Abstract
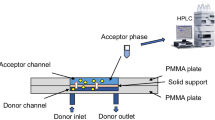
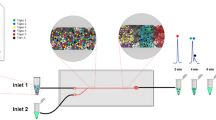
Radix Salvia Miltiorrhiza, a famous herb medicine is widely used in China and limitedly used in USA, Japan, and other countries for the treatment of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. This herb medicine has two groups (non-polar and polar) of active ingredients with distinct clinical effects, and thus theses ingredients should be separately used to enhance therapeutic efficacy and reduce side effect. In this article, as an alternative of conventional mechanical shaking and separatory funnel, laminar flow extraction in microfluidic chip is proposed to separate the two kinds of herb ingredients. Compared with conventional methods, microfluidic chip provides continuous extraction, less labor intensity, and better performance. Furthermore, we employ three-phase laminar flow to provide double liquid–liquid interface area, circumventing the low efficiency of two-phase laminar flow. Therefore, the extraction ratio is dramatically improved to 92% (tanshinone IIA). To predict the extraction ratio, a straightforward theoretical model is also established and agrees well with the experimental results. This microfluidic chip would be a powerful technical platform for handling complicated natural products.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aota A, Nonaka M, Hibara A, Kitamori T (2007) Countercurrent laminar microflow for highly efficient solvent extraction. Angew Chem Int Ed 46(6):878–880
Aota A, Mawatari K, Takahashi S, Matsumoto T, Kanda K, Anraku R, Hibara A, Tokeshi M, Kitamori T (2009) Phase separation of gas-liquid and liquid-liquid microflows in microchips. Microchim Acta 164(3–4):249–255
Bruus H (2008) Theoretical microfluidics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Chen H, Fang Q, Yin XF, Fang ZL (2005) Microfluidic chip-based liquid-liquid extraction and preconcentration using a subnanoliter-droplet trapping technique. Lab Chip 5(7):719–725
Cheng TO (2007) Cardiovascular effects of Danshen. Int J Cardiol 121(1):9–22
Cui L, Wu T, Liu YY, Deng YF, Ai CM, Chen HQ (2004) Tanshinone prevents cancellous bone loss induced by ovariectomy in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(5):678–684
Favre E (1996) Swelling of crosslinked polydimethylsiloxane networks by pure solvents: influence of temperature. Eur Polym J 32(10):1183–1188
Hibara A, Nonaka M, Hisamoto H, Uchiyama K, Kikutani Y, Tokeshi M, Kitamori T (2002) Stabilization of liquid interface and control of two-phase confluence and separation in glass microchips by utilizing octadecylsilane modification of microchannels. Anal Chem 74(7):1724–1728
Hisamoto H, Horiuchi T, Uchiyama K, Tokeshi M, Hibara A, Kitamori T (2001) On-chip integration of sequential ion-sensing system based on intermittent reagent pumping and formation of two-layer flow. Anal Chem 73(22):5551–5556
Hu P, Liang QL, Luo GA, Zhao ZZ, Jiang ZH (2005a) Multi-component HPLC fingerprinting of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae and its LC-MS-MS identification. Chem Pharm Bull 53(6):677–683
Hu P, Luo GA, Zhao ZZ, Jiang ZH (2005b) Quantitative determination of four diterpenoids in Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae using LC-MS-MS. Chem Pharm Bull 53(6):705–709
Hu P, Luo GA, Zhao ZZ, Jiang ZH (2005c) Quality assessment of Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae. Chem Pharm Bull 53(5):481–486
Kenis PJA, Ismagilov RF, Whitesides GM (1999) Microfabrication inside capillaries using multiphase laminar flow patterning. Science 285(5424):83–85
Lay IS, Chiu JH, Shiao MS, Lu WY, Wu CW (2003) Crude extract of Salvia miltiorrhiza and salvianolic acid B enhance in vitro angiogenesis in murine SVR endothelial cell line. Planta Med 69(1):26–32
Lee JN, Park C, Whitesides GM (2003) Solvent compatibility of poly(dimethylsiloxane)-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 75(23):6544–6554
Li LN (1997) Water soluble active components of Salvia miltiorrhiza and related plants. J Chin Pharm Sci 6:57–64
Li LD, Zhang RL, Liu CY, Ning KY, Li YK, Feng XQ, He J (2003) Establishment of Chinese Miniswine Model of myocardial infarct by catheterization in coronary artery. Chin J New Drugs 12:999–1004
Lo TC, Baird MHI, Carl H (1983) Handbook of solvent extraction. Wiley, New York
Maruyama T, Uchida J, Ohkawa T, Futami T, Katayama K, Nishizawa K, Sotowa K, Kubota F, Kamiyaa N, Goto M (2003) Enzymatic degradation of p-chlorophenol in a two-phase flow microchannel system. Lab Chip 3(4):308–312
Maruyama T, Matsushita H, Uchida J, Kubota F, Kamiya N, Goto M (2004) Liquid membrane operations in a microfluidic device for selective separation of metal ions. Anal Chem 76(15):4495–4500
Mata C, Longmire EK, McKenna DH, Glass KK, Hubel A (2008) Experimental study of diffusion-based extraction from a cell suspension. Microfluid Nanofluid 5(4):529–540
