167
Matsunaga T, Kamiya S (1987) Use of magnetic particles isolated from magnetotactic bacteria for enzyme immobilization. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26(4):328
Dressman D, Yan H, Traverso G, Kinzler K, Vogelstein B (2003) Transforming single DNA molecules into fluorescent magnetic particles for detection and enumeration of genetic variations. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(15):8817
Yoza B, Matsumoto M, Matsunaga T (2002) DNA extraction using modified bacterial magnetic particles in the presence of amino silane compound. J Biotechnol 94(3):217
Rida A, Gijs M (2004) Anal Chem 76(21):6239
Astalan A, Ahrentorp F, Johansson C, Larsson K, Krozer A (2004) Manipulation of self-assembled structures of magnetic beads for microfluidic mixing and assaying. Biosensors Bioelectron 19(8):945
Shinkai M (2002) Functional magnetic particles for medical application. J Biosci Bioeng 94(6):606
Korneva G, Ye H, Gogotsi Y, Halverson D, Friedman G, Bradley J, Kornev K (2005) Carbon nanotubes loaded with magnetic particles. Nano Lett 5(5):879
Nguyen NT (2011) Micro magnetofluidics—interactions between magnetism and fluid flow on the microscale. Microfluid Nanofluid 12(1–4):1
Zhu T, Lichlyter D, Haidekker M, Mao L (2011) Analytical model of microfluidic transport of non-magnetic particles in ferrofluids under the influence of a permanent magnet. Microfluid Nanofluid 10(6):1233
Zhu T, Cheng R, Mao L (2011) Focusing microparticles in a microfluidic channel with ferrofluids in Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems Conference (TRANSDUCERS). In: 16th international IEEE, 2011, pp 1280–1283
Zhu T, Marrero F, Mao L (2010) Continuous separation of non-magnetic particles inside ferrofluids. Microfluid Nanofluid 9(4):1003
Zhu T, Cheng R, Lee S, Rajaraman E, Eiteman M, Querec T, Unger E, Mao L (2012) Continuous-flow ferrohydrodynamic sorting of particles and cells in microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 12:1–10
Kose A, Fischer B, Mao L, Koser H (2009) Label-free cellular manipulation and sorting via biocompatible ferrofluids. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(51):21478
Liang L, Xuan X (2012) Diamagnetic particle focusing using ferromicrofluidics with a single magnet. Microfluid Nanofluid, 1–7
Blums E (1980) Some aspects of heat and mass transfer in magnetic fluids. IEEE Trans Magn 16(2):347
Wang Y, Zhe J, Chung B, Dutta P (2008) A rapid magnetic particle driven micromixer. Microfluid Nanofluid 4(5):375
Le T, Suh Y, Kang S (2009) Efficient mixing in microchannel by using magnetic nanoparticles. Int J Math Models Methods Appl Sci, 58–67
Reza Habibi M, Ghasemi M (2011) Numerical study of magnetic nanoparticles concentration in biofluid (blood) under influence of high gradient magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 323(1):32
Furlani E, Xue X (2012) Field, force and transport analysis for magnetic particle-based gene delivery. Microfluid Nanofluid, 1–14
Wei Z, Lee C, Lai M (2010) Magnetic particle separation using controllable magnetic force switches. J Magn Magn Mater 322(1):19
Zolgharni M, Azimi S, Bahmanyar M, Balachandran W (2007) A numerical design study of chaotic mixing of magnetic particles in a microfluidic bio-separator. Microfluid Nanofluid 3(6):677
Thurm S, Odenbach S (2002) Magnetoviscous separation of ferrofluids. J Magn Magn Mater 252(1-3 SPEC ISS):247
Wu Z, Nguyen NT (2005) Convective-diffusive transport in parallel lamination micromixers. Microfluid Nanofluid 1(3):208
Odenbach S, Thurm S (2003) Magnetoviscous effects in ferrofluids. Ferrofluids, 185–201
Blums E (1995) Some new problems of complex thermomagnetic and diffusion-driven convection in magnetic colloids. J Magn Magn Mater 149(1):111
Blums E (1999) Mass transfer in nonisothermal ferrocolloids under the effect of a magnetic field. J Magn Magn Mater 201(1):242
Wen C, Liang K, Chen H, Fu L (2011) Numerical analysis of a rapid magnetic microfluidic mixer. Electrophoresis 32(22):3268
Patankar S (1981) A calculation procedure for two-dimensional elliptic situations. Numer Heat Transf 4(4):409
Wu Z, Nguyen NT (2005) Rapid mixing using two-phase hydraulic focusing in microchannels. Biomedical Microdevices 7(1):13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, GP., Nguyen, NT. Magnetofluidic spreading in microchannels. Microfluid Nanofluid 13, 655–663 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1056-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-012-1056-x