Abstract
Aim
The objective of this study was to test whether the recently developed ALPHA (Instruments for Assessing Levels of Physical Activity and Fitness) environmental questionnaire for Europe is a reliable and valid instrument to assess perceptions of the physical environment in a German population.
Subject and methods
We conducted a survey at the University of Stuttgart. One hundred five participants (mean age 27.5 years, SD = 9.7; 68.1% men) were contacted by e-mail and filled in a computer-assisted self-administered version of the ALPHA environmental questionnaire and of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire long version. We calculated bivariate Pearson correlations between environmental sum scores and domain—as well as intensity-specific PA. After 1 week, we contacted all participants a second time by e-mail. All in all, 42 participants answered the German version of the ALPHA environmental questionnaire twice. We calculated intra-class correlations to assess test-retest stability.
Results
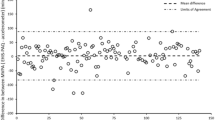
Most of the scales and items of the ALPHA environmental questionnaire showed a moderate to good test-retest reliability. Domain- and intensity-specific PA correlated with different attributes of the physical environment. The correlations were low, but pointed in the expected direction.
Conclusion
The computer-assisted self-administered German version of the ALPHA environmental questionnaire appears to be a recommendable instrument to assess the perceived environment of a neighborhood for young adults. More representative studies across Europe are essential to finally determine the validity and reliability of this questionnaire.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander A, Bergman P, Hagströmer M, Sjöström M (2006) IPAQ environmental module; reliability testing. J Public Health 14(2):76–80
Brownson RC, Hoehner CM, Day K, Forsyth A, Sallis JF (2009) Measuring the built environment for physical activity: state of the science. Am J Prev Med 36 (4 Suppl):S99-123 e112. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2009.01.005
Giles-Corti B, Donovan RJ (2002) The relative influence of individual, social and physical environment determinants of physical activity 9. Soc Sci Med 54(12):1793–1812
Giles-Corti B, Timperio A, Bull F, Pikora T (2005) Understanding physical activity environmental correlates: increased specificity for ecological models. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 33(4):175–181
Humpel N, Owen N, Leslie E (2002) Environmental factors associated with adults’ participation in physical activity: a review. Am J Prev Med 22(3):188–199
Saelens BE, Handy SL (2008) Built environment correlates of walking: a review. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(7 Suppl):S550–566. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e31817c67a400005768-200807002-00007
Saelens BE, Sallis JF, Black JB, Chen D (2003) Neighborhood-based differences in physical activity: an environment scale evaluation. Am J Public Health 93(9):1552–1558
Sallis JF, Cervero RB, Ascher W, Henderson KA, Kraft MK, Kerr J (2006) An ecological approach to creating active living communities. Annu Rev Public Health 27:297–322. doi:10.1146/annurev.publhealth.27.021405.102100
Sallis JF, Bowles HR, Bauman A, Ainsworth BE, Bull FC, Craig CL, Sjostrom M, De Bourdeaudhuij I, Lefevre J, Matsudo V, Matsudo S, Macfarlane DJ, Gomez LF, Inoue S, Murase N, Volbekiene V, McLean G, Carr H, Heggebo LK, Tomten H, Bergman P (2009) Neighborhood environments and physical activity among adults in 11 countries. Am J Prev Med 36(6):484–490. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2009.01.031
Spittaels H, Foster C, Oppert JM, Rutter H, Oja P, Sjostrom M, De Bourdeaudhuij I (2009) Assessment of environmental correlates of physical activity: development of a European questionnaire. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 6(1):39. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-6-39
Spittaels H, Verloigne M, Gidlow C, Gloanec J, Titze S, Foster C, Oppert JM, Rutter H, Oja P, Sjostrom M, De Bourdeaudhuij I (2010) Measuring physical activity-related environmental factors: reliability and predictive validity of the European environmental questionnaire ALPHA. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 7(1):48. doi:10.1186/1479-5868-7-48
Stokols D (1996) Translating social ecological theory into guidelines for community health promotion. Am J Health Promot 10(4):282–298
Sue VM, Ritter LA (2007) Conducting online surveys. Sage Publication, Thousands Oaks
Sugiyama T, Leslie E, Giles-Corti B, Owen N (2009) Physical activity for recreation or exercise on neighbourhood streets: associations with perceived environmental attributes. Health Place 15(4):1058–1063. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2009.05.001
Van Dyck D, Deforche B, Cardon G, De Bourdeaudhuij I (2009) Neighbourhood walkability and its particular importance for adults with a preference for passive transport. Health Place 15(2):496–504. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2008.08.010
Van Dyck D, Cerin E, Cardon G, Deforche B, Sallis JF, Owen N, de Bourdeaudhuij I (2010) Physical activity as a mediator of the associations between neighborhood walkability and adiposity in Belgian adults. Health Place 16(5):952–960. doi:10.1016/j.healthplace.2010.05.011
Wendel-Vos W, Droomers M, Kremers S, Brug J, van Lenthe F (2007) Potential environmental determinants of physical activity in adults: a systematic review. Obes Rev 8(5):425–440. doi:10.1111/j.1467-789X.2007.00370.x
Williams CH (2007) The built environment and physical activity: What is the relationship? The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, Princeton
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bucksch, J., Spittaels, H. Reliability and validity findings of the ALPHA environmental questionnaire in Germany. J Public Health 19, 417–423 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0416-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-011-0416-4