Miyaguchi H, Tokeshi M, Kikutani Y, Hibara A, Inoue H, Kitamori T (2006) Microchip-based liquid-liquid extraction for gas-chromatography analysis of amphetamine-type stimulants in urine. J Chromatogr A 1129(1):105–110
Mu X, Liang QL, Hu P, Ren KN, Wang YM, Luo GA (2009a) Laminar flow used as “liquid etch mask” in wet chemical etching to generate glass microstructures with an improved aspect ratio. Lab Chip 9(14):1994–1996
Mu X, Liang QL, Hu P, Yao B, Ren KN, Wang YM, Luo GA (2009b) Prototypical nonelectrochemical method for surface regeneration of an integrated electrode in a PDMS microfluidic chip. Anal Lett 42(13):1986–1996
Rani SA, Pitts B, Stewart PS (2005) Rapid diffusion of fluorescent tracers into Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms visualized by time lapse microscopy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49(2):728–732
Ren KN, Liang QL, Mu X, Luo GA, Wang YM (2009) Miniaturized high throughput detection system for capillary array electrophoresis on chip with integrated light emitting diode array as addressed ring-shaped light source. Lab Chip 9(5):733–736
Shen H, Fang Q (2008) Improved microfluidic chip-based sequential-injection trapped-droplet array liquid-liquid extraction system for determination of aluminium. Talanta 77(1):269–272
Shen H, Fang Q, Fang ZL (2006) A microfluidic chip based sequential injection system with trapped droplet liquid-liquid extraction and chemiluminescence detection. Lab Chip 6(10):1387–1389
Shui L, Eijkel JCT, van den Berg A (2007) Multiphase flow in microfluidic systems—control and applications of droplets and interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 133(1):35–49
Sia SK, Whitesides GM (2003) Microfluidic devices fabricated in poly(dimethylsiloxane) for biological studies. Electrophoresis 24(21):3563–3576
Surmeian M, Slyadnev MN, Hisamoto H, Hibara A, Uchiyama K, Kitamori T (2002) Three-layer flow membrane system on a microchip for investigation of molecular transport. Anal Chem 74(9):2014–2020
Swickrath MJ, Shenoy S, Mann JA, Belcher J, Kovar R, Wnek GE (2008) The design and fabrication of autonomous polymer-based surface tension-confined microfluidic platforms. Microfluid Nanofluid 4(6):601–611
Tetala KKR, Swarts JW, Chen B, Janssen AEM, van Beek TA (2009) A three-phase microfluidic chip for rapid sample clean-up of alkaloids from plant extracts. Lab Chip 9(14):2085–2092
Tokeshi M, Minagawa T, Kitamori T (2000) Integration of a microextraction system on a glass chip: ion-pair solvent extraction of Fe(II) with 4,7-diphenyl-1,10-phenanthrolinedisulfonic acid and tri-n-octylmethylammonium chloride. Anal Chem 72(7):1711–1714
Wong I, Ho CM (2009) Surface molecular property modifications for poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) based microfluidic devices. Microfluid Nanofluid 7(3):291–306
Woolford B, Maynes D, Webb BW (2009) Liquid flow through microchannels with grooved walls under wetting and superhydrophobic conditions. Microfluid Nanofluid 7(1):121–135
Yao B, Luo GA, Feng X, Wang W, Chen LX, Wang YM (2004) A microfluidic device based on gravity and electric force driving for flow cytometry and fluorescence activated cell sorting. Lab Chip 4(6):603–607
Yao B, Yang HH, Liang QL, Luo G, Wang LD, Ren KN, Gao YD, Wang YM, Qiu Y (2006) High-speed, whole-column fluorescence imaging detection for isoelectric focusing on a microchip using an organic light emitting diode as light source. Anal Chem 78(16):5845–5850
Yung CW, Fiering J, Mueller AJ, Ingber DE (2009) Micromagnetic-microfluidic blood cleansing device. Lab Chip 9(9):1171–1177
Zhou LM, Zuo Z, Chow MSS (2005) Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol 45(12):1345–1359
Zhou JH, Yan H, Ren KN, Dai W, Wu HK (2009) Convenient method for modifying poly(dimethylsiloxane) with poly(ethylene glycol) in microfluidics. Anal Chem 81(16):6627–6632
Znidarsic-Plazl P, Plazl I (2007) Steroid extraction in a microchannel system—mathematical modelling and experiments. Lab Chip 7(7):883–889
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB714505) and Ministry of Education of China (20080031012). The authors would like to thank Professor Yao Bo (Zhejiang University) for fruitful discussions, Dr. Zhang Min (ECUST) and Qi Xiaocheng (JXUTCM) for helping in herb medicine, and Professor Zhang Xi and Wan Pengbo (Tsinghua University) for measuring contact angle.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, X., Liang, Q., Hu, P. et al. Selectively modified microfluidic chip for solvent extraction of Radix Salvia Miltiorrhiza using three-phase laminar flow to provide double liquid–liquid interface area. Microfluid Nanofluid 9, 365–373 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0554-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10404-009-0554-y